The free-forever Python Simple GUI software.
pip install FreeSimpleGUITo migrate from PySimpleGUI:
- import PySimpleGUI as sg
+ import FreeSimpleGUI as sgIf you encounter any issues or have any questions, please feel welcome to open an issue.
Contributions are welcome! Contributions can be made via pull request. Ideally, please try to make sure there is an open issue associated with your pull request first or create one if necessary.
FreeSimpleGUI is a Python package that enables Python programmers of all levels to create GUIs. You specify your GUI window using a "layout" which contains widgets (they're called "Elements" in FreeSimpleGUI). Your layout is used to create a window using one of the 4 supported frameworks to display and interact with your window. Supported frameworks include tkinter, Qt, WxPython, or Remi. The term "wrapper" is sometimes used for these kinds of packages.
Your FreeSimpleGUI code is simpler and shorter than writing directly using the underlying framework because FreeSimpleGUI implements much of the "boilerplate code" for you. Additionally, interfaces are simplified to require as little code as possible to get the desired result. Depending on the program and framework used, a FreeSimpleGUI program may require 1/2 to 1/10th amount of code to create an identical window using one of the frameworks directly.
While the goal is to encapsulate/hide the specific objects and code used by the GUI framework you are running on top of, if needed you can access the frameworks' dependent widgets and windows directly. If a setting or feature is not yet exposed or accessible using the FreeSimpleGUI APIs, you are not walled off from the framework. You can expand capabilities without directly modifying the FreeSimpleGUI package itself.
This type of program is called a "one-shot" window because the window is displayed one time, the values collected, and then it is closed. It doesn't remain open for a long time like you would in a Word Processor.
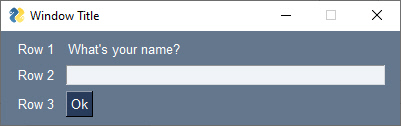
There are 5 sections to a FreeSimpleGUI program
import FreeSimpleGUI as sg # Part 1 - The import
# Define the window's contents
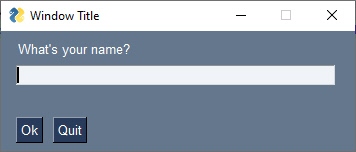
layout = [ [sg.Text("What's your name?")], # Part 2 - The Layout
[sg.Input()],
[sg.Button('Ok')] ]
# Create the window
window = sg.Window('Window Title', layout) # Part 3 - Window Defintion
# Display and interact with the Window
event, values = window.read() # Part 4 - Event loop or Window.read call
# Do something with the information gathered
print('Hello', values[0], "! Thanks for trying FreeSimpleGUI")
# Finish up by removing from the screen
window.close() # Part 5 - Close the WindowThe code produces this window
In this example, our window will remain on the screen until the user closes the window or clicks the Quit button. The main difference between the one-shot window you saw earlier and an interactive window is the addition of an "Event Loop". The Event Loop reads events and inputs from your window. The heart of your application lives in the event loop.
import FreeSimpleGUI as sg
# Define the window's contents
layout = [[sg.Text("What's your name?")],
[sg.Input(key='-INPUT-')],
[sg.Text(size=(40,1), key='-OUTPUT-')],
[sg.Button('Ok'), sg.Button('Quit')]]
# Create the window
window = sg.Window('Window Title', layout)
# Display and interact with the Window using an Event Loop
while True:
event, values = window.read()
# See if user wants to quit or window was closed
if event == sg.WINDOW_CLOSED or event == 'Quit':
break
# Output a message to the window
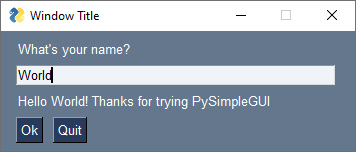
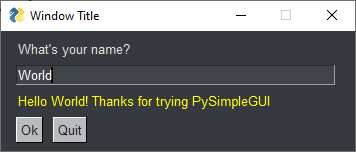
window['-OUTPUT-'].update('Hello ' + values['-INPUT-'] + "! Thanks for trying FreeSimpleGUI")
# Finish up by removing from the screen
window.close()This is the window that Example 2 produces.
And here's what it looks like after you enter a value into the Input field and click the Ok button.
Let's take a quick look at some of the differences between this example and the one-shot window.
First, you'll notice differences in the layout. Two changes in particular are important. One is the addition of the key parameter to the Input element and one of the Text elements. A key is like a name for an element. Or, in Python terms, it's like a dictionary key. The Input element's key will be used as a dictionary key later in the code.
Another difference is the addition of this Text element:
[sg.Text(size=(40,1), key='-OUTPUT-')],There are 2 parameters, the key we already covered. The size parameter defines the size of the element in characters. In this case, we're indicating that this Text element is 40 characters wide, by 1 character high. Notice that there is no text string specified which means it'll be blank. You can easily see this blank row in the window that's created.
We also added a button, "Quit".
The Event Loop has our familiar window.read() call.
Following the read is this if statement:
if event == sg.WINDOW_CLOSED or event == 'Quit':
breakThis code is checking to see if the user closed the window by clicking the "X" or if they clicked the "Quit" button. If either of these happens, then the code will break out of the event loop.
If the window wasn't closed nor the Quit button clicked, then execution continues. The only thing that could have happened is the user clicked the "Ok" button. The last statement in the Event Loop is this one:
window['-OUTPUT-'].update('Hello ' + values['-INPUT-'] + "! Thanks for trying FreeSimpleGUI")This statement updates the Text element that has the key -OUTPUT- with a string. window['-OUTPUT-'] finds the element with the key -OUTPUT-. That key belongs to our blank Text element. Once that element is returned from the lookup, then its update method is called. Nearly all elements have an update method. This method is used to change the value of the element or to change some configuration of the element.
If we wanted the text to be yellow, then that can be accomplished by adding a text_color parameter to the update method so that it reads:
window['-OUTPUT-'].update('Hello ' + values['-INPUT-'] + "! Thanks for trying FreeSimpleGUI",
text_color='yellow')After adding the text_color parameter, this is our new resulting window:
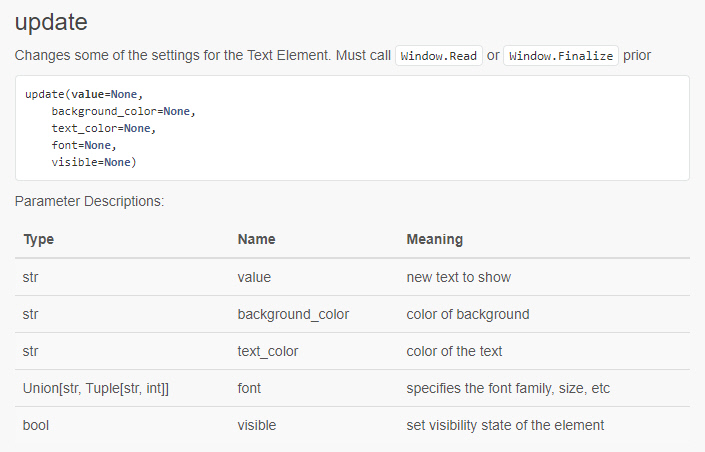
The parameters available for each element are documented in both the call reference documentation as well as the docstrings. FreeSimpleGUI has extensive documentation to help you understand all of the options available to you. If you lookup the update method for the Text element, you'll find this definition for the call:
As you can see several things can be changed for a Text element. The call reference documentation is a valuable resource that will make programming in FreeSimpleGUI, uhm, simple.
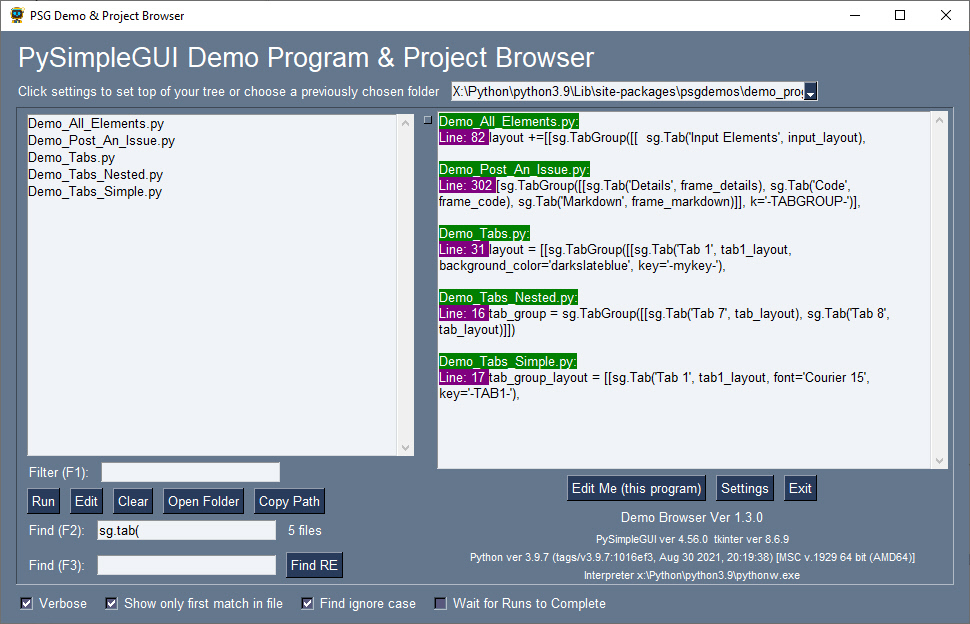
The over 300 Demo Programs will give you a jump-start and provide many design patterns for you to learn how to use FreeSimpleGUI and how to integrate FreeSimpleGUI with other packages. By far the best way to experience these demos is using the Demo Browser. This tool enables you to search, edit and run the Demo Programs.
