Replace this line with a short description about your project!
First, activate a virtual environment (recommended).
Install the package in editable mode so you can modify the source directly:
pip install -e .
To add new dependencies, simply add them to the setup.py.
These hooks will:
-
validate flake8 before any commit
-
check that jupyter notebook outputs have been stripped
cd .git/hooks/ && ln -s ../../hooks/pre-commit .
Alternatively, to only lint files that have been staged in git, use cd .git/hooks/ && ln -s ../../hooks/pre-commit_staged pre-commit
Continuous integration will run the following:
- Unit tests under
tests. - End-to-end test under
exmaples/local. flake8to check the code syntax.- Checks on documentation presence and format (using
sphinx).
We support the GitHub Actions for running CI.
Github actions are already configured in .github/workflows/tests.yml.
Github actions are already enabled by default when using Github, so, when
pushing to github, they will be executed automatically for pull requests to
main and to develop.
Just run (from the root folder):
pytest
Note that the code should already compile at this point.
Running examples can be found under the examples folder.
In particular, you will find examples for:
- local machine (e.g., your laptop).
- a slurm cluster.
For both these cases, there is the possibility to run with or without Orion. (Orion is a hyper-parameter search tool - see https://github.com/Epistimio/orion - that is already configured in this project)
For example, to run on your local machine without Orion:
cd examples/local
sh run.sh
This will run a simple MLP on a simple toy task: sum 5 float numbers. You should see an almost perfect loss of 0 after a few epochs.
Note you have a new output folder which contains models and a summary of results:
- best_model: the best model checkpoint during training
- last_model: the last model checkpoint during training
- lightning_logs: contains the tensorboard logs.
To view tensorboard logs, simply run:
tensorboard --logdir output
First, bring you project on the cluster (assuming you didn't create your project directly there). To do so, simply login on the cluster and git clone your project:
git clone [email protected]:${GITHUB_USERNAME}/${PROJECT_NAME}.git
Then activate your virtual env, and install the dependencies:
cd crystal_diffusion
pip install -e .
To run with Slurm, just:
cd examples/slurm
sh run.sh
Check the log to see that you got an almost perfect loss (i.e., 0).
You can track down the GPU time (and other resources) of your jobs by
associating a tag to the job (when using sbatch).
To associate a tag to a job, replace my_tag with a proper tag,
and uncomment the line (i.e., remove one #) from the line:
##SBATCH --wckey=my_tag
This line is inside the file examples/slurm_mila/to_submit.sh.
