-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
mesoSPIM_optical_design
A mesoSPIM is comprised of two (left & right) excitation arms and a detection arm.
The key capability of the current generation of mesoSPIM instrument is axially scanned light-sheet microscopy (ASLM). Learn more about ASLM on the mesoSPIM webpage.
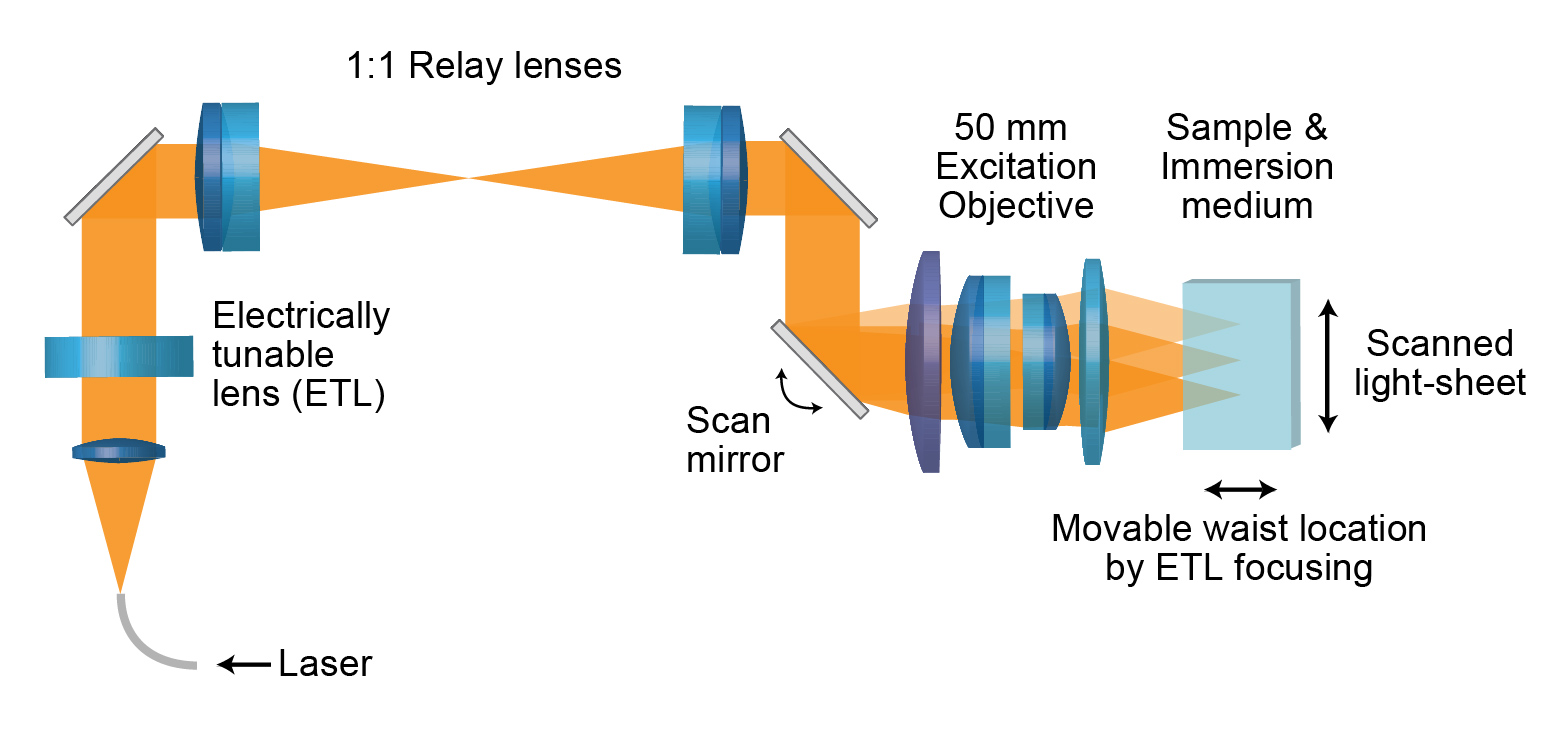 Simplified overview of the mesoSPIM excitation arm (several additional fold mirrors
are missing here).
Simplified overview of the mesoSPIM excitation arm (several additional fold mirrors
are missing here).
The excitation arms each contain an electrically tunable lens (ETL) and a galvo scanner - the tunable lens allows repositioning of the waist location of the light-sheet within the sample. The galvo scanner is used to generated the light-sheet my scanning a Gaussian beam up and down. A 1:1 relay is used in between ETL and galvos - this ensures telecentric imaging conditions while moving the waist location. For further information regarding the use of such a relay, see the Optotune white paper on ETLs in microscopy and a BioPhotonics article.