To get them installed quickly along with the Demo Browser, use pip to install psgdemos:
python -m pip install psgdemos
or if you're in Linux, Mac, etc, that uses python3 instead of python to launch Python:
python3 -m pip install psgdemos
Once installed, launch the demo browser by typing psgdemos from the command line"
psgdemos
Your window's layout is a "list of lists" (LOL). Windows are broken down into "rows". Each row in your window becomes a list in your layout. Concatenate together all of the lists and you've got a layout...a list of lists.
Here is the same layout as before with an extra Text element added to each row so that you can more easily see how rows are defined:
layout = [ [sg.Text('Row 1'), sg.Text("What's your name?")],
[sg.Text('Row 2'), sg.Input()],
[sg.Text('Row 3'), sg.Button('Ok')] ]Each row of this layout is a list of elements that will be displayed on that row in your window.
Using lists to define your GUI has some huge advantages over how GUI programming is done using other frameworks. For example, you can use Python's list comprehension to create a grid of buttons in a single line of code.
These 3 lines of code:
import FreeSimpleGUI as sg
layout = [[sg.Button(f'{row}, {col}') for col in range(4)] for row in range(4)]
event, values = sg.Window('List Comprehensions', layout).read(close=True)produces this window which has a 4 x 4 grid of buttons:
Recall how "fun" is one of the goals of the project. It's fun to directly apply Python's powerful basic capabilities to GUI problems. Instead of pages of code to create a GUI, it's a few (or often 1) lines of code.
It's possible to condense a window's code down to a single line of code. The layout definition, window creation, display, and data collection can all be written in this line of code:
event, values = sg.Window('Window Title', [[sg.Text("What's your name?")],[sg.Input()],[sg.Button('Ok')]]).read(close=True)The same window is shown and returns the same values as the example showing the sections of a FreeSimpleGUI program. Being able to do so much with so little enables you to quickly and easily add GUIs to your Python code. If you want to display some data and get a choice from your user, it can be done in a line of code instead of a page of code.
By using short-hand aliases, you can save even more space in your code by using fewer characters. All of the Elements have one or more shorter names that can be used. For example, the Text element can be written simply as T. The Input element can be written as I and the Button as B. Your single-line window code thus becomes:
event, values = sg.Window('Window Title', [[sg.T("What's your name?")],[sg.I()],[sg.B('Ok')]]).read(close=True)FreeSimpleGUI is currently capable of running on 4 Python GUI Frameworks. The framework to use is specified using the import statement. Change the import and you'll change the underlying GUI framework. For some programs, no other changes are needed than the import statement to run on a different GUI framework. In the example above, changing the import from FreeSimpleGUI to FreeSimpleGUIQt, FreeSimpleGUIWx, FreeSimpleGUIWeb will change the framework.
| Import Statement | Resulting Window |
|---|---|
| FreeSimpleGUI |  |
| FreeSimpleGUIQt | 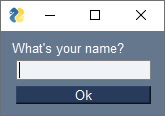 |
| FreeSimpleGUIWx | 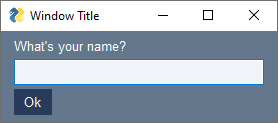 |
| FreeSimpleGUIWeb |  |
Porting GUI code from one framework to another (e.g. moving your code from tkinter to Qt) usually requires a rewrite of your code. FreeSimpleGUI is designed to enable you to have easy movement between the frameworks. Sometimes some changes are required of you, but the goal is to have highly portable code with minimal changes.
Some features, like a System Tray Icon, are not available on all of the ports. The System Tray Icon feature is available on the Qt and WxPython ports. A simulated version is available on tkinter. There is no support for a System Tray icon in the FreeSimpleGUIWeb port.
| Environment | Supported |
|---|---|
| Python | Python 3.4+ |
| Operating Systems | Windows, Linux, Mac |
| Hardware | Desktop PCs, Laptops, Raspberry Pi, Android devices running PyDroid3 |
| Online | repli.it, Trinket.com (both run tkinter in a browser) |
| GUI Frameworks | tkinter, pyside2, WxPython, Remi |
Among the more than 200 "Demo Programs", you'll find examples of how to integrate many popular Python packages into your GUI.
Want to embed a Matplotlib drawing into your window? No problem, copy the demo code and instantly have a Matplotlib drawing of your dreams into your GUI.
These packages and more are ready for you to put into your GUI as there are demo programs or a demo repo available for each:
| Package | Description |
|---|---|
| Matplotlib | Many types of graphs and plots |
| OpenCV | Computer Vision (often used for AI) |
| VLC | Video playback |
| pymunk | Physics engine |
| psutil | System environment statistics |
| prawn | Reddit API |
| json | FreeSimpleGUI wraps a special API to store "User Settings" |
| weather | Integrates with several weather APIs to make weather apps |
| mido | MIDI playback |
| beautiful soup | Web Scraping (GitHub issue watcher example) |
Two common ways of installing FreeSimpleGUI:
- pip to install from PyPI
- Download the file FreeSimpleGUI.py and place in your application's folder
The current suggested way of invoking the pip command is by running it as a module using Python. Previously the command pip or pip3 was directly onto a command-line / shell. The suggested way
Initial install for Windows:
python -m pip install FreeSimpleGUI
Initial install for Linux and MacOS:
python3 -m pip install FreeSimpleGUI
To upgrade using pip, you simply add 2 parameters to the line --upgrade --no-cache-dir.
Upgrade installation on Windows:
python -m pip install --upgrade --no-cache-dir FreeSimpleGUI
Upgrade for Linux and MacOS:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade --no-cache-dir FreeSimpleGUI
FreeSimpleGUI was created as a single .py file so that it would be very easy for you to install it, even on systems that are not connected to the internet like a Raspberry Pi. It's as simple as placing the FreeSimpleGUI.py file into the same folder as your application that imports it. Python will use your local copy when performing the import.
When installing using just the .py file, you can get it from either PyPI or if you want to run the most recent unreleased version then you'll download it from GitHub.
To install from PyPI, download either the wheel or the .gz file and unzip the file. If you rename the .whl file to .zip you can open it just like any normal zip file. You will find the FreeSimpleGUI.py file in one of the folders. Copy this file to your application's folder and you're done.
The PyPI link for the tkinter version of FreeSimpleGUI is: https://pypi.org/project/FreeSimpleGUI/#files
The GitHub repo's latest version can be found here: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spyoungtech/FreeSimpleGUI/main/FreeSimpleGUI.py
Now some of you are thinking, "yea, but, wait, having a single huge source file is a terrible idea". And, yea, sometimes it can be a terrible idea. In this case, the benefits greatly outweighed the downside. Lots of concepts in computer science are tradeoffs or subjective. As much as some would like it to be, not everything is black and white. Many times the answer to a question is "it depends".
Work on a more formal gallery of user-submitted GUIs as well as those found on GitHub is underway but as of this writing it's not complete. There are currently 2 places you can go to see some screenshots in a centralized way. Hopefully, a Wiki or other mechanism can be released soon to do justice to the awesome creations people are making.
The first is a user submitted screenshots issue located on the GitHub. It's an informal way for people to show off what they've made. It's not ideal, but it was a start.
The second is a massive gallery of over 3,000 images scraped from 1,000 projects on GitHub that are reportedly using FreeSimpleGUI. It's not been hand-filtered and there are plenty of old screenshots that were used in the early documentation. But, you may find something in there that sparks your imagination.