To get a sumary for a particular tag, just run:
sacct --allusers --wckeys=my_tag --format=JobID,JobName,Start,Elapsed -X -P --delimiter=','
(again, remember to change my_tag into the real tag name)
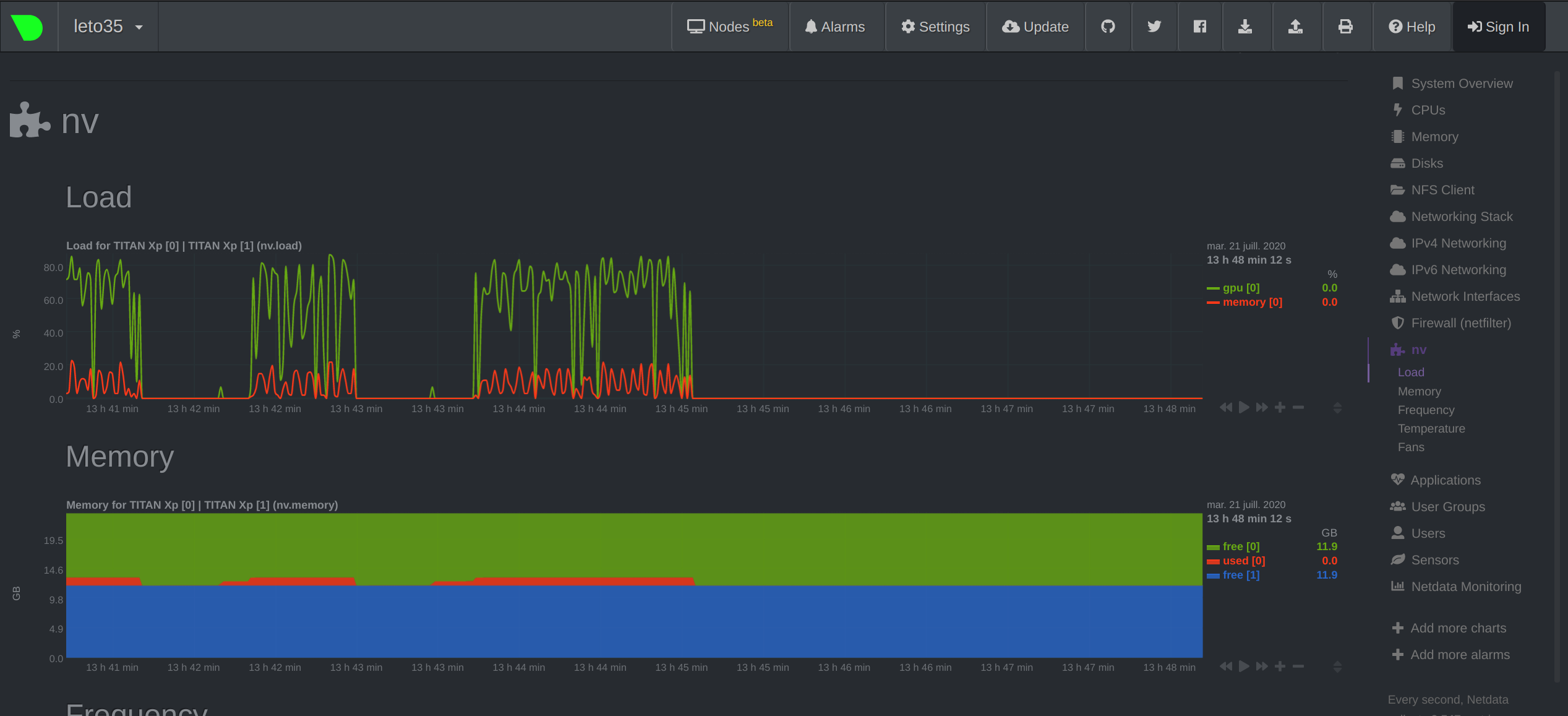
It can be useful to monitor and profile how you utilise your GPU (usage, memory, etc.). For the time being, you can only monitor your profiling in real-time from the Mila cluster, i.e. while your experiments are running. To monitor your GPU, you need to setup port-forwarding on the host your experiments are running on. This can be done in the following way:
Once you have launched your job on the mila cluster, open the log for your current experiment:
head logs/crystal_diffusion/__<your_slurm_job_id>.err
You should see printed in the first few lines the hostname of your machine, e.g.,
INFO:crystal_diffusion.utils.logging_utils:Experiment info:
hostname: leto35
git code hash: a51bfc5447d188bd6d31fac3afbd5757650ef524
data folder: ../data
data folder (abs): /network/tmp1/bronzimi/20191105_cookiecutter/crystal_diffusion/examples/data
In a separate shell on your local computer, run the following command:
ssh -L 19999:<hostname>.server.mila.quebec:19999 <username>@login.server.mila.quebec -p 2222
where <username> is your user name on the Mila cluster and <hostname> is the name of the machine your job is currenty running on (leto35 in our example). You can then navigate your local browser to http://localhost:19999/ to view the ressources being used on the cluster and monitor your job. You should see something like this:
This example will run orion for 2 trials (see the orion config file).
To do so, go into examples/slurm_orion.
Here you can find the orion config file (orion_config.yaml), as well as the config
file (config.yaml) for your project (that contains the hyper-parameters).
In general, you will want to run Orion in parallel over N slurm jobs.
To do so, simply run sh run.sh N times.
When Orion has completed the trials, you will find the orion db file.
You will also find the output of your experiments in orion_working_dir, which
will contain a folder for every trial.
Inside these folders, you can find the models (the best one and the last one), the config file with
the hyper-parameters for this trial, and the log file.
You can check orion status with the following commands:
(to be run from examples/slurm_orion)
export ORION_DB_ADDRESS='orion_db.pkl'
export ORION_DB_TYPE='pickleddb'
orion status
orion info --name my_exp
Documentation is built using sphinx. It will automatically document all functions based on docstrings.
To automatically generate docs for your project, navigate to the docs folder and build the documentation:
cd docs
make html
To view the docs locally, open docs/_build/html/index.html in your browser.
- TODO