-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Merge pull request #87 from mila-iqia/oct21_refactor
Oct21 refactor
- Loading branch information
Showing
224 changed files
with
14,295 additions
and
7,729 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -1,7 +1,10 @@ | ||
| .idea | ||
| .DS_Store | ||
| mlruns | ||
| analysis_results/ | ||
|
|
||
| mlip-3/ | ||
|
|
||
| examples/data/ | ||
| examples/*/output/ | ||
| examples/*/lightning_logs/ | ||
|
|
||
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1 @@ | ||
| 3.10 |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -1,184 +1,87 @@ | ||
| # Crystal Diffusion | ||
| # Diffusion for Multiscale Molecular Dynamics | ||
|
|
||
| Replace this line with a short description about your project! | ||
| This project implements diffusion-based generative models for periodic atomistic systems (i.e., crystals). | ||
| The aim of this project is to be able to train such a model and use it as part of an active learning | ||
| framework, where a Machine Learning Interatomic Potential (MLIP) is continually fine-tuned on labels obtained | ||
| from a costly oracle such as Density Functional Theory (DFT). The generative model is used to create | ||
| few-atom configurations that are computationally tractable for the costly oracle by inpainting | ||
| around problematic atomic configurations. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Instructions to setup the project | ||
| # Instructions to set up the project for development | ||
|
|
||
| ### Install the dependencies: | ||
| First, activate a virtual environment (recommended). | ||
| Install the package in `editable` mode so you can modify the source directly: | ||
| ## Creating a Virtual Environment | ||
| The project dependencies are stated in the `pyproject.toml` file. They must be installed in a virtual environment. | ||
|
|
||
| pip install -e . | ||
|
|
||
| To add new dependencies, simply add them to the setup.py. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Setup pre-commit hooks: | ||
| These hooks will: | ||
| * validate flake8 before any commit | ||
| * check that jupyter notebook outputs have been stripped | ||
|
|
||
| cd .git/hooks/ && ln -s ../../hooks/pre-commit . | ||
|
|
||
| Alternatively, to only lint files that have been staged in git, use | ||
| cd .git/hooks/ && ln -s ../../hooks/pre-commit_staged pre-commit | ||
|
|
||
| ### Setup Continuous Integration | ||
|
|
||
| Continuous integration will run the following: | ||
| - Unit tests under `tests`. | ||
| - End-to-end test under `exmaples/local`. | ||
| - `flake8` to check the code syntax. | ||
| - Checks on documentation presence and format (using `sphinx`). | ||
|
|
||
| We support the GitHub Actions for running CI. | ||
|
|
||
| Github actions are already configured in `.github/workflows/tests.yml`. | ||
| Github actions are already enabled by default when using Github, so, when | ||
| pushing to github, they will be executed automatically for pull requests to | ||
| `main` and to `develop`. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Running the code | ||
|
|
||
| ### Run the tests | ||
| Just run (from the root folder): | ||
|
|
||
| pytest | ||
|
|
||
| ### Run the code/examples. | ||
| Note that the code should already compile at this point. | ||
|
|
||
| Running examples can be found under the `examples` folder. | ||
|
|
||
| In particular, you will find examples for: | ||
| * local machine (e.g., your laptop). | ||
| * a slurm cluster. | ||
|
|
||
| For both these cases, there is the possibility to run with or without Orion. | ||
| (Orion is a hyper-parameter search tool - see https://github.com/Epistimio/orion - | ||
| that is already configured in this project) | ||
|
|
||
| #### Run locally | ||
|
|
||
| For example, to run on your local machine without Orion: | ||
|
|
||
| cd examples/local | ||
| sh run.sh | ||
| ### uv | ||
| The recommended way of creating a virtual environment is to use the tool [`uv`](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/). | ||