The following sections showcase a fraction of the uses for FreeSimpleGUI. There are over 1,000 projects on GitHub alone that use FreeSimpleGUI. It's truly amazing how possibilities have opened up for so many people. Many users have spoken about previously attempting to create a GUI in Python and failing, but finally achieving their dreams when they tried FreeSimpleGUI.
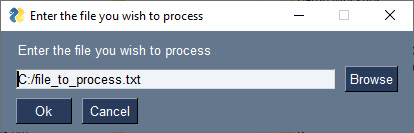
Of course one of the best uses of FreeSimpleGUI is getting you into making GUIs for your Python projects. You can start as small as requesting a filename. For this, you only need to make a single call to one of the "high-level functions" called popup. There are all kinds of popups, some collect information.
popup on itself makes a window to display information. You can pass multiple parameters just like a print. If you want to get information, then you will call functions that start with popup_get_ such as popup_get_filename.
Adding a single line to get a filename instead of specifying a filename on the command line can transform your program into one that "normal people" will feel comfortable using.
import FreeSimpleGUI as sg
filename = sg.popup_get_file('Enter the file you wish to process')
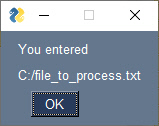
sg.popup('You entered', filename)This code will display 2 popup windows. One to get the filename, which can be browsed to or pasted into the input box.
The other window will output what is collected.
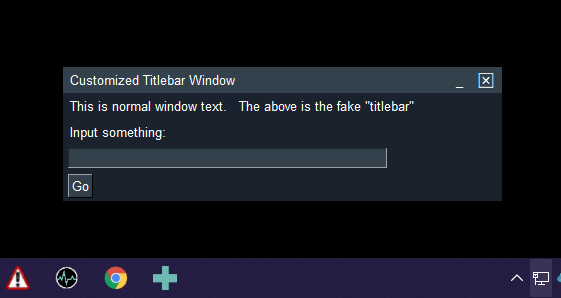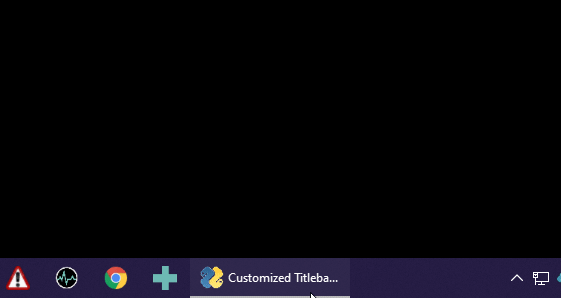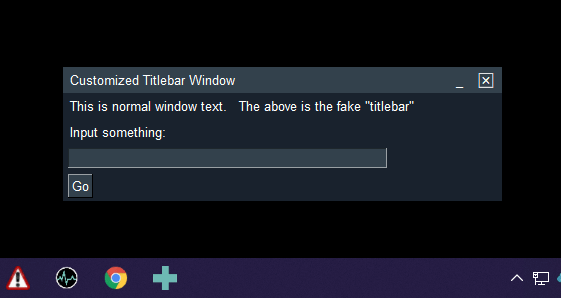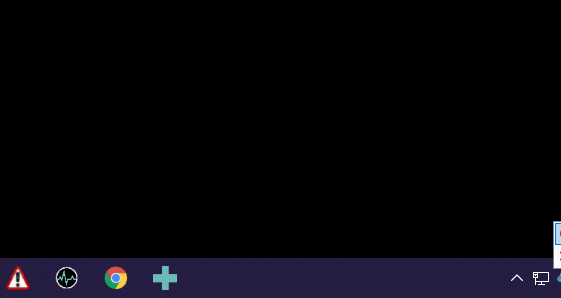
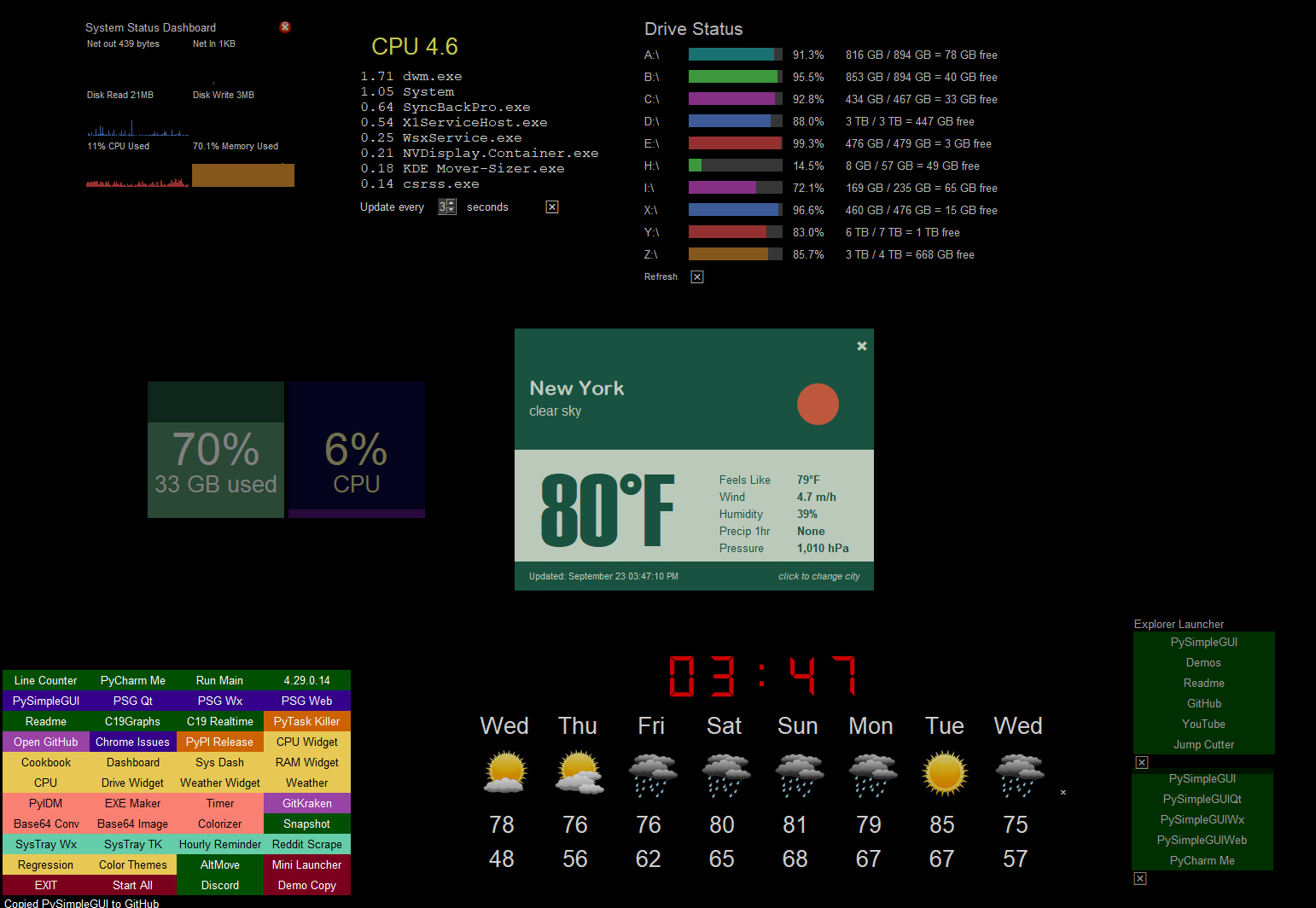 The default settings for GUI frameworks don't tend to produce the nicest looking windows. However, with some attention to detail, you can do several things to make windows look attractive. FreeSimpleGUI makes it easier to manipulate colors and features like removing the title bar. The result is windows that don't look like your typical tkinter windows.
The default settings for GUI frameworks don't tend to produce the nicest looking windows. However, with some attention to detail, you can do several things to make windows look attractive. FreeSimpleGUI makes it easier to manipulate colors and features like removing the title bar. The result is windows that don't look like your typical tkinter windows.
Here is an example of how you can create windows that don't look like your typical tkinter in windows. In this example, the windows have their titlebars removed. The result is windows that look much like those found when using Rainmeter, a desktop widget program.
You can easily set the transparency of a window as well. Here are more examples of desktop widgets in the same Rainmeter style. Some are dim appearing because they are semi-transparent.
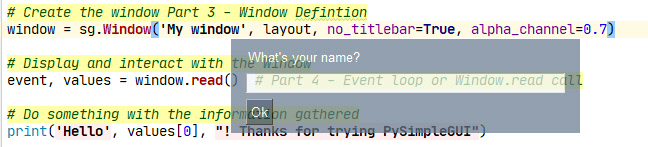
Both of these effects; removing the titlebar and making a window semi-transparent, are achieved by setting 2 parameters when creating the window. This is an example of how FreeSimpleGUI enables easy access to features. And because FreeSimpleGUI code is portable across the GUI frameworks, these same parameters work for the other ports such as Qt.
