-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
tutorial_localization
Sería excelente que el mundo hablara solo un idioma. Unfortunately for us developers, that is not the case. While not generally a big requirement when developing indie or niche games, it is also very common that games going into a more massive market require localization.
Godot offers many tools to make this process more straightforward, so this tutorial is more like a collection of tips and tricks.
Localization is usually done by specific studios hired for the job and, despite the huge amount of software and file formats available for this, the most common way to do localization to this day is still with spreadsheets. The process of creating the spreadsheets and importing them is already covered in the Import Translations tutorial, so this one could be seen more like a follow up to that one.
The translations can get updated and re-imported when they change, but they still have to be added to the project. This is done in Scene -> Project Settings -> Localization:
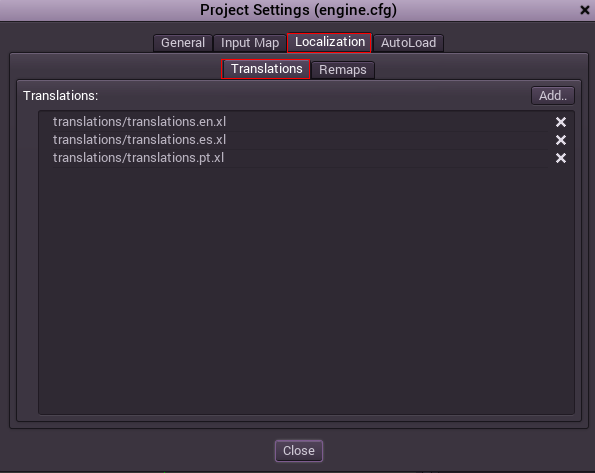
This dialog allows to add or remove translations project-wide.
It is also possible to instruct Godot to open alternative versions of assets (resources) depending on the current language. For this the "Remaps" tab exists:

Select the resource to be remapped, and the alternatives for each locale.
Some controls such as Button,Label,etc. will automatically fetch a translation each time they are set a key instead of a text. For example, if a label is assigned "MAIN_SCREEN_GREETING1" and a key to different languages exists in the translations, this will be automatically converted. This process is done upon load though, so if the project in question has a dialog that allows changing the language in the settings, the scenes (or at least the settings scene) will have to be re-loaded for new text to have effect.
For code, the Object.tr() function can be used. This will just look-up the text into the translations and convert it if found:
level.set_text(tr("LEVEL_5_NAME"))
status.set_text(tr("GAME_STATUS_"+str(status_index)))The same text in different languages can vary greatly in length. For this, make sure to read the tutorial on GUI Control Repositioning, as having dynamically adjusted control sizes may help. Containers can be very useful, as well as the multiple options in Label for text wrapping.
Godot has a server for handling the low level translation management called the TranslationServer. Translations can be added or removed during run-time, and the current language be changed too.
Language can be tested when running Godot from command line. For example, to test a game in french, the following arguments can be supplied:
c:\MyGame> godot -lang fr
The project name becomes the app name when exporting to different operating systems and platforms. To specify the project name in more than one language. In the project settings dialog, create a new setting application/name and append it the locale identifier. For example:
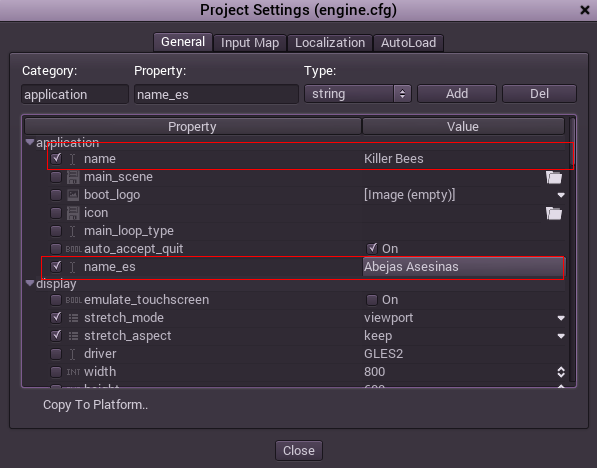
As always, If you don't know the code of a language or zone, check the list.
(c) Juan Linietsky, Ariel Manzur, Distributed under the terms of the CC By license.