| Once `uv` is installed locally, the virtual environment can be created with the command | ||
|
|
||
| uv sync | ||
|
|
||
| This will run a simple MLP on a simple toy task: sum 5 float numbers. | ||
| You should see an almost perfect loss of 0 after a few epochs. | ||
| which will install the exact environment described in file `uv.lock`. The environment can then be activated with | ||
| the command | ||
|
|
||
| Note you have a new `output` folder which contains models and a summary of results: | ||
| * best_model: the best model checkpoint during training | ||
| * last_model: the last model checkpoint during training | ||
| * lightning_logs: contains the tensorboard logs. | ||
| source .venv/bin/activate | ||
|
|
||
| To view tensorboard logs, simply run: | ||
| ### pip | ||
|
|
||
| tensorboard --logdir output | ||
| Alternatively, `pip` can be used to create the virtual environment. Assuming `python` and `pip` are already | ||
| available on the system, create a virtual env folder in the root directory with the command | ||
|
|
||
| #### Run on a remote cluster (with Slurm) | ||
| python -m venv ./.venv/ | ||
|
|
||
| First, bring you project on the cluster (assuming you didn't create your | ||
| project directly there). To do so, simply login on the cluster and git | ||
| clone your project: | ||
| The environment must then be activated with the command | ||
|
|
||
| git clone [email protected]:${GITHUB_USERNAME}/${PROJECT_NAME}.git | ||
| source .venv/bin/activate | ||
|
|
||
| Then activate your virtual env, and install the dependencies: | ||
| and the environment should be created in `editable` mode so that the source code can be modified directly, | ||
|
|
||
| cd crystal_diffusion | ||
| pip install -e . | ||
|
|
||
| To run with Slurm, just: | ||
| ### Testing the Installation | ||
| The test suite should be executed to make sure that the environment is properly installed. After activating the | ||
| environment, the tests can be executed with the command | ||
|
|
||
| cd examples/slurm | ||
| sh run.sh | ||
| pytest [--quick] | ||
|
|
||
| Check the log to see that you got an almost perfect loss (i.e., 0). | ||
| the argument `--quick` is optional; a few tests are a bit slow and will be skipped if this flag is present. | ||
|
|
||
| #### Measure GPU time (and others) on the Mila cluster | ||
|
|
||
| You can track down the GPU time (and other resources) of your jobs by | ||
| associating a tag to the job (when using `sbatch`). | ||
| To associate a tag to a job, replace `my_tag` with a proper tag, | ||
| and uncomment the line (i.e., remove one #) from the line: | ||
| ## Setting up the Development Tools | ||
| Various automated tools are used in order to maintain a high quality code base. These must be set up | ||
| to start developing. We use | ||
|
|
||
| ##SBATCH --wckey=my_tag | ||
| * [flake8](https://flake8.pycqa.org/en/latest/) to insure the coding style is enforced. | ||
| * [isort](https://pycqa.github.io/isort/) to insure that the imports are properly ordered. | ||
| * [black](https://pypi.org/project/black/) to format the code. | ||
|
|
||
| This line is inside the file `examples/slurm_mila/to_submit.sh`. | ||
| ### Setup pre-commit hooks | ||
| The folder `./hooks/` contain "pre-commit" scripts that automate various checks at every git commit. | ||
| These hooks will | ||
| * validate flake8 before any commit; | ||
| * check that jupyter notebook outputs have been stripped. | ||
|
|
||
| To get a sumary for a particular tag, just run: | ||
| There are two pre-commit scripts, `pre-commit` and `pre-commit_staged`. Both scripts perform the same | ||
| checks; `pre-commit` is used within the continuous integration (CI), while `pre-commit_staged` only | ||
| validates files that are staged in git, making it more developer-friendly. | ||
|
|
||
| sacct --allusers --wckeys=my_tag --format=JobID,JobName,Start,Elapsed -X -P --delimiter=',' | ||
| To activate the pre-commit hook, | ||
|
|
||
| (again, remember to change `my_tag` into the real tag name) | ||
|
|
||
| #### GPU profiling on the Mila cluster | ||