Changing the Window creation call in Example 1 to this line of code produces a similar semi-transparent window:
window = sg.Window('My window', layout, no_titlebar=True, alpha_channel=0.5)While not specifically written as a game development SDK, FreeSimpleGUI makes the development of some games quite easy.
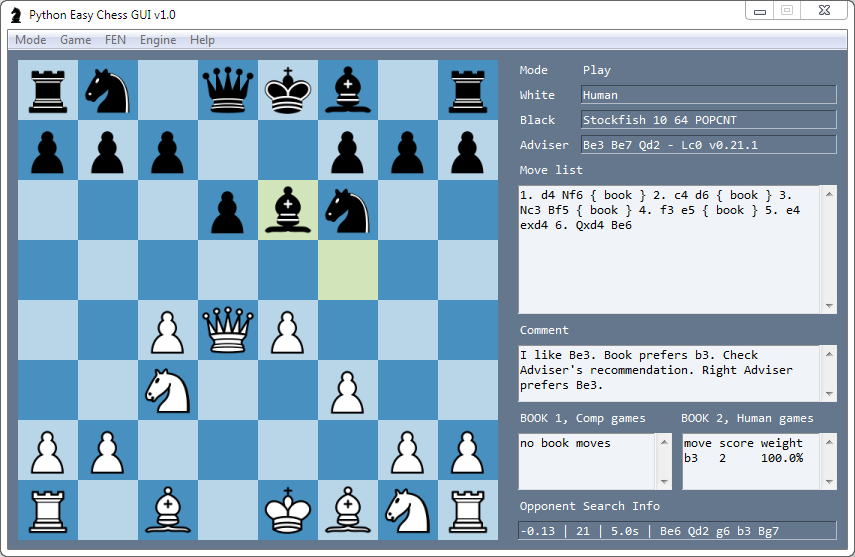 This Chess program not only plays chess, but it integrates with the Stockfish chess-playing AI.
This Chess program not only plays chess, but it integrates with the Stockfish chess-playing AI.
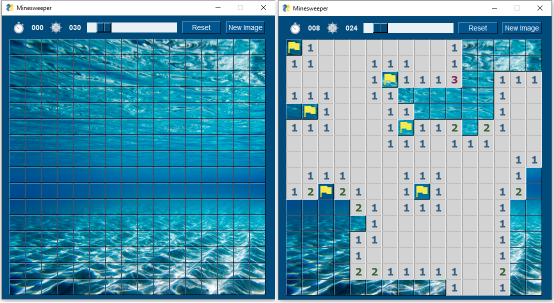
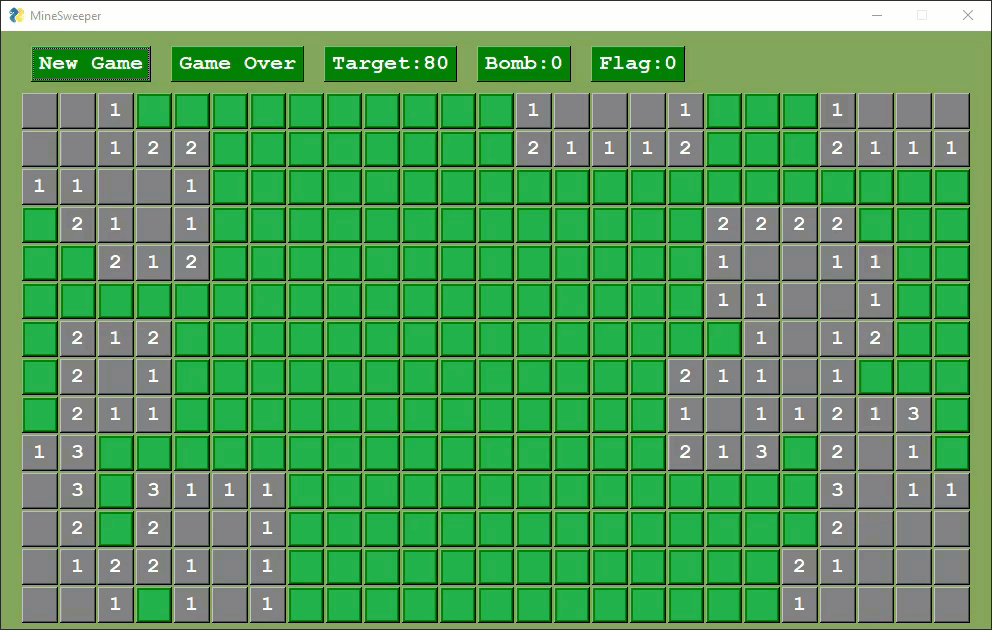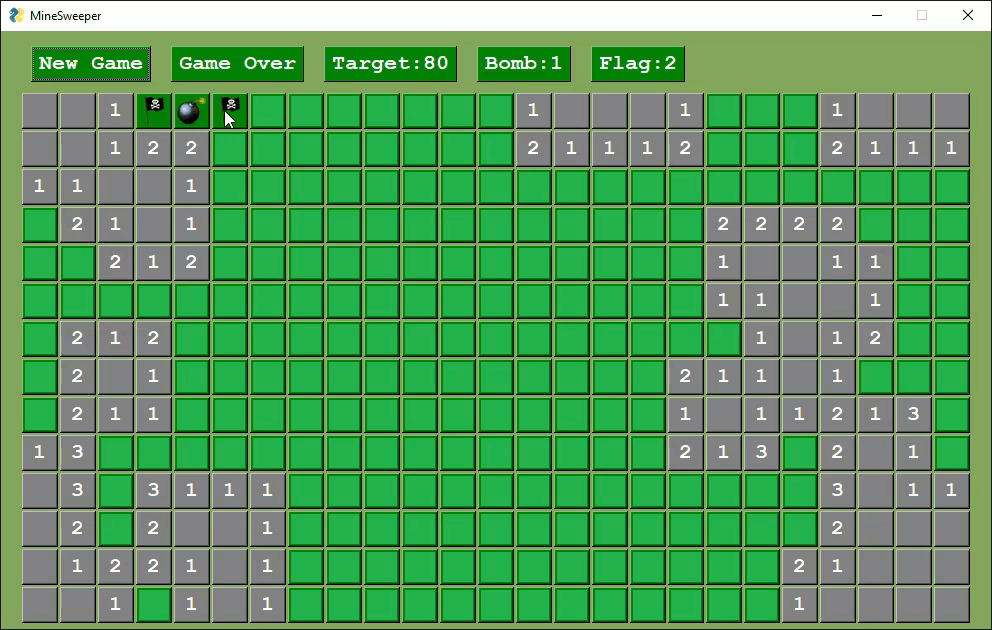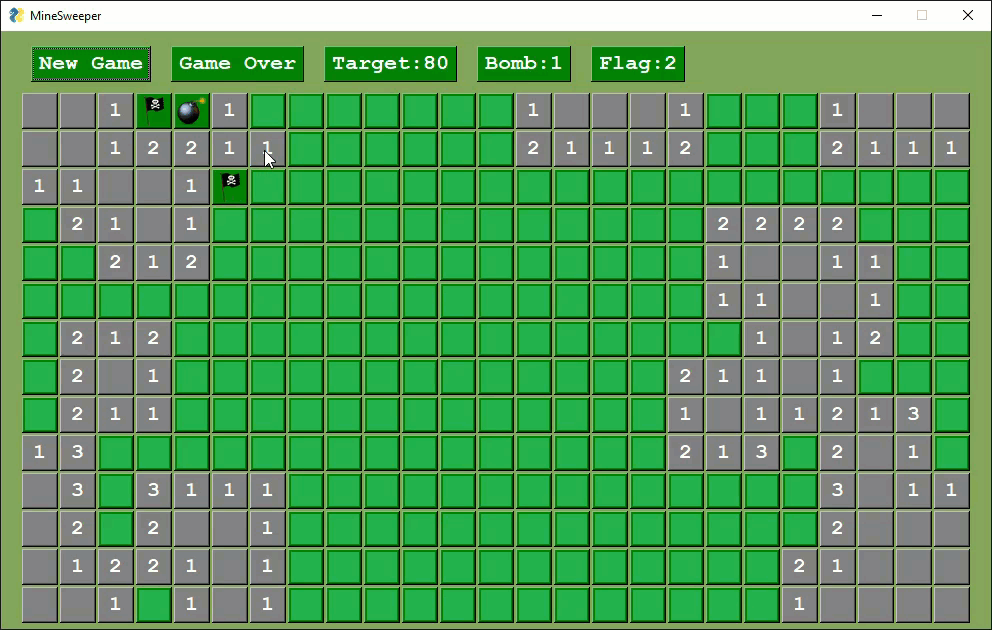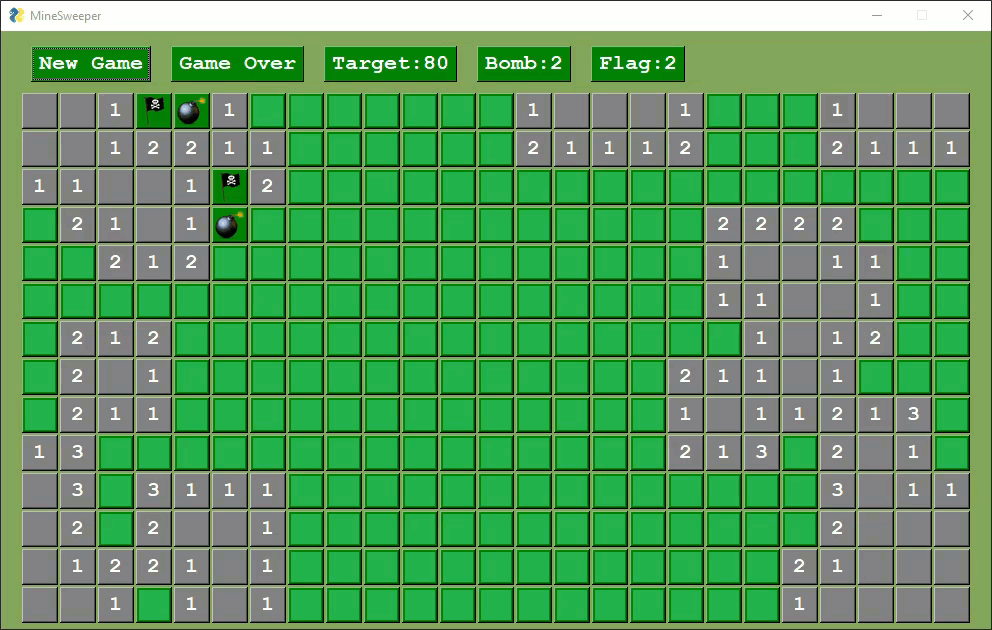 Several variants of Minesweeper have been released by users.
