You are given an array nums that consists of positive integers.
The GCD of a sequence of numbers is defined as the greatest integer that divides all the numbers in the sequence evenly.
- For example, the GCD of the sequence
[4,6,16]is2.
A subsequence of an array is a sequence that can be formed by removing some elements (possibly none) of the array.
- For example,
[2,5,10]is a subsequence of[1,2,1,2,4,1,5,10].
Return the number of different GCDs among all non-empty subsequences of nums.
Example 1:
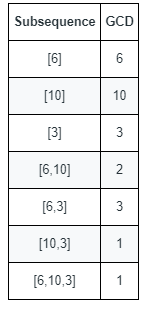
Input: nums = [6,10,3] Output: 5 Explanation: The figure shows all the non-empty subsequences and their GCDs. The different GCDs are 6, 10, 3, 2, and 1.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,15,40,5,6] Output: 7
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 2 * 105
class Solution:
def countDifferentSubsequenceGCDs(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
mx = max(nums)
vis = set(nums)
ans = 0
for x in range(1, mx + 1):
g = 0
for y in range(x, mx + 1, x):
if y in vis:
g = gcd(g, y)
if g == x:
ans += 1
break
return ansclass Solution {
public int countDifferentSubsequenceGCDs(int[] nums) {
int mx = Arrays.stream(nums).max().getAsInt();
boolean[] vis = new boolean[mx + 1];
for (int x : nums) {
vis[x] = true;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int x = 1; x <= mx; ++x) {
int g = 0;
for (int y = x; y <= mx; y += x) {
if (vis[y]) {
g = gcd(g, y);
if (x == g) {
++ans;
break;
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private int gcd(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
}class Solution {
public:
int countDifferentSubsequenceGCDs(vector<int>& nums) {
int mx = *max_element(nums.begin(), nums.end());
vector<bool> vis(mx + 1);
for (int& x : nums) {
vis[x] = true;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int x = 1; x <= mx; ++x) {
int g = 0;
for (int y = x; y <= mx; y += x) {
if (vis[y]) {
g = gcd(g, y);
if (g == x) {
++ans;
break;
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func countDifferentSubsequenceGCDs(nums []int) (ans int) {
mx := 0
for _, x := range nums {
mx = max(mx, x)
}
vis := make([]bool, mx+1)
for _, x := range nums {
vis[x] = true
}
for x := 1; x <= mx; x++ {
g := 0
for y := x; y <= mx; y += x {
if vis[y] {
g = gcd(g, y)
if g == x {
ans++
break
}
}
}
}
return
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
func gcd(a, b int) int {
if b == 0 {
return a
}
return gcd(b, a%b)
}