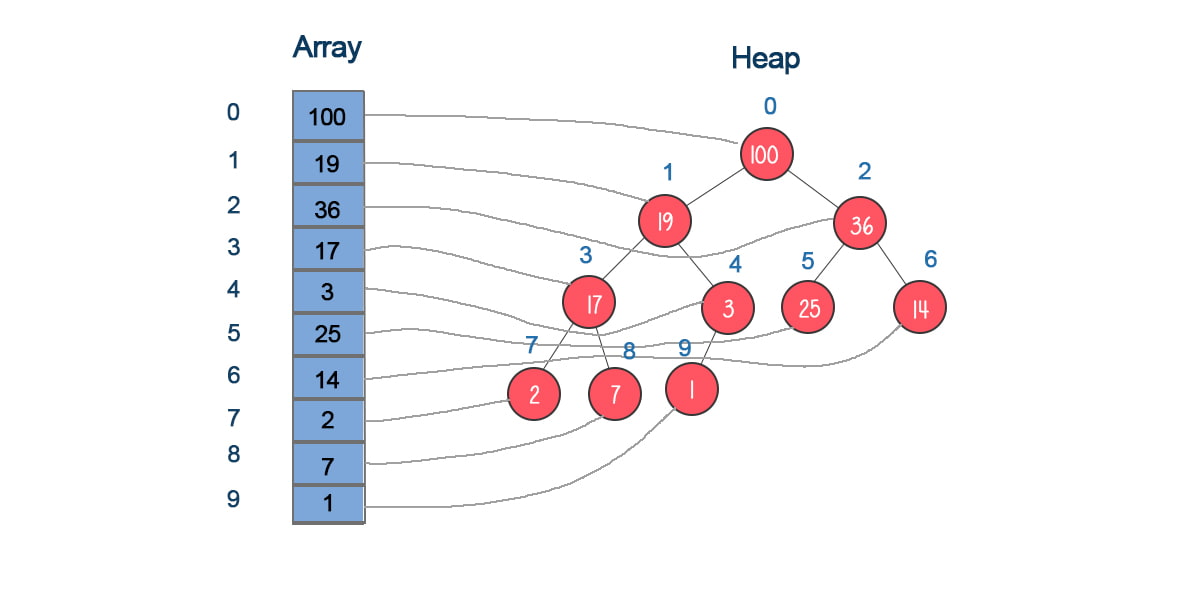
Our goal is to make every data structure as convenient and efficient as JavaScript's Array.
npm i data-structure-typed --saveyarn add data-structure-typedimport {
Heap, Graph, Queue, Deque, PriorityQueue, BST, Trie, DoublyLinkedList,
AVLTree, SinglyLinkedList, DirectedGraph, RedBlackTree, TreeMultiMap,
DirectedVertex, Stack, AVLTreeNode
} from 'data-structure-typed';If you only want to use a specific data structure independently, you can install it separately, for example, by running
npm i heap-typed --saveDo you envy C++ with STL (std::), Python with collections, and Java with java.util ? Well, no need to envy
anymore! JavaScript and TypeScript now have data-structure-typed.Benchmark compared with C++ STL.
API standards aligned with ES6 and Java. Usability is comparable to Python
Performance surpasses that of native JS/TS
| Method | Time Taken | Data Scale | Belongs To | big O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Queue.push & shift | 5.83 ms | 100K | Ours | O(1) |
| Array.push & shift | 2829.59 ms | 100K | Native JS | O(n) |
| Deque.unshift & shift | 2.44 ms | 100K | Ours | O(1) |
| Array.unshift & shift | 4750.37 ms | 100K | Native JS | O(n) |
| HashMap.set | 122.51 ms | 1M | Ours | O(1) |
| Map.set | 223.80 ms | 1M | Native JS | O(1) |
| Set.add | 185.06 ms | 1M | Native JS | O(1) |
In java.utils, you need to memorize a table for all sequential data structures(Queue, Deque, LinkedList),
| Java ArrayList | Java Queue | Java ArrayDeque | Java LinkedList |
|---|---|---|---|
| add | offer | push | push |
| remove | poll | removeLast | removeLast |
| remove | poll | removeFirst | removeFirst |
| add(0, element) | offerFirst | unshift | unshift |
whereas in our data-structure-typed, you only need to remember four methods: push, pop, shift, and unshift for all sequential data structures(Queue, Deque, DoublyLinkedList, SinglyLinkedList and Array).