A detailed description of the mesoSPIM excitation arm can be found here
The detection arm consists of a Olympus MVX-10 zoom macroscope equipped with a Ludl filterwheel and a Hamamatsu Orca Flash 4.0 camera.
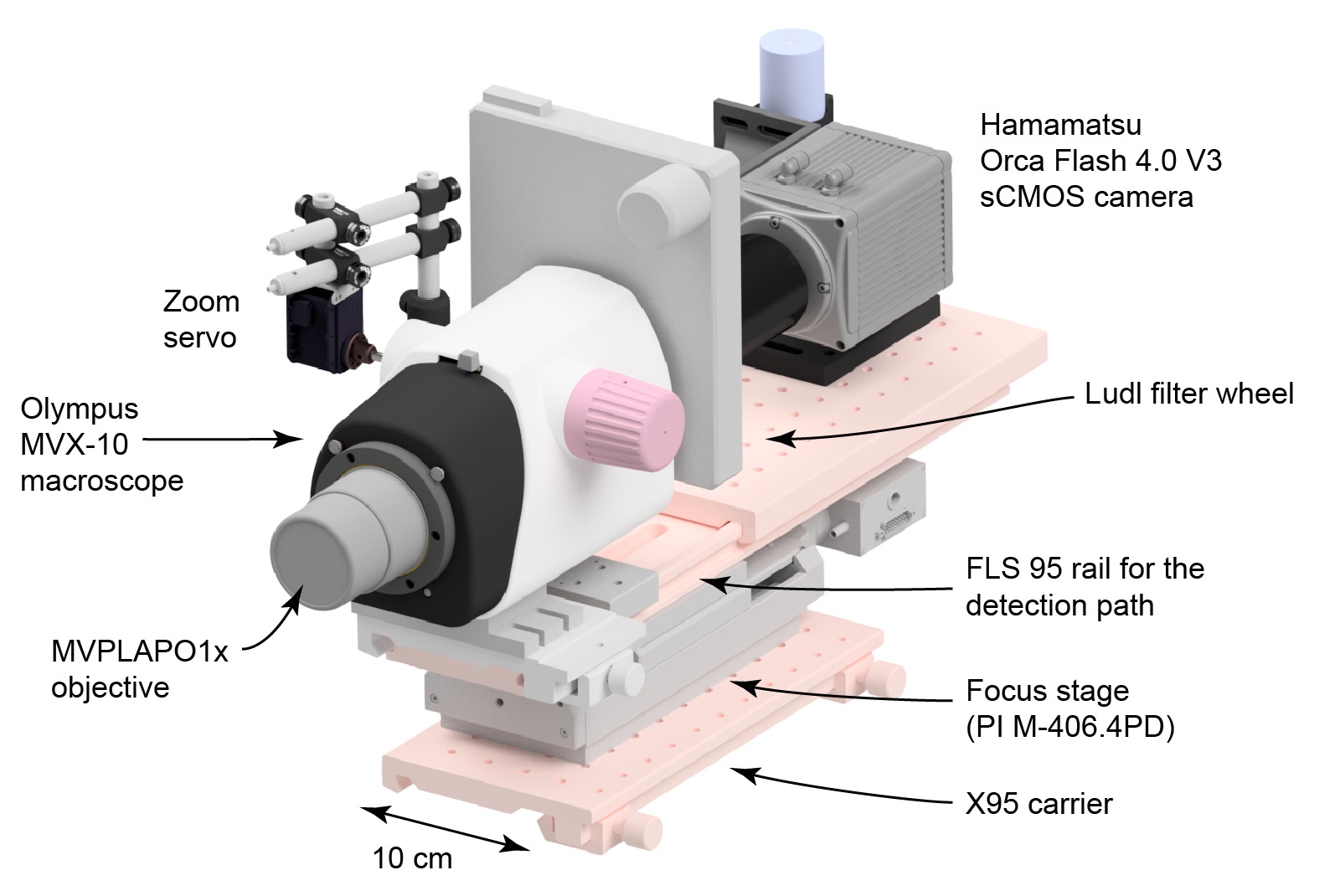 Overview of the mesoSPIM detection arm.
Overview of the mesoSPIM detection arm.
A detailed description can be found here.
-
Background
- mesoSPIM history
- Optical design
- Electronics
-
Setting up a mesoSPIM
- First steps
- Preparing the software and electronics
- Preparing the microscope optics
-
Setting the microscope up
- General alignment tips and tricks
- Installing the microscope base
- Setting up the detection path
- Alignment of the detection path
- Setup of the sample XYZ stages
- Setup of the excitation path
- Immersion cuvettes
- Set up a microscope config file
- Light-sheet co-alignment
- Set up initial ETL parameters
- Setting up lasers with the GUI
- Sample Handling
- Test Samples
- Troubleshooting
- Upgrades and custom variants