Forget about setting up your own infrastructure, vps, network, orchestrators, etc... go serverless
- Quickstart
- Deployment examples
- Django
- Yandex Cloud authorization
- Limitations
- Articles
- Roadmap
- Troubleshooting
- Support and contribution
- Acknowledgements
- setup virtual env, create your app
- create account at Yandex Cloud
- install Yappa
$ pip install yappa -U
$ pip freeze > requirements.txt- use Yappa:
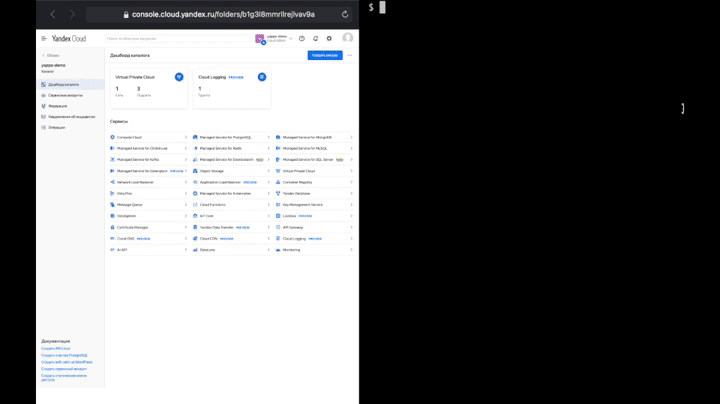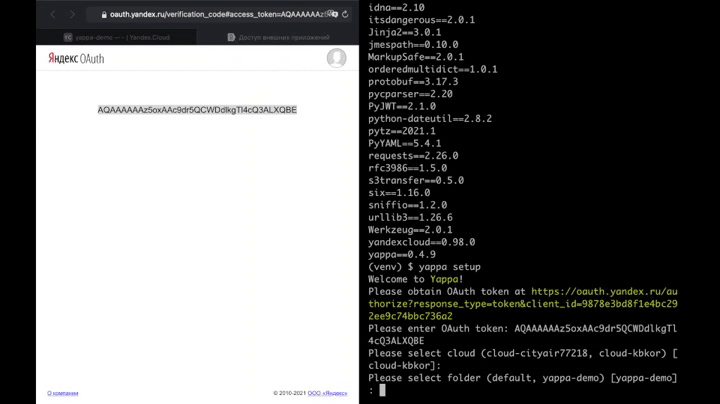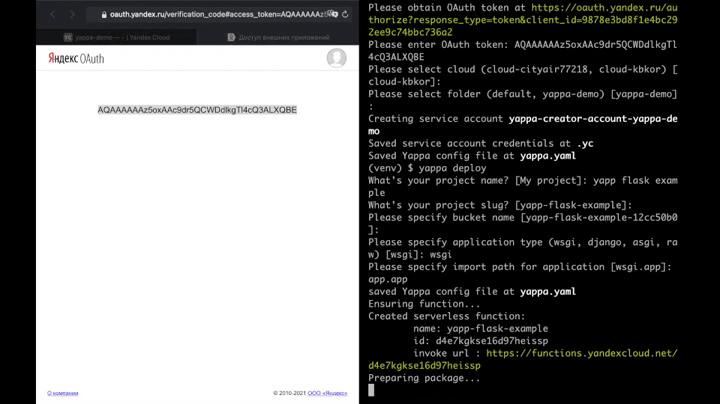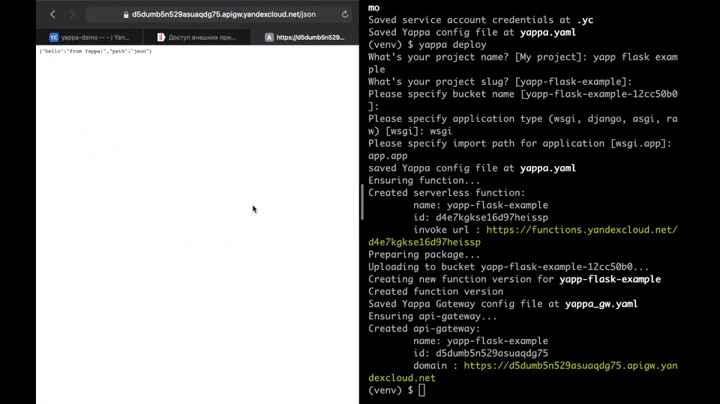
$ yappa setup
$ yappa deploy...that's it! Your application is deployed
when your code is updated just run
$ yappa deployBoth WSGI and ASGI applications are supported (as well as raw functions). So Django, Flask, FastAPI... etc could be easily deployed.
Furthermore, not just regular json API could be deployed this way. Several types of applications could be launched with Yappa:
- raw serverless function
- raw serverless function + Postgres
- json API (Flask, FastAPI, Django rest framework)
- single page application
- SPA + multiple API versions
...
more examples will be added soon
please see examples:
- Django Rest Framework basic - basic DRF app. To explore serverless and Yappa features, like management commands
- Django Rest Framework + Postgres -
- DRF app with managed Postgres connectivity
django manage.py commands are supported. just run
$ yappa manage migrateIn order to support management commands, for Django projects second cloud function is being created every deploy. It's made only for handling management commands, and it's not public. Therefore, commands do not support user inputs: to every command '--no-input' flag is added.
As of Django 3.0 env variables are supported for createsuperuser command. So you should deploy your app with DJANGO_SUPERUSER_USERNAME, DJANGO_SUPERUSER_PASSWORD environment variables. Then run
$ yappa manage createsuperuserThe other way around would be to implement custom management command (see StackOverflow topic)
Command '$ yappa setup' prompts you for OAuth token. Then, Yappa creates service account "yappa-uploader-service" with roles editor and serverless.functions.admin for the specified folder. Key for this account is created and saved locally at .yc file.
Command '$ yappa deploy' supports two types of authorization
- service account key saved at .yc file (generated during '$ yappa setup')
- environment variables YC_OAUTH and YC_FOLDER
There are some limitations, however YandexCloud team is constantly releasing new features and services. Also, the team of this project will try to keep up. So stay tuned :)
Managed Postgres and YandexDB is supported inside Yandex Cloud. In case any other DB - it has to have public IP address
For details on how te set up connection with managed postgres please refer to
Please note that some request headers (like Authorization) are deleted before function is invoked
Habr:
Please see project boards and issues. With any questions and suggestions please visit our telegram chat
In the near future we will be focused on documentation improvements (mainly deployment examples) and support of async tasks (serverless workers and scheduler for celery).
- installing grpcio on Apple M1: installing with anaconda may help. Also look at stackoverflow
- versions of python 3.7 support yappa up to 0.3.12. You should use python 3.8 and above for new versions of yappa.
- Mikhail Novikov for starting this project two years ago
- httpx as a great tool for calling WSGI/ASGI apps offline
- Zappa for inspiration