This project brings an interface to use rematerialization in the TensorFlow XLA Compiler.
This patch adds rematerialization support to TensorFlow 2.0 XLA branch. To install it, execute the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow
git checkout 64c3d382cadf7bbe8e7e99884bede8284ff67f56
cd tensorflow
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/tensorflow-rematerialization
git apply -v tensorflow-rematerialization/remat.patch
After cloning TensorFlow and applying the remat patch, you can compile and install it by following the TensorFlow documentation: https://www.tensorflow.org/install/source
You can control the rematerialization in XLA by passing different flags to the environment variable XLA_FLAGS. The available flags are:
• --xla_use_hlo_rematerialization
○ This flag enables the rematerialization to pass after all optimizations and just before code emission. This flag is necessary for the use of any other of the following flags.
• --xla_rematerialization_mem_limit={NUMBER}
○ This flag sets the memory budget for your application.
The remat heuristic will try to fit the model in that amount of memory.
If the memory budget is larger than the model size no rematerialization is applied. The parameter {NUMBER} is in bytes.
• --xla_rematerialization_scheduler={SCHEDULER_NAME}
○ This flag allows us to choose which scheduler to use just before rematerialization. The scheduling can impact in the performance of the heuristics.
Four options are available:
(1) if no scheduler is set the default TF behavior is to apply the three next heuristics and select the best in terms of performance (not considering the remat here);
(2) "postorder";
(3) "DFS" and;
(4) "list".
• --xla_rematerialization_algorithm={HEURISTIC_NAME}
○ This flag sets which heuristics to use to rematerialize.
Four options are available:
(1) "standard" which uses the original implementation of the rematerialization that can be found inside the TF source tree;
(2) "compress" which tries to reorder dimensions of tensors in order to reduce their representation size (this is also an implementation that is inside TF, but it is not a rematerialization);
(3) "standardcompress" which applies both the standard remat and the compress technique; and, finally, (4) "path", our approach to remat which recursively tries to rematerialize paths and then derematerialize articulation operations while still in the memory budget.
• --xla_rematerialization_small_node_limit={NUMBER}
○ This flag sets the minimum size that an HLO node has to be considered for rematerialization. The expect {NUMBER} is in MiB and 0 disables this feature. Having a limit of 1 MiB showed to increase significantly the performance of both standard and path heuristics.
• --xla_rematerialization_disable_cuda
○ This flag disables part of the CUDA fusions in the HLO graph making it easier to apply rematerialization as fewer side effect nodes will exist.
• --xla_rematerialization_dump_dot
○ Dumps a dot graph of the HLO before and after the rematerialization.
• --xla_rematerialization_dump_memlog
○ Dumps a log of the memory use and remat decisions information for each HLO instruction.
Note: TF_XLA_FLAGS="--tf_xla_auto_jit=2" needs to be set to activate XLA compiler.
Example:
TF_XLA_FLAGS="--tf_xla_auto_jit=2" XLA_FLAGS="--xla_dump_to=dump --xla_dump_hlo_as_text --xla_use_hlo_rematerialization --xla_rematerialization_mem_limit=1073741824 --xla_rematerialization_algorithm=path --xla_rematerialization_small_node_limit=1" python resnet_cifar_main.py
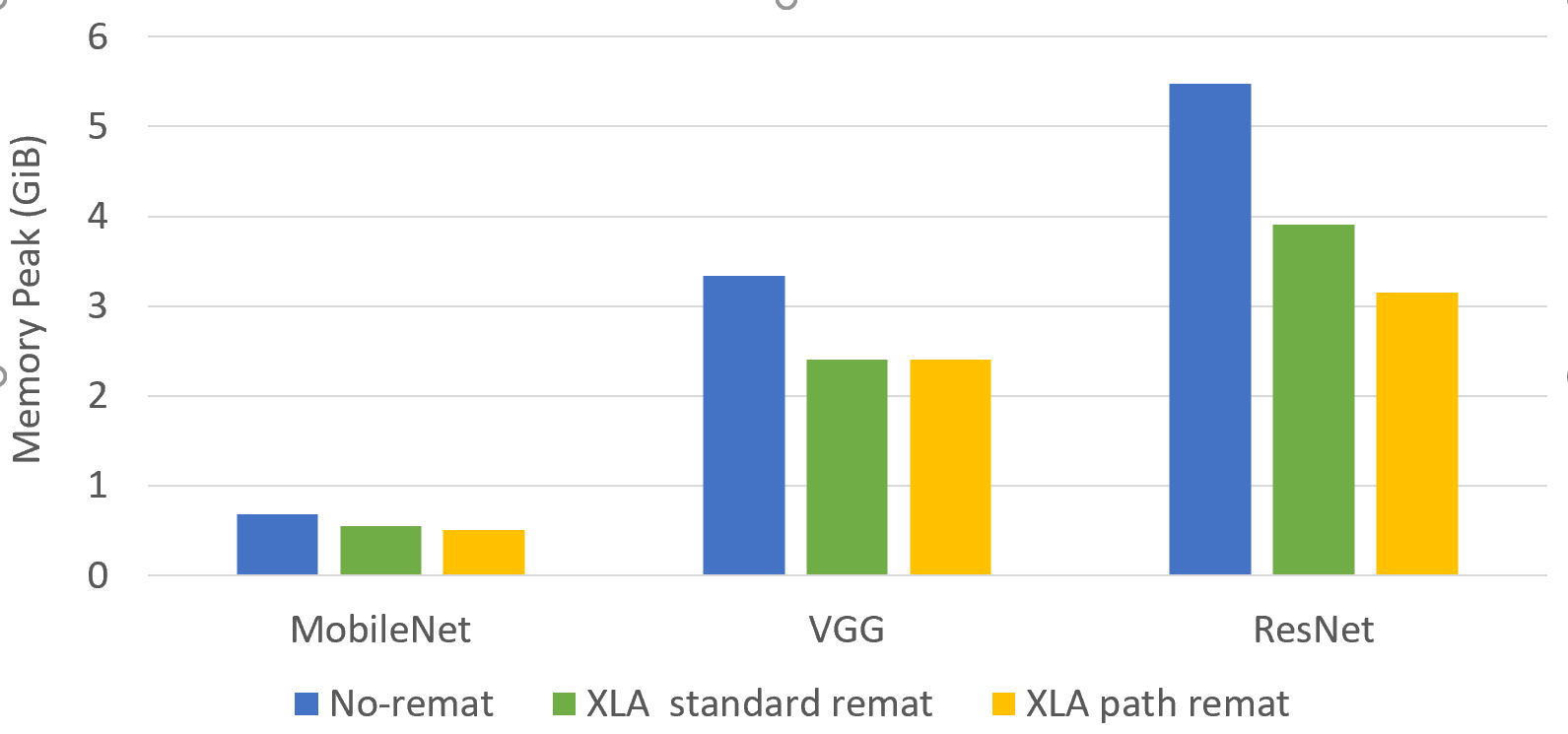
Using rematerialization in TensorFlow XLA can help reduce the amount of memory necessary to run a model making it fit in your accelerator.
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact [email protected] with any additional questions or comments.