06/04/2022: v1.0.3 Fix package size
ABB Aurora PV inverter library for Arduino, esp8266 and esp32
I create this library to develop this Web Monitor interface.
Here the base information of RS485 ABB Aurora communication Protocol.
ABB PowerOne Aurora communication protocol Library arduino esp8266 esp32 Main
The communication between Host and processor works via a Serial Interface RS485 or RS232. Configuration parameters in both cases are:
- 19200 baud (default value)
- 1 stop bit
- no parity
The structure of the answer has also fixed length (6 Bytes + 2 Bytes for Checksum) :
Transmission State is coded as follows:
0 = Everything is OK.
51 = Command is not implemented
52 = Variable does not exist
53 = Variable value is out of range
54 = EEprom not accessible
55 = Not Toggled Service Mode
56 = Can not send the command to internal micro
57 = Command not Executed
58 = The variable is not available, retry
Global State shows the state of the addressed device, the details are specified in the description of the commands.
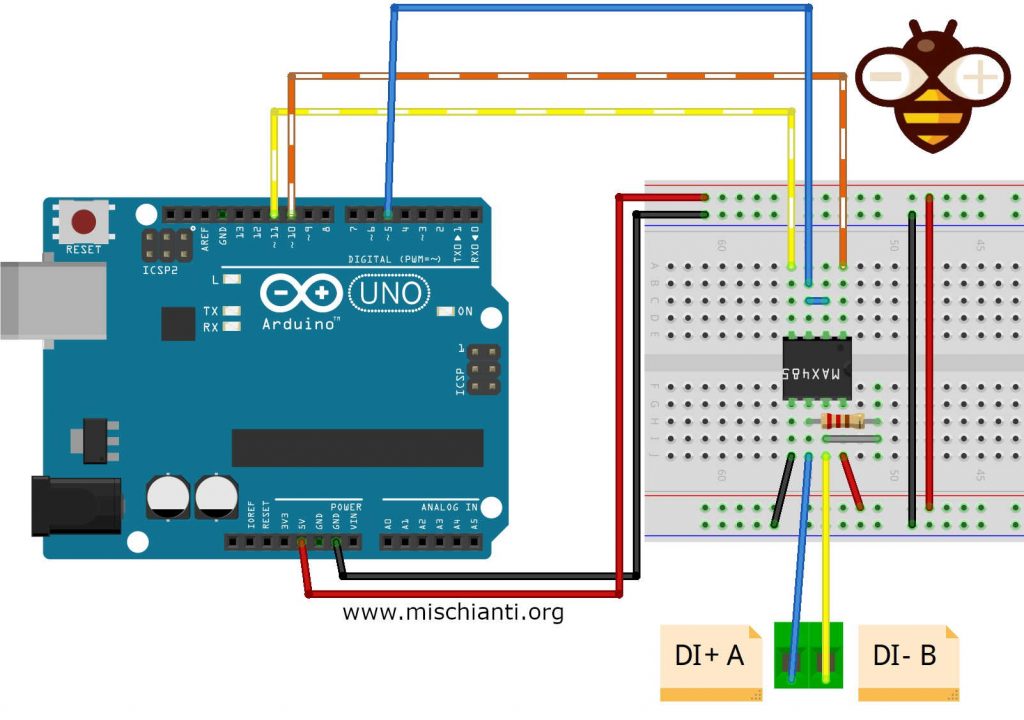
You can use an Arduino UNO and a MAX485 IC, if you prefer can buy a module.
You can find IC on AliExpress
You can find module on AliExpress
You can ArduinoUNO on AliExpress
Here the simple connection schema, the resistor must be 120Ω, i use 104Ω.
MAX485 Arduino connection schema
I create a library derived from a project that you can find in the web created by drhack, It’s a fantastic works (thanks to drhack) but I find It quite difficult to use, with specific hardware and not so reusable.
So I try to standardize the library and made It simple (the people that use my library know that “simplify first” It’s my motto.
If you want use an esp8266 (I create a centraline with Wemos D1 mini) you must buy a MAX3485 tha work at the correct voltage.
You can find IC on AliExpress eBay
You can find module on AliExpress eBay
You can find WeMos D1 mini on AliExpress
Here the simple connection schema, the resistor must be 120Ω, i use 104Ω.
