StellarJay is a helpful framework for parsing GeoJSON content in Swift.
StellarJay parses and marshals GeoJSON objects type-safely, using Swift Decodable protocol and JSONDecoder API. It provides you a Swift generic API to inject custom Decodeable types for your service into the graph. You get a type-safe object graph of your GeoJSON content, including your own unique types.
.package(url: "[email protected]:sstadelman/stellarjay.git", from: "1.2")
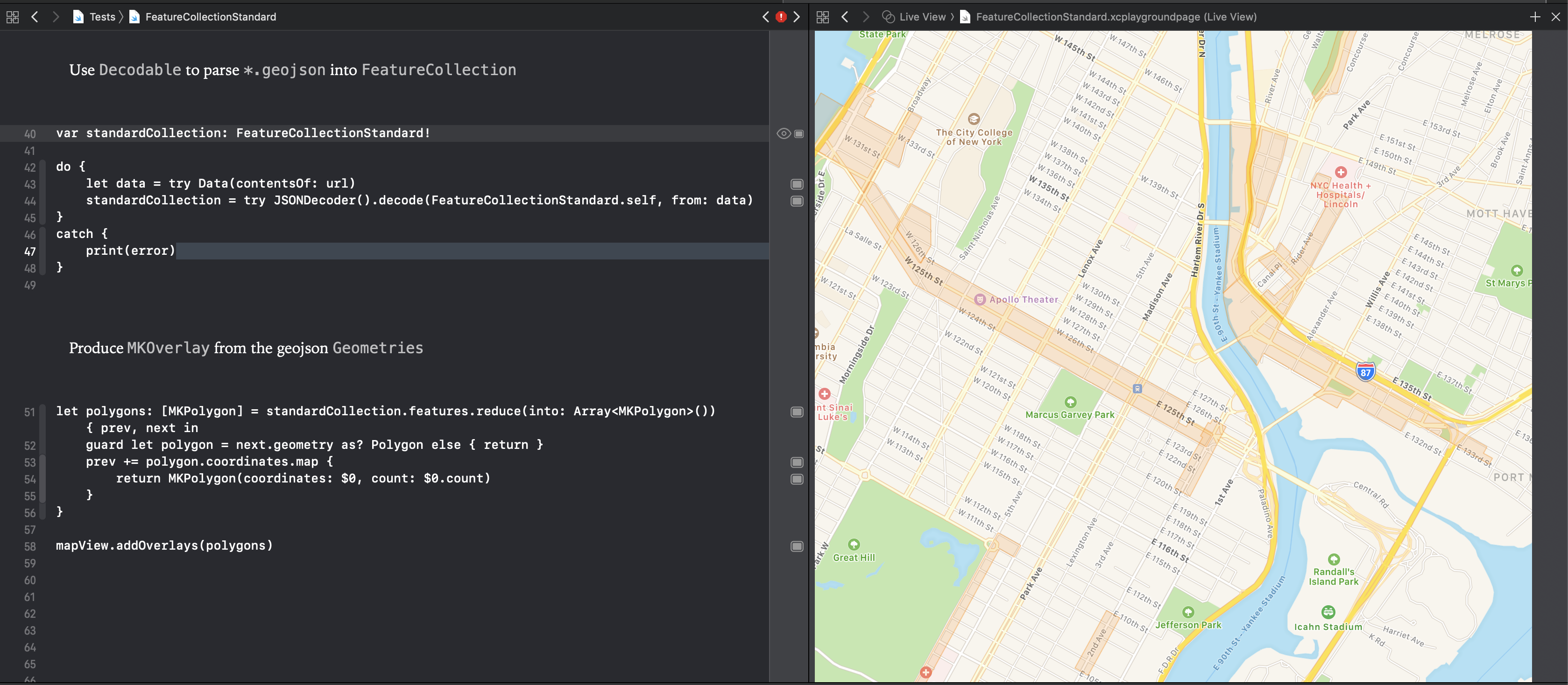
Using bear_transit.geojson as an example, we have a FeatureCollection with an array of 4 Feature's. Each Feature has a Geometry of type MultiLineString (a polyline), and a dictionary of properties. All these types are standard GeoJSON.
To parse these as standard GeoJSON, use the JSONDecoder API to decode the FeatureCollection, specifying that the Feature will parse the properties dictionary as Dictionary<String, Any>.
let bundle = Bundle(for: type(of: self))
let data = try Data(contentsOf: bundle.url(forResource:"bear_transit",
withExtension: "geojson")!, options: [])
let routeCollection: FeatureCollectionStandard = try JSONDecoder()
.decode(FeatureCollectionStandard.self, from: data)To test this in action, see Tests.playground in the workspace.
That's well and good, but it would be much more powerful if we could access the unique content of the properties dictionary from our model in a strongly-typed API, instead of navigating nested dictionaries. To do this, we create a Swift type which implements Decodable protocol, which exposes all the properties which we want to access from the Feature.properties dictionary.
struct Route: Decodable {
private enum CodingKeys: String, CodingKey {
case name
case vehicleType = "vehicle_type"
case color
case stops = "stops_served_by_route"
}
init(from decoder: Decoder) throws {
let values = try decoder.container(keyedBy: CodingKeys.self)
self.name = try values.decode(String.self, forKey: .name)
self.vehicleType = try values.decode(String.self, forKey: .vehicleType)
if let hex = try values.decodeIfPresent(String.self, forKey: .color) {
self.color = UIColor(hexString: hex)
} else {
self.color = nil
}
self.stops = try values.decode(Array<Dictionary<String, String>>.self, forKey: .stops)
}
let name: String
let vehicleType: String
let color: UIColor?
let stops: [[String: String]]
}Now, you can use the generic variant of the StellarJay FeatureCollection API, passing in your custom type of Feature:
// using same file "bear_transit.geojson" as above
let routeCollection = try JSONDecoder().decode(FeatureCollection<Feature<Route>>.self, from: data)Both of these decode(...) operations return a FeatureCollection, with 4 Feature items. But, the FeatureCollectionStandard's features have let properties: Dictionary<String, Any>, while the generic typed FeatureCollection<Feature<Route>>'s features have let properties: Route.
StellarJay has been used with data from these services:
- transit.land: Super-cool API for accessing transit provider route, stop, and schedule info. (Stops, Routes)
- BetaNYC: Open data platform for NYC (Single-part polygons)
- Uber Common: Bart Geojson showing Bart lines and stations.
Services listed are simply compatible examples, and do not represent endorsements by the providers ;)
- support for
GeometryCollectiongeometry type - support for bounding box
- API improvements
- broader support for "Foreign Members" (beyond
properties) - per-geometry unit tests
Released under MIT license. See LICENSE file.
Please file Issues.