|
|
||
| It can be useful to monitor and profile how you utilise your GPU (usage, memory, etc.). For the | ||
| time being, you can only monitor your profiling in real-time from the Mila cluster, i.e. while your | ||
| experiments are running. To monitor your GPU, you need to setup port-forwarding on the host your | ||
| experiments are running on. This can be done in the following way: | ||
|
|
||
| Once you have launched your job on the mila cluster, open the log for your current experiment: | ||
|
|
||
| `head logs/crystal_diffusion/__<your_slurm_job_id>.err` | ||
|
|
||
| You should see printed in the first few lines the hostname of your machine, e.g., | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| INFO:crystal_diffusion.utils.logging_utils:Experiment info: | ||
| hostname: leto35 | ||
| git code hash: a51bfc5447d188bd6d31fac3afbd5757650ef524 | ||
| data folder: ../data | ||
| data folder (abs): /network/tmp1/bronzimi/20191105_cookiecutter/crystal_diffusion/examples/data | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| In a separate shell on your local computer, run the following command: | ||
|
|
||
| `ssh -L 19999:<hostname>.server.mila.quebec:19999 <username>@login.server.mila.quebec -p 2222` | ||
|
|
||
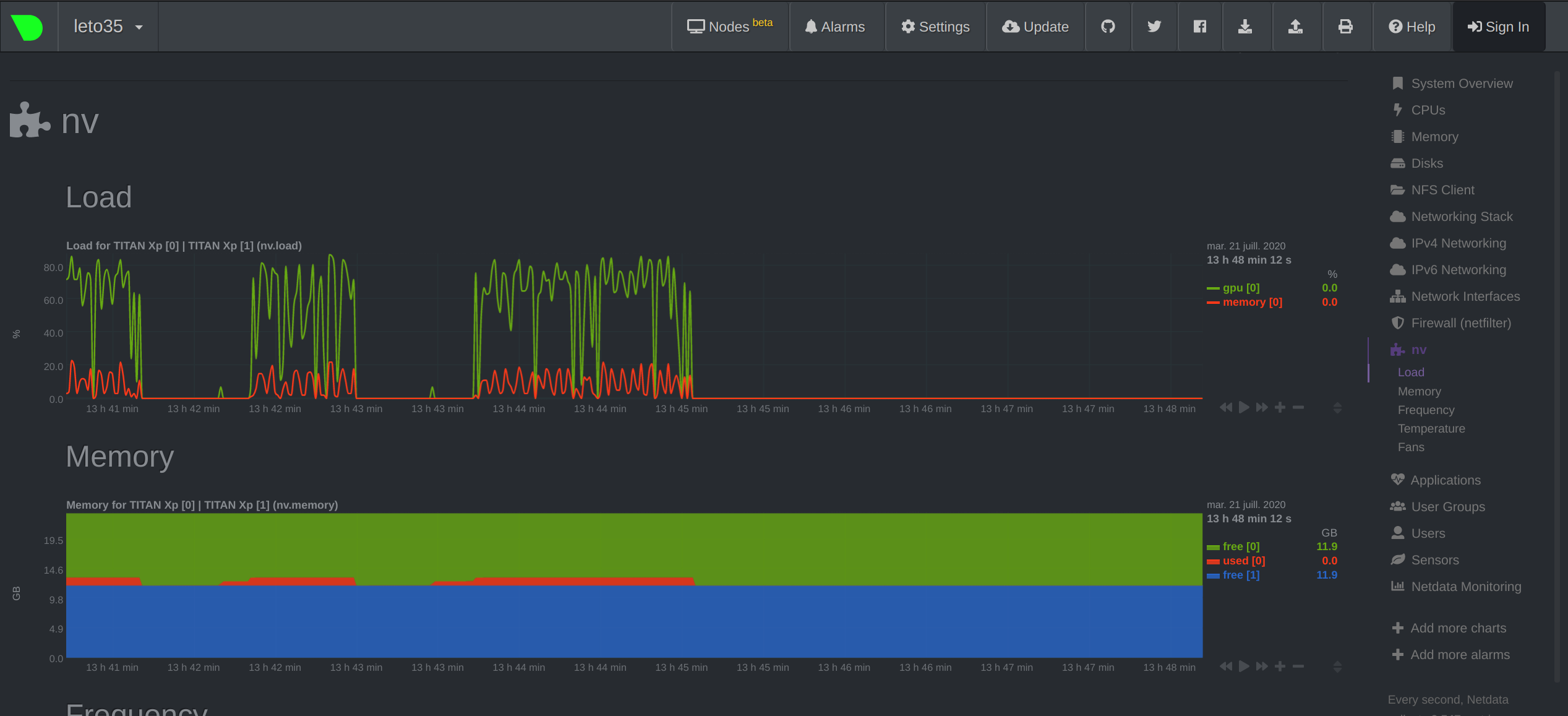
| where `<username>` is your user name on the Mila cluster and `<hostname>` is the name of the machine your job is currenty running on (`leto35` in our example). You can then navigate your local browser to `http://localhost:19999/` to view the ressources being used on the cluster and monitor your job. You should see something like this: | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
| {%- endif %} | ||
|
|
||
| #### Run with Orion on the Slurm cluster | ||
|
|
||
| This example will run orion for 2 trials (see the orion config file). | ||
| To do so, go into `examples/slurm_orion`. | ||
| Here you can find the orion config file (`orion_config.yaml`), as well as the config | ||
| file (`config.yaml`) for your project (that contains the hyper-parameters). | ||
|
|
||
| In general, you will want to run Orion in parallel over N slurm jobs. | ||
| To do so, simply run `sh run.sh` N times. | ||
|
|
||
| When Orion has completed the trials, you will find the orion db file. | ||
|
|
||
| You will also find the output of your experiments in `orion_working_dir`, which | ||
| will contain a folder for every trial. | ||
| Inside these folders, you can find the models (the best one and the last one), the config file with | ||
| the hyper-parameters for this trial, and the log file. | ||
|
|
||
| You can check orion status with the following commands: | ||
| (to be run from `examples/slurm_orion`) | ||
|
|
||
| export ORION_DB_ADDRESS='orion_db.pkl' | ||
| export ORION_DB_TYPE='pickleddb' | ||
| orion status | ||
| orion info --name my_exp | ||
|
|
||
| ### Building docs: | ||
| cd .git/hooks/ && ln -s ../../hooks/pre-commit . | ||
|
|
||
| Documentation is built using sphinx. It will automatically document all functions based on docstrings. | ||
| To automatically generate docs for your project, navigate to the `docs` folder and build the documentation: | ||
| Alternatively, to only lint files that have been staged in git, use | ||
|
|
||
| cd docs | ||
| make html | ||
| cd .git/hooks/ && ln -s ../../hooks/pre-commit_staged pre-commit | ||
|
|
||
| To view the docs locally, open `docs/_build/html/index.html` in your browser. | ||
| ### Setup Continuous Integration | ||
|
|
||
| GitHub Actions is used for running continuous integration (CI) checks. | ||
| The cI workflow is described in `.github/workflows/ci.yml`. | ||
|
|
||
| ## YOUR PROJECT README: | ||
| CI will run the following: | ||
| - check the code syntax with `flake8` | ||
| - execute the unit tests in `./tests/`. | ||
| - Checks on documentation presence and format (using `sphinx`). | ||
|
|
||
| * __TODO__ | ||
| Since the various tests are relatively costly, the CI actions will only be executed for | ||
| pull requests to the `main` branch. |
Oops, something went wrong.