MAX3485 and esp8266 connection schema
As you can see It’s quite simple to connect.
As usual I try to create It more generic as possible, so If you want use HardwareSerial or SoftwareSerial you are free to choiche.
You must specify an address, that address normally is 2, but you must check It in your inverter menu.
You can create a chain of inverters that communicate via RS485. An address can be chosen from 2 to 63. The address on the inverter is set through the display and the pushbutton panel.
To change address go to SETTINGS --> Insert password (default 0000) --> Address.
This menu allows you to set the serial port addresses of the individual inverters connected to the RS485 line. The addresses that can be assigned are 2 to 63. The UP and DOWN buttons scroll through the numerical scale. ‘AUTO’ selection cannot be used at present.
// Aurora(byte inverterAddress, HardwareSerial* serial, byte serialCommunicationControlPin)
Aurora inverter = Aurora(2, &Serial, 5); |
inverterAddress: as described is the inverter address set on device.serial: is theHardwareSerial.serialCommunicationControlPin: is the pin that activate transmission of serial communication.
// Aurora(byte inverterAddress, byte rxPin, byte txPin, byte serialCommunicationControlPin)
Aurora inverter = Aurora(2, 10, 11, 5); |
inverterAddress: as described is the inverter address set on device.rxPin:is the SoftwareSerial RX pin.txPin:is the SoftwareSerial TX pin.serialCommunicationControlPin: is the pin that activate transmission of serial communication.
For software serial you can pass external SoftwareSerial instance.
// Aurora(byte inverterAddress, SoftwareSerial* serial, byte serialCommunicationControlPin) |
You can refer the complete documentation on my site ABB Aurora PV inverter library for Arduino, esp8266 and esp32
First you must startup the communication with begin command:
inverter.begin();|
Than there are a lot of command that you can use to make query to your Inverter:
void begin();
void clearReceiveData();
DataState readState();
DataVersion readVersion();
DataDSP readDSP(byte type, byte global = (byte)1);
DataTimeDate readTimeDate();
bool writeTimeDate(unsigned long epochTime);
DataLastFourAlarms readLastFourAlarms();
DataJunctionBoxState readJunctionBoxState(byte nj);
bool readJunctionBoxVal(byte nj, byte par);
DataSystemPN readSystemPN();
DataSystemSerialNumber readSystemSerialNumber();
DataManufacturingWeekYear readManufacturingWeekYear();
DataFirmwareRelease readFirmwareRelease();
DataCumulatedEnergy readCumulatedEnergy(byte par);
bool writeBaudRateSetting(byte baudcode);
DataConfigStatus readConfig();
DataTimeCounter readTimeCounter(byte param);
// Central
bool readFlagsSwitchCentral();
bool readCumulatedEnergyCentral(byte var, byte ndays_h, byte ndays_l, byte global);
bool readFirmwareReleaseCentral(byte var);
bool readBaudRateSettingCentral(byte baudcode, byte serialline);
bool readSystemInfoCentral(byte var);
bool readJunctionBoxMonitoringCentral(byte cf, byte rn, byte njt, byte jal, byte jah);
bool readSystemPNCentral();
bool readSystemSerialNumberCentral();Here an example of reading via Arduino.