We provide data structures that are not available in JS/TS
| Data Structure | Unit Test | Perf Test | API Doc | NPM | Downloads |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary Tree |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Binary Search Tree (BST) |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| AVL Tree |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Red Black Tree |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Tree Multimap |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Heap |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Priority Queue |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Max Priority Queue |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Min Priority Queue |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Trie |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Graph |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Directed Graph |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Undirected Graph |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Queue |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Deque |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Hash Map |  |
 |
Docs | ||
| Linked List |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Singly Linked List |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Doubly Linked List |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Stack |  |
 |
Docs | NPM |  |
| Segment Tree |  |
Docs | |||
| Binary Indexed Tree |  |
Docs |
Try it out, or you can run your own code using our visual tool
import { RedBlackTree } from 'data-structure-typed';
const rbTree = new RedBlackTree<number>();
rbTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
rbTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
rbTree.delete(10);
rbTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
rbTree.print()
// ___6________
// / \
// ___4_ ___11________
// / \ / \
// _2_ 5 _8_ ____14__
// / \ / \ / \
// 1 3 7 9 12__ 15__
// \ \
// 13 16import { RedBlackTree } from 'data-structure-typed';
const rbTree = new RedBlackTree();
rbTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
rbTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
rbTree.delete(10);
rbTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
rbTree.print()
// ___6________
// / \
// ___4_ ___11________
// / \ / \
// _2_ 5 _8_ ____14__
// / \ / \ / \
// 1 3 7 9 12__ 15__
// \ \
// 13 16const orgArr = [6, 1, 2, 7, 5, 3, 4, 9, 8];
const orgStrArr = ["trie", "trial", "trick", "trip", "tree", "trend", "triangle", "track", "trace", "transmit"];
const entries = [[6, "6"], [1, "1"], [2, "2"], [7, "7"], [5, "5"], [3, "3"], [4, "4"], [9, "9"], [8, "8"]];
const queue = new Queue(orgArr);
queue.print();
// [6, 1, 2, 7, 5, 3, 4, 9, 8]
const deque = new Deque(orgArr);
deque.print();
// [6, 1, 2, 7, 5, 3, 4, 9, 8]
const sList = new SinglyLinkedList(orgArr);
sList.print();
// [6, 1, 2, 7, 5, 3, 4, 9, 8]
const dList = new DoublyLinkedList(orgArr);
dList.print();
// [6, 1, 2, 7, 5, 3, 4, 9, 8]
const stack = new Stack(orgArr);
stack.print();
// [6, 1, 2, 7, 5, 3, 4, 9, 8]
const minHeap = new MinHeap(orgArr);
minHeap.print();
// [1, 5, 2, 7, 6, 3, 4, 9, 8]
const maxPQ = new MaxPriorityQueue(orgArr);
maxPQ.print();
// [9, 8, 4, 7, 5, 2, 3, 1, 6]
const biTree = new BinaryTree(entries);
biTree.print();
// ___6___
// / \
// ___1_ _2_
// / \ / \
// _7_ 5 3 4
// / \
// 9 8
const bst = new BST(entries);
bst.print();
// _____5___
// / \
// _2_ _7_
// / \ / \
// 1 3_ 6 8_
// \ \
// 4 9
const rbTree = new RedBlackTree(entries);
rbTree.print();
// ___4___
// / \
// _2_ _6___
// / \ / \
// 1 3 5 _8_
// / \
// 7 9
const avl = new AVLTree(entries);
avl.print();
// ___4___
// / \
// _2_ _6___
// / \ / \
// 1 3 5 _8_
// / \
// 7 9
const treeMulti = new TreeMultiMap(entries);
treeMulti.print();
// ___4___
// / \
// _2_ _6___
// / \ / \
// 1 3 5 _8_
// / \
// 7 9
const hm = new HashMap(entries);
hm.print()
// [[6, "6"], [1, "1"], [2, "2"], [7, "7"], [5, "5"], [3, "3"], [4, "4"], [9, "9"], [8, "8"]]
const rbTreeH = new RedBlackTree(hm);
rbTreeH.print();
// ___4___
// / \
// _2_ _6___
// / \ / \
// 1 3 5 _8_
// / \
// 7 9
const pq = new MinPriorityQueue(orgArr);
pq.print();
// [1, 5, 2, 7, 6, 3, 4, 9, 8]
const bst1 = new BST(pq);
bst1.print();
// _____5___
// / \
// _2_ _7_
// / \ / \
// 1 3_ 6 8_
// \ \
// 4 9
const dq1 = new Deque(orgArr);
dq1.print();
// [6, 1, 2, 7, 5, 3, 4, 9, 8]
const rbTree1 = new RedBlackTree(dq1);
rbTree1.print();