Several variants of Minesweeper have been released by users.
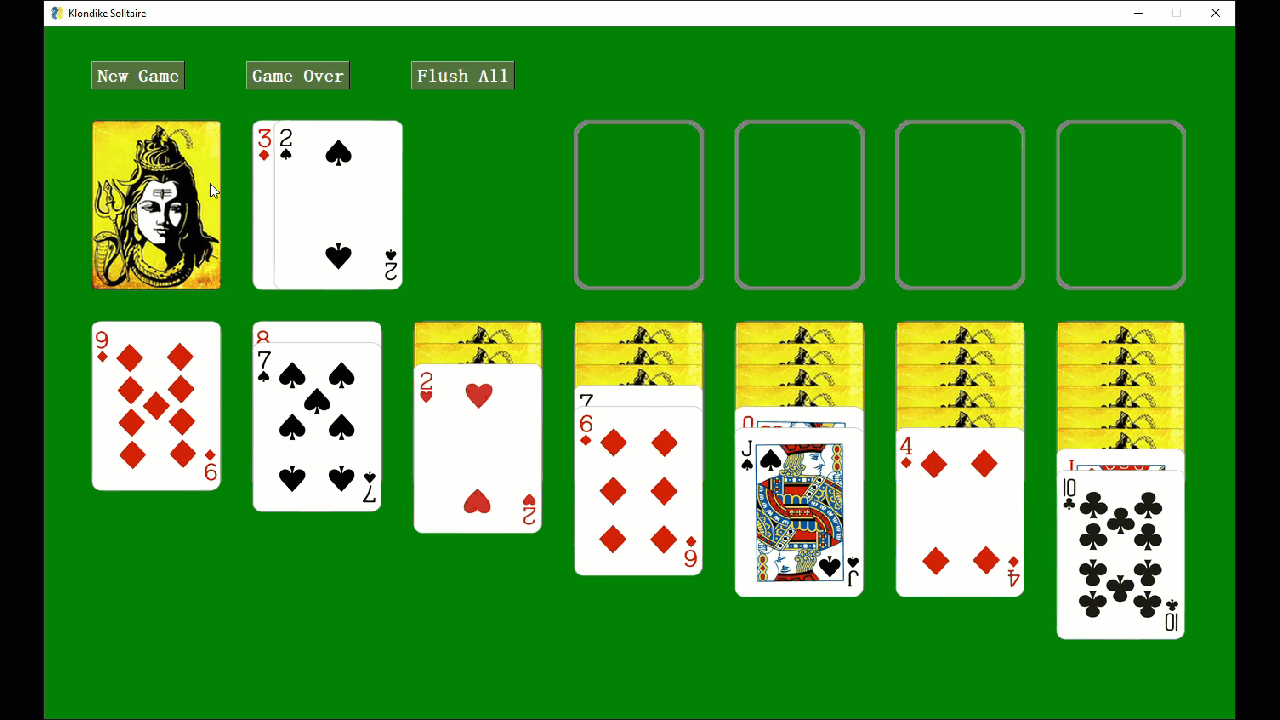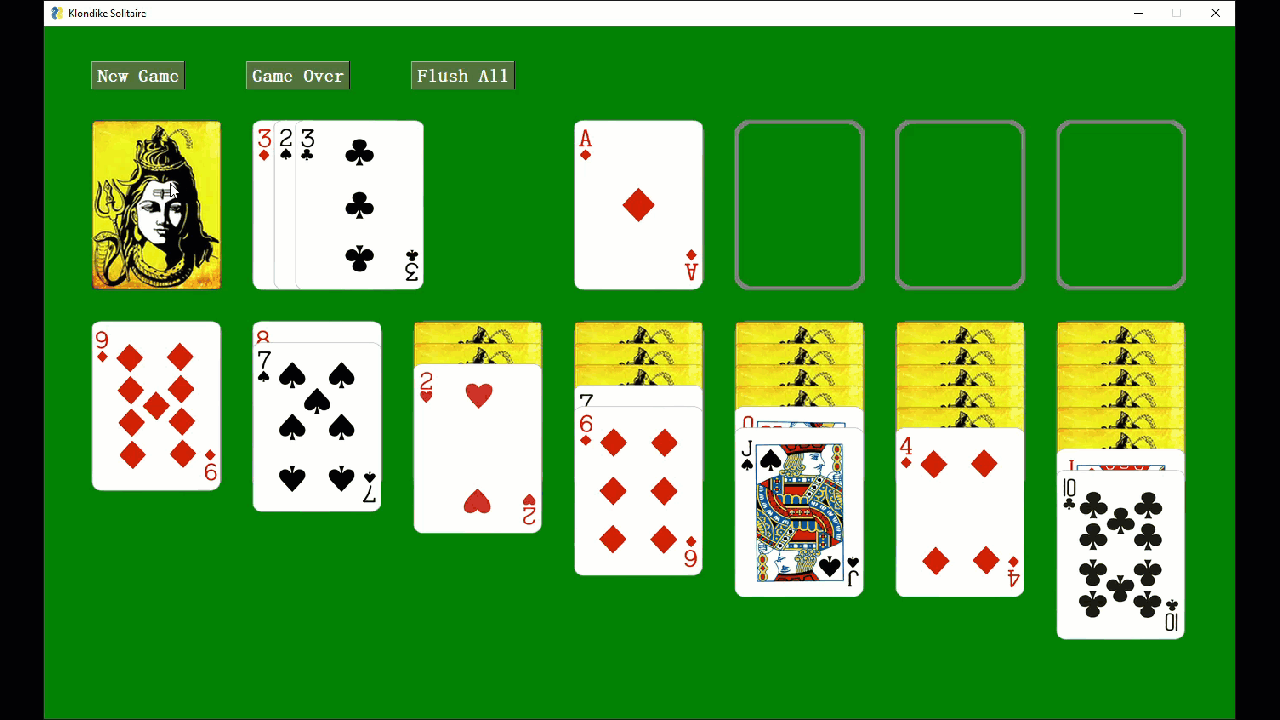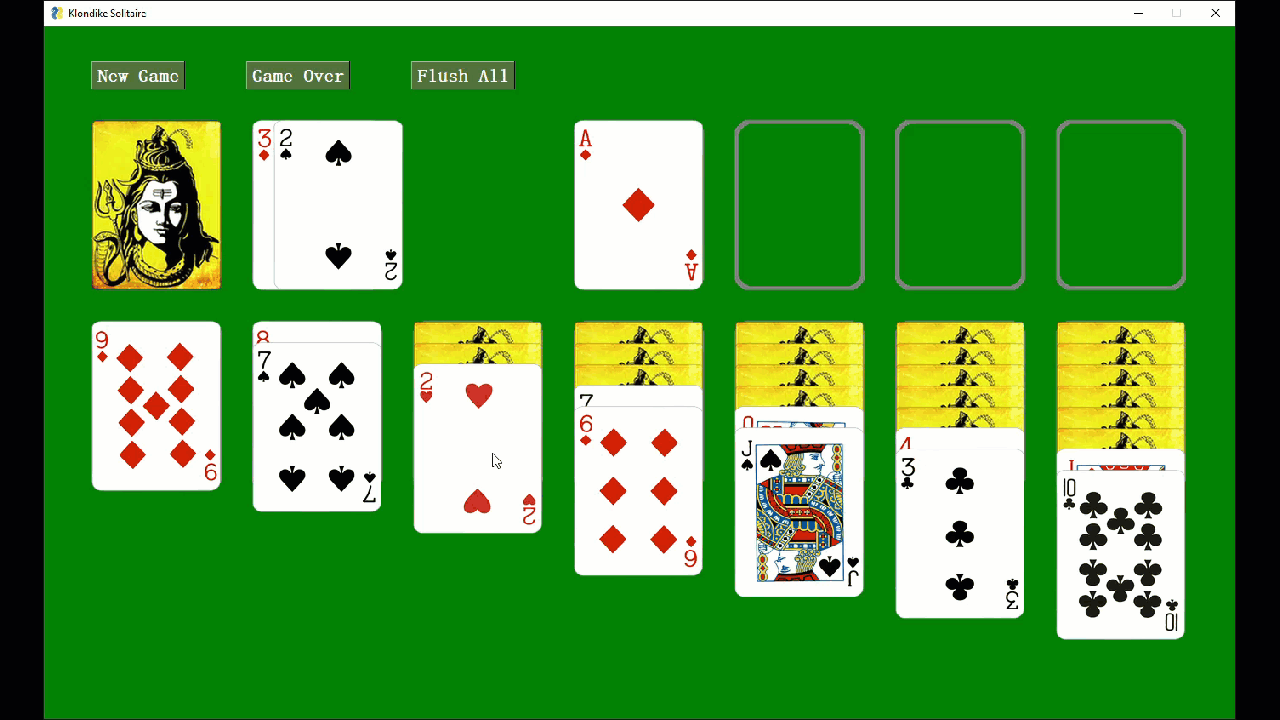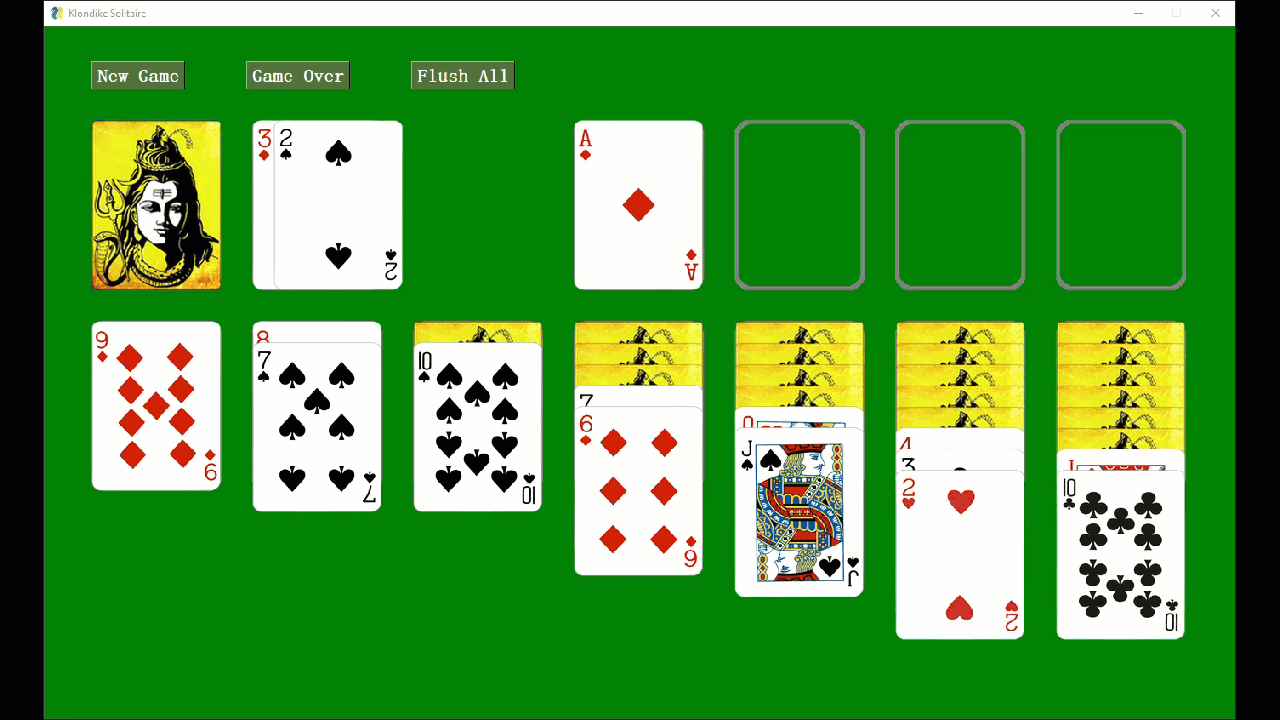
Card games work well with FreeSimpleGUI as manipulating images is simple when using the FreeSimpleGUI Graph element.
While not specifically written as a game development SDK, FreeSimpleGUI makes development of some games quite easy.
Capturing and displaying video from your webcam in a GUI is 4 lines of FreeSimpleGUI code. Even more impressive is that these 4 lines of code work with the tkinter, Qt, and Web ports. You can display your webcam, in realtime, in a browser using the same code that displays the image using tkinter.
Media playback, audio and video, can also be achieved using the VLC player. A demo application is provided to you so that you have a working example to start from. Everything you see in this readme is available to you as a starting point for your own creations.
AI and Python have long been a recognized superpower when the two are paired together. What's often missing however is a way for users to interact with these AI algorithms familiarly, using a GUI.