/*
Test Arduino MAX485 Aurora ABB connection
by Mischianti Renzo <https://www.mischianti.org>
https://www.mischianti.org/
*/
#include "Arduino.h"
#include <Aurora.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <MemoryFree.h>
//SoftwareSerial mySerial(10, 11); // RX, TX
//Aurora inverter = Aurora(2, &Serial1, 5);
Aurora inverter = Aurora(2, 10, 11, 5);
void SerialPrintData(byte *data) {
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
Serial.print((int)data[i]);
Serial.print(F(" "));
}
Serial.println(F(" "));
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(19200);
inverter.begin();
}
// The loop function is called in an endless loop
void loop()
{
Serial.print(F("freeMemory(1)="));Serial.println(freeMemory());
Aurora::DataCumulatedEnergy cumulatedEnergy = inverter.readCumulatedEnergy((byte)1);
Serial.println(F("------------------------------------------"));
Serial.println(F("INVERTER 2"));
Serial.print(F(" Data ROW = ")); SerialPrintData(inverter.receiveData);
Serial.print(F(" Read State = ")); Serial.println(cumulatedEnergy.state.readState);
Serial.print(F("Transmission State = ")); Serial.println(cumulatedEnergy.state.getTransmissionState());
Serial.print(F(" Global State = ")); Serial.println(cumulatedEnergy.state.getGlobalState());
Serial.print(F(" Energia = ")); Serial.print(cumulatedEnergy.energy); Serial.println(" Wh");
// free(&cumulatedEnergy);
Serial.println(F("------------------------------------------"));
Aurora::DataLastFourAlarms lastFour = inverter.readLastFourAlarms();
Serial.println(F("INVERTER 2"));
Serial.print(F(" Data ROW = ")); SerialPrintData(inverter.receiveData);
Serial.print(F(" Read State = ")); Serial.println(lastFour.state.readState);
Serial.print(F("Transmission State = ")); Serial.println(lastFour.state.getTransmissionState());
Serial.print(F(" Global State = ")); Serial.println(lastFour.state.getGlobalState());
Serial.print(F(" Alarms 1 = ")); Serial.println(lastFour.getAlarm1State());
Serial.print(F(" Alarms 2 = ")); Serial.println(lastFour.getAlarm2State());
Serial.print(F(" Alarms 3 = ")); Serial.println(lastFour.getAlarm3State());
Serial.print(F(" Alarms 4 = ")); Serial.println(lastFour.getAlarm4State());
// free(&lastFour);
Serial.println(F("------------------------------------------"));
Aurora::DataVersion version = inverter.readVersion();
Serial.println("INVERTER 2");
Serial.print(F(" Data ROW = ")); SerialPrintData(inverter.receiveData);
Serial.print(F(" Read State = ")); Serial.println(version.state.readState);
Serial.print(F("Transmission State = ")); Serial.println(version.state.getTransmissionState());
Serial.print(F(" Global State = ")); Serial.println(version.state.getGlobalState());
Serial.print(F(" Version = ")); Serial.print(version.getModelName().name); Serial.print(F(" ")); Serial.print(version.getIndoorOutdoorAndType()); Serial.print(F(" ")); Serial.print(version.getGridStandard()); Serial.print(F(" ")); Serial.print(version.getTrafoOrNonTrafo()); Serial.print(F(" ")); Serial.println(version.getWindOrPV());
Serial.println(F("------------------------------------------"));
// free(&version);
Aurora::DataConfigStatus configStatus = inverter.readConfig();
Serial.print(F(" Data ROW = ")); SerialPrintData(inverter.receiveData);
Serial.print(F(" Read State = ")); Serial.println(configStatus.state.readState);
Serial.print(F("Transmission State = ")); Serial.println(configStatus.state.getTransmissionState());
Serial.print(F(" Global State = ")); Serial.println(configStatus.state.getGlobalState());
Serial.print(F(" config = ")); Serial.println(configStatus.getConfigStatus());
Serial.println(F("------------------------------------------"));
// free(&version);
Serial.print(F("freeMemory(2)="));Serial.println(freeMemory());
Aurora::DataTimeCounter timeCounter = inverter.readTimeCounter(CT_TOTAL_RUN);
Serial.print(F(" Data ROW = ")); SerialPrintData(inverter.receiveData);
Serial.print(F(" Read State = ")); Serial.println(timeCounter.state.readState);
Serial.print(F("Transmission State = ")); Serial.println(timeCounter.state.getTransmissionState());
Serial.print(F(" Global State = ")); Serial.println(timeCounter.state.getGlobalState());
Serial.print(F(" time in sec = ")); Serial.println(timeCounter.upTimeInSec);
Serial.print(F(" time in verb = ")); Serial.print(timeCounter.getSecondsInDateElements()[0]); Serial.print(F("Y ")); Serial.print(timeCounter.getSecondsInDateElements()[1]); Serial.print(F("D "));Serial.print(timeCounter.getSecondsInDateElements()[2]);Serial.print(F("H "));Serial.print(timeCounter.getSecondsInDateElements()[3]);+Serial.print(F("M "));Serial.print(timeCounter.getSecondsInDateElements()[4]);Serial.println(F("S "));
Serial.println(F("------------------------------------------"));
// free(&version);
Serial.print(F("freeMemory(2)="));Serial.println(freeMemory());
delay(4000);
}As you can see the usage is quite simple.
Here the video of the result call.