// _____5___
// / \
// _2___ _7___
// / \ / \
// 1 _4 6 _9
// / /
// 3 8
const trie2 = new Trie(orgStrArr);
trie2.print();
// ['trie', 'trial', 'triangle', 'trick', 'trip', 'tree', 'trend', 'track', 'trace', 'transmit']
const heap2 = new Heap(trie2, { comparator: (a, b) => Number(a) - Number(b) });
heap2.print();
// ['transmit', 'trace', 'tree', 'trend', 'track', 'trial', 'trip', 'trie', 'trick', 'triangle']
const dq2 = new Deque(heap2);
dq2.print();
// ['transmit', 'trace', 'tree', 'trend', 'track', 'trial', 'trip', 'trie', 'trick', 'triangle']
const entries2 = dq2.map((el, i) => [i, el]);
const avl2 = new AVLTree(entries2);
avl2.print();
// ___3_______
// / \
// _1_ ___7_
// / \ / \
// 0 2 _5_ 8_
// / \ \
// 4 6 9import { BST, BSTNode } from 'data-structure-typed';
const bst = new BST<number>();
bst.add(11);
bst.add(3);
bst.addMany([15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5]);
bst.size === 16; // true
bst.has(6); // true
const node6 = bst.getNode(6); // BSTNode
bst.getHeight(6) === 2; // true
bst.getHeight() === 5; // true
bst.getDepth(6) === 3; // true
bst.getLeftMost()?.key === 1; // true
bst.delete(6);
bst.get(6); // undefined
bst.isAVLBalanced(); // true
bst.bfs()[0] === 11; // true
bst.print()
// ______________11_____
// / \
// ___3_______ _13_____
// / \ / \
// 1_ _____8____ 12 _15__
// \ / \ / \
// 2 4_ _10 14 16
// \ /
// 5_ 9
// \
// 7
const objBST = new BST<number, { height: number, age: number }>();
objBST.add(11, { "name": "Pablo", "size": 15 });
objBST.add(3, { "name": "Kirk", "size": 1 });
objBST.addMany([15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5], [
{ "name": "Alice", "size": 15 },
{ "name": "Bob", "size": 1 },
{ "name": "Charlie", "size": 8 },
{ "name": "David", "size": 13 },
{ "name": "Emma", "size": 16 },
{ "name": "Frank", "size": 2 },
{ "name": "Grace", "size": 6 },
{ "name": "Hannah", "size": 9 },
{ "name": "Isaac", "size": 12 },
{ "name": "Jack", "size": 14 },
{ "name": "Katie", "size": 4 },
{ "name": "Liam", "size": 7 },
{ "name": "Mia", "size": 10 },
{ "name": "Noah", "size": 5 }
]
);
objBST.delete(11);import { AVLTree } from 'data-structure-typed';
const avlTree = new AVLTree<number>();
avlTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
avlTree.delete(10);
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // trueimport { DirectedGraph } from 'data-structure-typed';
const graph = new DirectedGraph<string>();
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.hasVertex('A'); // true
graph.hasVertex('B'); // true
graph.hasVertex('C'); // false
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.hasEdge('A', 'B'); // true
graph.hasEdge('B', 'A'); // false
graph.deleteEdgeSrcToDest('A', 'B');
graph.hasEdge('A', 'B'); // false
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.addEdge('B', 'C');
const topologicalOrderKeys = graph.topologicalSort(); // ['A', 'B', 'C']import { UndirectedGraph } from 'data-structure-typed';
const graph = new UndirectedGraph<string>();
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addVertex('D');
graph.deleteVertex('C');
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.addEdge('B', 'D');
const dijkstraResult = graph.dijkstra('A');
Array.from(dijkstraResult?.seen ?? []).map(vertex => vertex.key) // ['A', 'B', 'D']
MacBook Pro (15-inch, 2018)
Processor 2.2 GHz 6-Core Intel Core i7
Memory 16 GB 2400 MHz DDR4
Graphics Radeon Pro 555X 4 GB
Intel UHD Graphics 630 1536 MB
macOS Big Sur
Version 11.7.9
| test name | time taken (ms) | sample mean (secs) | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100,000 add | 6.85 | 0.01 | 3.38e-4 |
| 100,000 add & poll | 35.35 | 0.04 | 8.44e-4 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | sample mean (secs) | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100,000 add | 302.89 | 0.30 | 0.01 |
| 100,000 add randomly | 381.83 | 0.38 | 0.00 |
| 100,000 get | 0.60 | 5.95e-4 | 2.33e-4 |
| 100,000 getNode | 150.61 | 0.15 | 0.00 |
| 100,000 iterator | 28.23 | 0.03 | 0.00 |
| 100,000 add & delete orderly | 505.57 | 0.51 | 0.01 |
| 100,000 add & delete randomly | 677.36 | 0.68 | 0.00 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | sample mean (secs) | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100,000 add | 212.77 | 0.21 | 9.84e-4 |
| 100,000 add randomly | 163.70 | 0.16 | 0.00 |
| 100,000 get | 1.19 | 0.00 | 2.44e-4 |
| 100,000 getNode | 347.39 | 0.35 | 0.01 |
| 100,000 node mode add randomly | 162.26 | 0.16 | 0.00 |