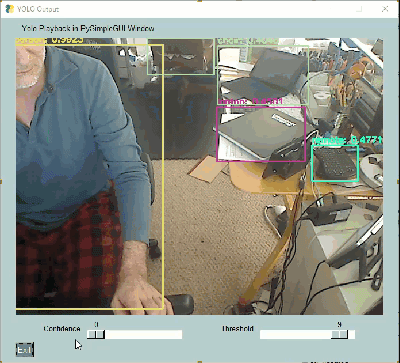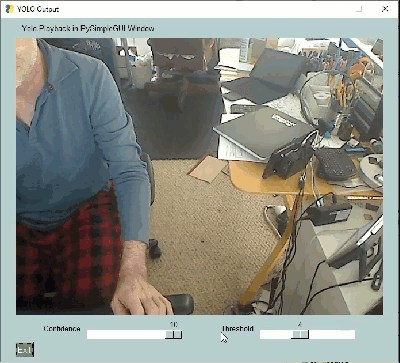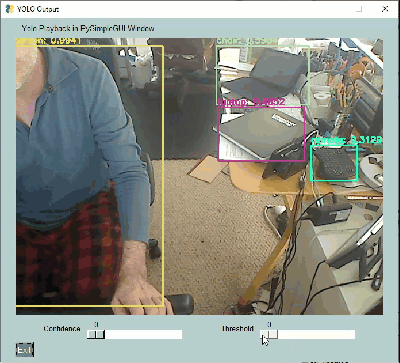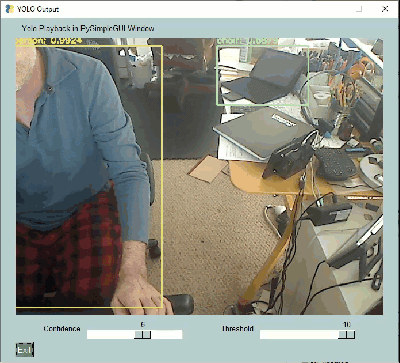
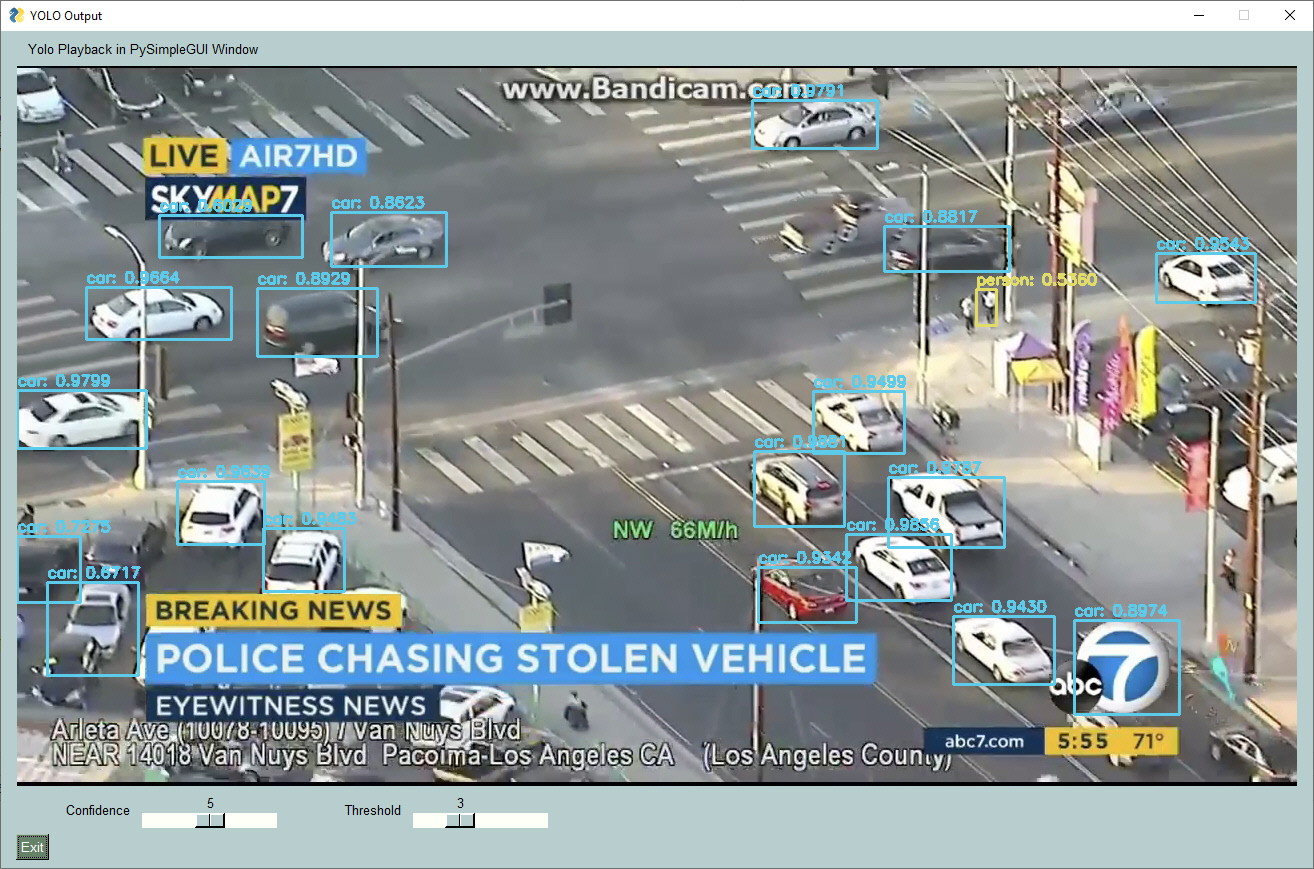
These YOLO demos are a great example of how a GUI can make a tremendous difference in interacting with AI algorithms. Notice two sliders at the bottom of these windows. These 2 sliders change a couple of the parameters used by the YOLO algorithm.
If you were tuning your YOLO demo using only the command line, you would need to set the parameters, once, when you launch the application, see how they perform, stop the application, change the parameters, and finally restart the application with the new parameters.
Contrast those steps against what can be done using a GUI. A GUI enables you to modify these parameters in real-time. You can immediately get feedback on how they are affecting the algorithm.
There are SO many AI programs that have been published that are command-line driven. This in itself isn't a huge hurdle, but it's enough of a "pain in the ass" to type/paste the filename you want to colorize on the command line, run the program, then open the resulting output file in a file viewer.
GUIs have the power to change the user experience, to fill the "GUI Gap". With this colorizer example, the user only needs to supply a folder full of images, and then click on an image to both colorize and display the result.
The program/algorithm to do the colorization was freely available, ready to use. What was missing is the ease of use that a GUI could bring.
Displaying and interacting with data in a GUI is simple with FreeSimpleGUI. You have several options.
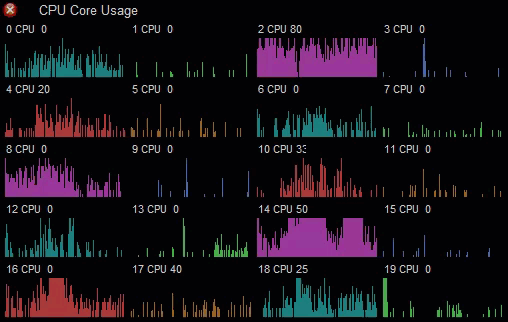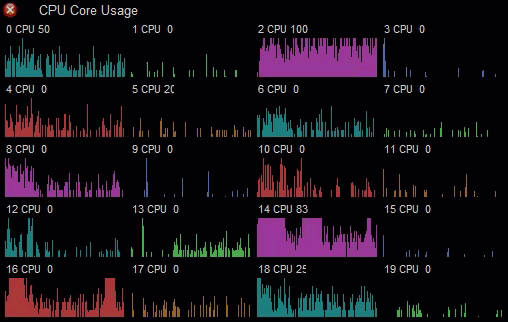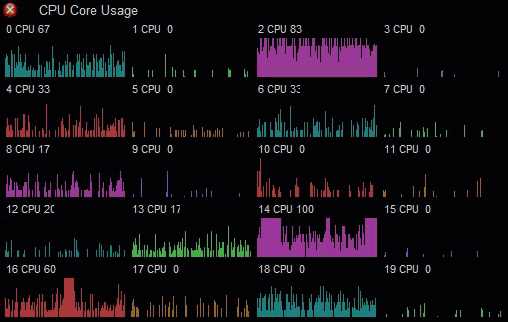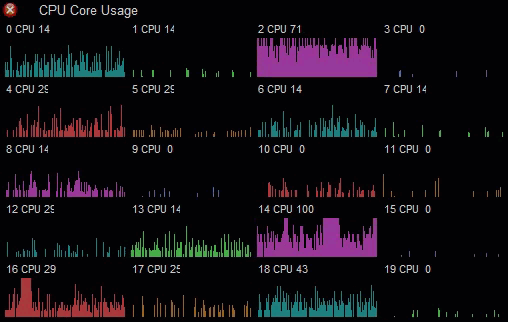
You can use the built-in drawing/graphing capabilities to produce custom graphs. This CPU usage monitor uses the Graph element
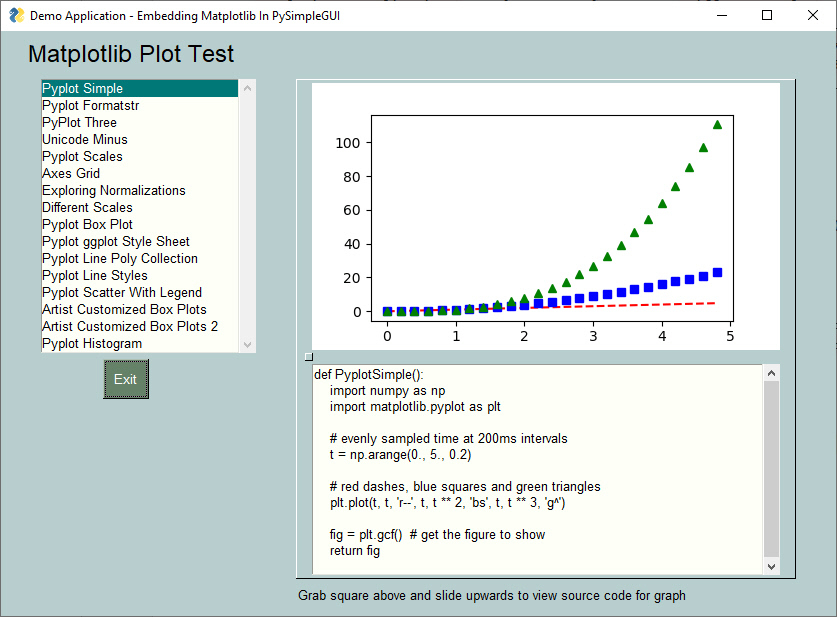
Matplotlib is a popular choice with Python users. FreeSimpleGUI can enable you to embed Matplotlib graphs directly into your GUI window. You can even embed the interactive controls into your window if you want to retain the Matplotlib interactive features.
