-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 48
Lecture 1 Summary
- Data abstraction
Let information be intelligent/meaningful.
- Function abstraction
If you can extract out a meaningful function within another function, do it.
- Packaging
Code of different functionalities should reside in different classes/places.
- Information hiding
Private access.
- Tell-Don't-Ask
Tell an object what to do, rather than asking an object for data and acting on it.
- Immutability
Void methods that mutate states should be avoided. Declaring fields as final helps to ensure immutability
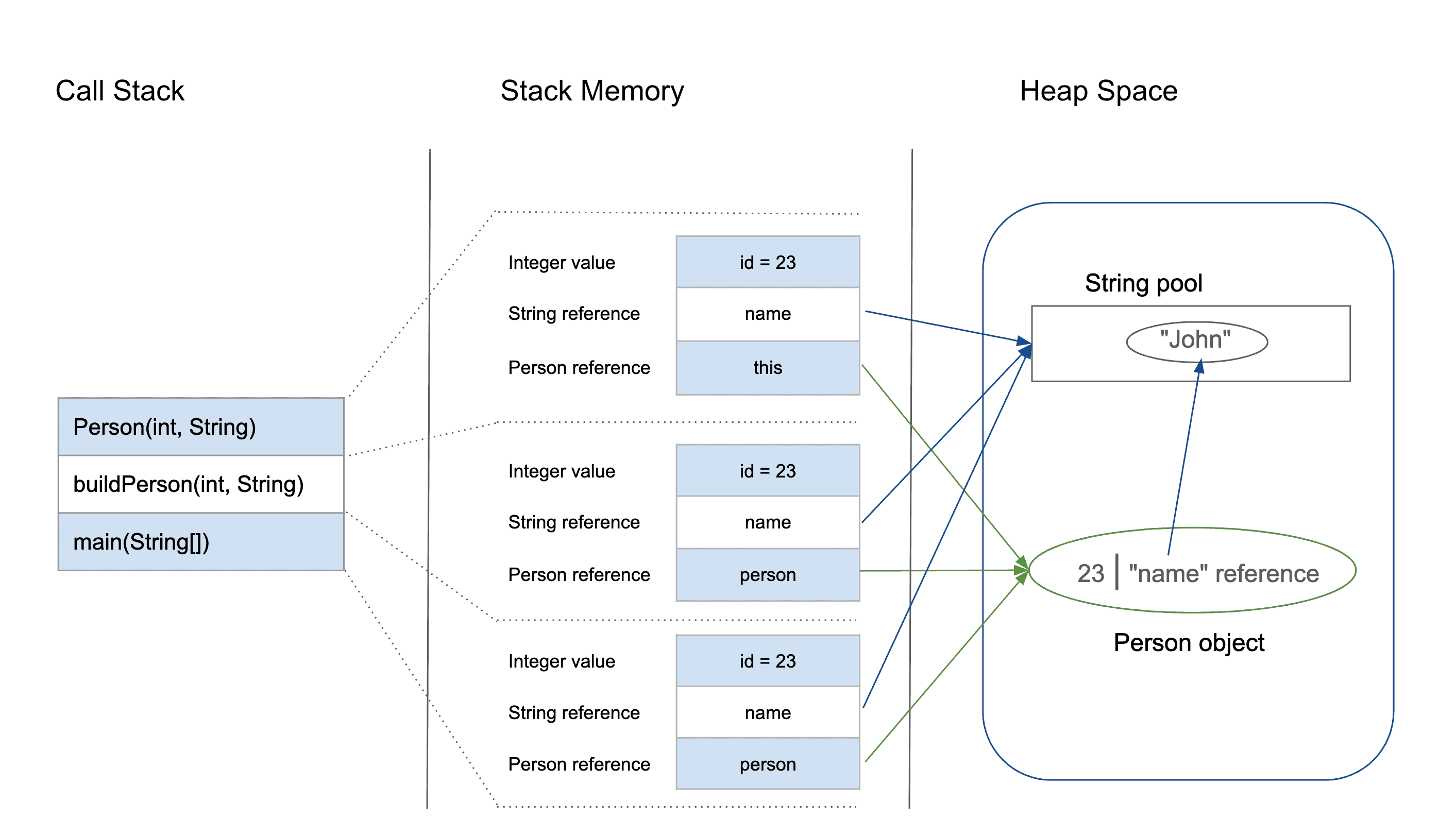
A quick dive into Java's memory model. Something that we learnt in CS2030 is to understand that Primitive types get stored in the heap and references to local variable gets stored in the stack. A quick illustration:
- Stack
- LIFO (Last In First Out) stack for storing activation records (stack frame) of method calls
- Local primitive type variables are stored in the stack
- References to local variables are stored in the stack, whereas their respective Objects are stored on the heap
- Note: The method local variables not stored here until the method is being called OR during the program run
- Heap
- Stores Java Objects upon invoking new
- Garbage collection when the variables are no longer used or referenced is done here (freeing up memory space by removing unused variables)
- Stack items (e.g. method variables) refer to objects on the heap
- Primitive reference types are stored here as well (e.g. Double, Integer, Character, etc.)
- Non-heap/Metaspace
- Stores loaded classes & other metadata
There was also discussion about it on issue : https://github.com/nus-cs2030/2021-s1/issues/527#issue-752621947
Peer Learning
Codecrunch Contributions
Piazza Contributions
Wiki Contributions
Guides
Setting Up Checkstyle
Setting Up Java
Setting Up MacVim
Setting Up Sunfire
Setting Up Unix For Mac
Setting Up Unix For Windows
Setting Up Vim
Setting up SSH Config
CS2030 Contents
Lecture 1 SummaryCompile-run vs Run-time Summary
Quick Guide To Abstraction
Generics and Variance of Types
Comparable vs Comparator
Summary of completable future
CS2030S Notes
ELI5 Optional.map vs Optional.flatMap
PECS Example Code
Java Collection Framework (Iterator)
Generic
Generic Type Parameter and Generic Wildcard
Calculator
Lambda-Expression
Single Abstract Method (SAM)
Method Reference
Functional Interfaces 2
Simple Usage of Sandbox
Associative-but-not-commutative
Higher Order function
Functional Programming
Calculator With Functor
Eager Evaluation VS Lazy Evaluation
Simple Usage of Lazy Evaluation
Lazy Evaluation for LazyList
Lazy Evaluation for BinaryTree
Stream
Parallel Stream
Optional
Simple Usage of Stream
Asynchronous Programming
Notes on CompletableFuture
Notes on CompletableFuture 2
Simple Usage of CompletableFuture
Mind Map
Exception Handling
Links
CS2030 Java Style Guide
CS2030 Javadoc Specification
JDK 11 Download Link
JDK 11 API Docs
Codecrunch
Piazza Forum