| 100,000 node mode get | 344.90 | 0.34 | 0.00 |
| 100,000 iterator | 27.48 | 0.03 | 0.00 |
| 100,000 add & delete orderly | 386.33 | 0.39 | 0.00 |
| 100,000 add & delete randomly | 520.66 | 0.52 | 0.00 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | sample mean (secs) | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000,000 push | 179.28 | 0.18 | 0.02 |
| 1,000,000 unshift | 197.22 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| 1,000,000 unshift & shift | 153.16 | 0.15 | 0.00 |
| 1,000,000 addBefore | 247.30 | 0.25 | 0.03 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | sample mean (secs) | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 addVertex | 0.10 | 9.92e-5 | 1.16e-6 |
| 1,000 addEdge | 6.44 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 1,000 getVertex | 0.10 | 9.82e-5 | 1.13e-6 |
| 1,000 getEdge | 22.60 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| tarjan | 186.56 | 0.19 | 0.00 |
| topologicalSort | 145.42 | 0.15 | 0.01 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | sample mean (secs) | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000,000 push | 47.74 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| 100,000 push & shift | 5.39 | 0.01 | 1.25e-4 |
| Native JS Array 100,000 push & shift | 2225.50 | 2.23 | 0.10 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | sample mean (secs) | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000,000 push | 22.88 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| 1,000,000 push & pop | 27.95 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| 1,000,000 push & shift | 29.83 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| 100,000 push & shift | 2.71 | 0.00 | 9.03e-4 |
| Native JS Array 100,000 push & shift | 2182.03 | 2.18 | 0.04 |
| 100,000 unshift & shift | 2.61 | 0.00 | 8.71e-4 |
| Native JS Array 100,000 unshift & shift | 4185.90 | 4.19 | 0.04 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | sample mean (secs) | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000,000 set | 253.45 | 0.25 | 0.07 |
| Native JS Map 1,000,000 set | 228.90 | 0.23 | 0.02 |
| Native JS Set 1,000,000 add | 179.65 | 0.18 | 0.01 |
| 1,000,000 set & get | 234.96 | 0.23 | 0.06 |
| Native JS Map 1,000,000 set & get | 284.90 | 0.28 | 0.01 |
| Native JS Set 1,000,000 add & has | 254.90 | 0.25 | 0.03 |
| 1,000,000 ObjKey set & get | 403.74 | 0.40 | 0.10 |
| Native JS Map 1,000,000 ObjKey set & get | 340.18 | 0.34 | 0.07 |
| Native JS Set 1,000,000 ObjKey add & has | 300.25 | 0.30 | 0.06 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | sample mean (secs) | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100,000 push | 44.11 | 0.04 | 8.55e-4 |
| 100,000 getWords | 86.67 | 0.09 | 0.00 |
| test name | time taken (ms) | sample mean (secs) | sample deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000,000 push | 43.18 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| 1,000,000 push & pop | 48.40 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| Data Structure Typed | C++ STL | java.util | Python collections |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heap<E> | - | - | heapq |
| PriorityQueue<E> | priority_queue<T> | PriorityQueue<E> | - |
| Deque<E> | deque<T> | ArrayDeque<E> | deque |
| Queue<E> | queue<T> | Queue<E> | - |
| HashMap<K, V> | unordered_map<K, V> | HashMap<K, V> | defaultdict |
| DoublyLinkedList<E> | list<T> | LinkedList<E> | - |
| SinglyLinkedList<E> | - | - | - |
| BinaryTree<K, V> | - | - | - |
| BST<K, V> | - | - | - |
| RedBlackTree<E> | set<T> | TreeSet<E> | - |
| RedBlackTree<K, V> | map<K, V> | TreeMap<K, V> | - |
| TreeMultiMap<K, V> | multimap<K, V> | - | - |
| TreeMultiMap<E> | multiset<T> | - | - |
| Trie | - | - | - |
| DirectedGraph<V, E> | - | - | - |
| UndirectedGraph<V, E> | - | - | - |
| PriorityQueue<E> | priority_queue<T> | PriorityQueue<E> | - |
| Array<E> | vector<T> | ArrayList<E> | list |
| Stack<E> | stack<T> | Stack<E> | - |
| HashMap<E> | unordered_set<T> | HashSet<E> | set |
| - | unordered_multiset | - | Counter |
| LinkedHashMap<K, V> | - | LinkedHashMap<K, V> | OrderedDict |
| - | unordered_multimap<K, V> | - | - |
| - | bitset<N> | - | - |
| Algorithm | Function Description | Iteration Type |
|---|---|---|
| Binary Tree DFS | Traverse a binary tree in a depth-first manner, starting from the root node, first visiting the left subtree, and then the right subtree, using recursion. | Recursion + Iteration |