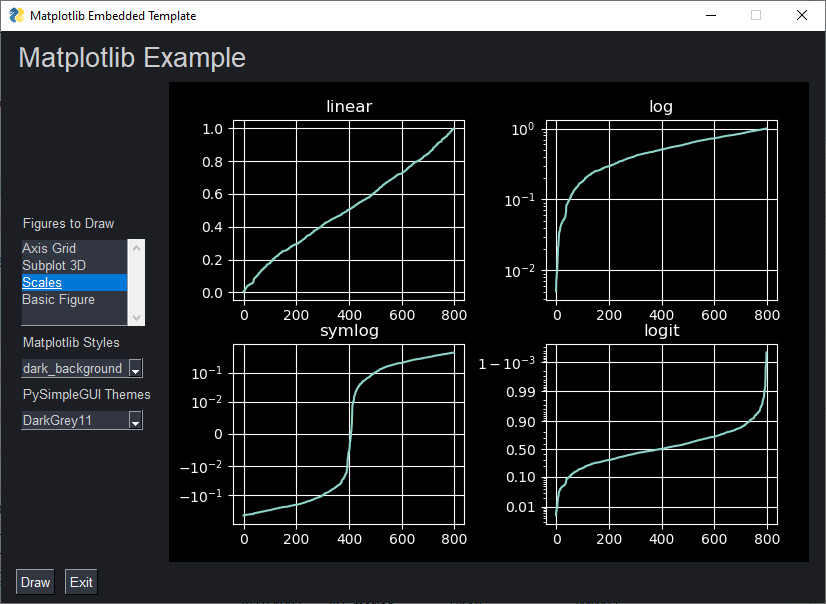 Using FreeSimpleGUI's color themes, you can produce graphs that are a notch above default graphs that most people create in Matplotlib.
Using FreeSimpleGUI's color themes, you can produce graphs that are a notch above default graphs that most people create in Matplotlib.
The "GUI Gap" mentioned earlier can be easily solved using FreeSimpleGUI. You don't even need to have the source code to the program you wish to add a GUI onto. A "front-end" GUI is one that collects information that is then passed to a command-line application.
Front-end GUIs are a fantastic way for a programmer to distribute an application that users were reluctant to use previously because they didn't feel comfortable using a command-line interface. These GUIs are your only choice for command-line programs that you don't have access to the source code for.
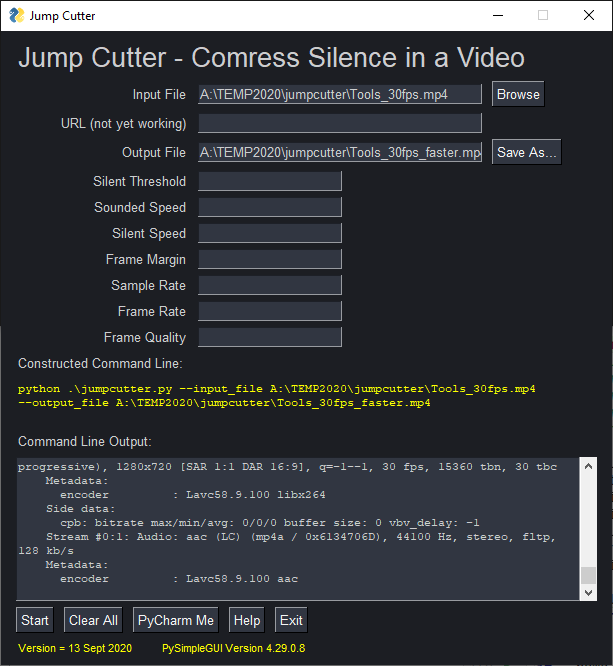
This example is a front-end for a program called "Jump Cutter". The parameters are collected via the GUI, a command-line is constructed using those parameters, and then the command is executed with the output from the command-line program being routed to the GUI interface. In this example, you can see in yellow the command that was executed.
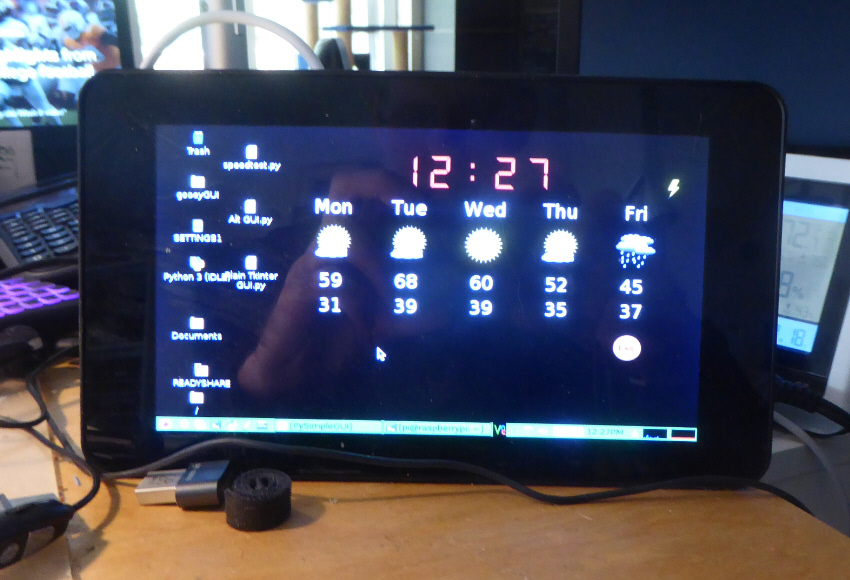
Because FreeSimpleGUI is compatible back to Python 3.4, it is capable of creating a GUI for your Raspberry Pi projects. It works particularly well when paired with a touchscreen. You can also use FreeSimpleGUIWeb to control your Pi if it doesn't have a monitor attached.
Because it's very easy to access many of the underlying GUI frameworks' features, it's possible to piece together capabilities to create applications that look nothing like those produced using the GUI framework directly.
For example, it's not possible to change the color/look-and-feel of a titlebar using tkinter or the other GUI packages, but with FreeSimpleGUI it's easy to create windows that appear as if they have a custom titlebar.
Unbelievably, this window is using tkinter to achieve what appears to be something like a screensaver.
On windows, tkinter can completely remove the background from your application. Once again, FreeSimpleGUI makes accessing these capabilities trivial. Creating a transparent window requires adding a single parameter to the call that creates your Window. One parameter change can result in a simple application with this effect:
You can interact with everything on your desktop, clicking through a full-screen window.
Tired of the default grey GUIs? FreeSimpleGUI makes it trivial for your window to look nice by making a single call to the theme function. There are over 150 different color themes available for you to choose:
With most GUI frameworks, you must specify the color for every widget you create. FreeSimpleGUI takes this chore from you and will automatically color the Elements to match your chosen theme.
To use a theme, call the theme function with the name of the theme before creating your window. You can add spaces for readability. To set the theme to "Dark Grey 9":
import FreeSimpleGUI as sg
sg.theme('dark grey 9')This single line of code changes the window's appearance entirely:
The theme changed colors of the background, text, input background, input text, and button colors. In other GUI packages, to change color schemes like this, you would need to specify the colors of each widget individually, requiring numerous changes to your code.
Want to share your FreeSimpleGUI program with friends and family that don't have Python installed on their computer? Try the GUI front-end for PyInstaller that you'll find in the psgcompiler project.
Your first stop should be the documentation and demo programs.
Be sure and install the Demo Browser (instructions in the Cookbook) so that you can search and run the 100s of demo programs.
If you still have a question or need help... no problem... help is available to you, at no cost. Simply file an Issue on the FreeSimpleGUI GitHub repo and you'll get help.
Nearly all software companies have a form that accompanies bug reports. It's not a bad trade... fill in the form, get free software support. This information helps get you an answer efficiently.
In addition to requesting information such as the version numbers of FreeSimpleGUI and underlying GUI frameworks, you're also given a checklist of items that may help you solve your problem.
Please fill in the form. It may feel pointless to you. It may feel painful, despite it taking just a moment. It helps get you a solution faster. If it wasn't useful and necessary information to help you get a speedy reply and fix, you wouldn't be asked to fill it out. "Help me help you".
© Copyright 2024, FreeSimpleGUI authors © Copyright 2021, 2022 PySimpleGui