| Binary Tree BFS | Traverse a binary tree in a breadth-first manner, starting from the root node, visiting nodes level by level from left to right. | Iteration |
| Graph DFS | Traverse a graph in a depth-first manner, starting from a given node, exploring along one path as deeply as possible, and backtracking to explore other paths. Used for finding connected components, paths, etc. | Recursion + Iteration |
| Binary Tree Morris | Morris traversal is an in-order traversal algorithm for binary trees with O(1) space complexity. It allows tree traversal without additional stack or recursion. | Iteration |
| Graph BFS | Traverse a graph in a breadth-first manner, starting from a given node, first visiting nodes directly connected to the starting node, and then expanding level by level. Used for finding shortest paths, etc. | Recursion + Iteration |
| Graph Tarjan's Algorithm | Find strongly connected components in a graph, typically implemented using depth-first search. | Recursion |
| Graph Bellman-Ford Algorithm | Finding the shortest paths from a single source, can handle negative weight edges | Iteration |
| Graph Dijkstra's Algorithm | Finding the shortest paths from a single source, cannot handle negative weight edges | Iteration |
| Graph Floyd-Warshall Algorithm | Finding the shortest paths between all pairs of nodes | Iteration |
| Graph getCycles | Find all cycles in a graph or detect the presence of cycles. | Recursion |
| Graph getCutVertices | Find cut vertices in a graph, which are nodes that, when removed, increase the number of connected components in the graph. | Recursion |
| Graph getSCCs | Find strongly connected components in a graph, which are subgraphs where any two nodes can reach each other. | Recursion |
| Graph getBridges | Find bridges in a graph, which are edges that, when removed, increase the number of connected components in the graph. | Recursion |
| Graph topologicalSort | Perform topological sorting on a directed acyclic graph (DAG) to find a linear order of nodes such that all directed edges go from earlier nodes to later nodes. | Recursion |
We strictly adhere to computer science theory and software development standards. Our LinkedList is designed in the traditional sense of the LinkedList data structure, and we refrain from substituting it with a Deque solely for the purpose of showcasing performance test data. However, we have also implemented a Deque based on a dynamic array concurrently.
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Practicality | Follows ES6 and ESNext standards, offering unified and considerate optional parameters, and simplifies method names. |
| Extensibility | Adheres to OOP (Object-Oriented Programming) principles, allowing inheritance for all data structures. |
| Modularization | Includes data structure modularization and independent NPM packages. |
| Efficiency | All methods provide time and space complexity, comparable to native JS performance. |
| Maintainability | Follows open-source community development standards, complete documentation, continuous integration, and adheres to TDD (Test-Driven Development) patterns. |
| Testability | Automated and customized unit testing, performance testing, and integration testing. |
| Portability | Plans for porting to Java, Python, and C++, currently achieved to 80%. |
| Reusability | Fully decoupled, minimized side effects, and adheres to OOP. |
| Security | Carefully designed security for member variables and methods. Read-write separation. Data structure software does not need to consider other security aspects. |
| Scalability | Data structure software does not involve load issues. |
Now you can use it in Node.js and browser environments
CommonJS:require export.modules =
ESModule: import export
Typescript: import export
UMD: var Deque = dataStructureTyped.Deque
Copy the line below into the head tag in an HTML document.
<script src='https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/data-structure-typed/dist/umd/data-structure-typed.js'></script><script src='https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/data-structure-typed/dist/umd/data-structure-typed.min.js'></script>Copy the code below into the script tag of your HTML, and you're good to go with your development.
const { Heap } = dataStructureTyped;
const {
BinaryTree, Graph, Queue, Stack, PriorityQueue, BST, Trie, DoublyLinkedList,
AVLTree, MinHeap, SinglyLinkedList, DirectedGraph, TreeMultiMap,
DirectedVertex, AVLTreeNode
} = dataStructureTyped;