Website • Docs • Blog • Twitter • Chat (Community & Support) • Tutorial • Mailing List
This version of DVC is patched by lacmus foundation. The patch fixes the following issue.
Data Version Control or DVC is an open-source tool for data science and machine learning projects. Key features:
- Simple command line Git-like experience. Does not require installing and maintaining any databases. Does not depend on any proprietary online services.
- Management and versioning of datasets and machine learning models. Data can be saved in S3, Google cloud, Azure, Alibaba cloud, SSH server, HDFS, or even local HDD RAID.
- Makes projects reproducible and shareable; helping to answer questions about how a model was built.
- Helps manage experiments with Git tags/branches and metrics tracking.
DVC aims to replace spreadsheet and document sharing tools (such as Excel or Google Docs) frequently used as both knowledge repositories and team ledgers. DVC also replaces both ad-hoc scripts to track, move, and deploy different model versions and ad-hoc data file suffixes and prefixes.
Contents
We encourage you to read our Get Started guide to better understand what DVC is and how it can fit your scenarios.
The easiest (but not perfect!) analogy to describe it: DVC is Git (or Git-LFS to be precise) & Makefiles made right and tailored specifically for ML and Data Science scenarios.
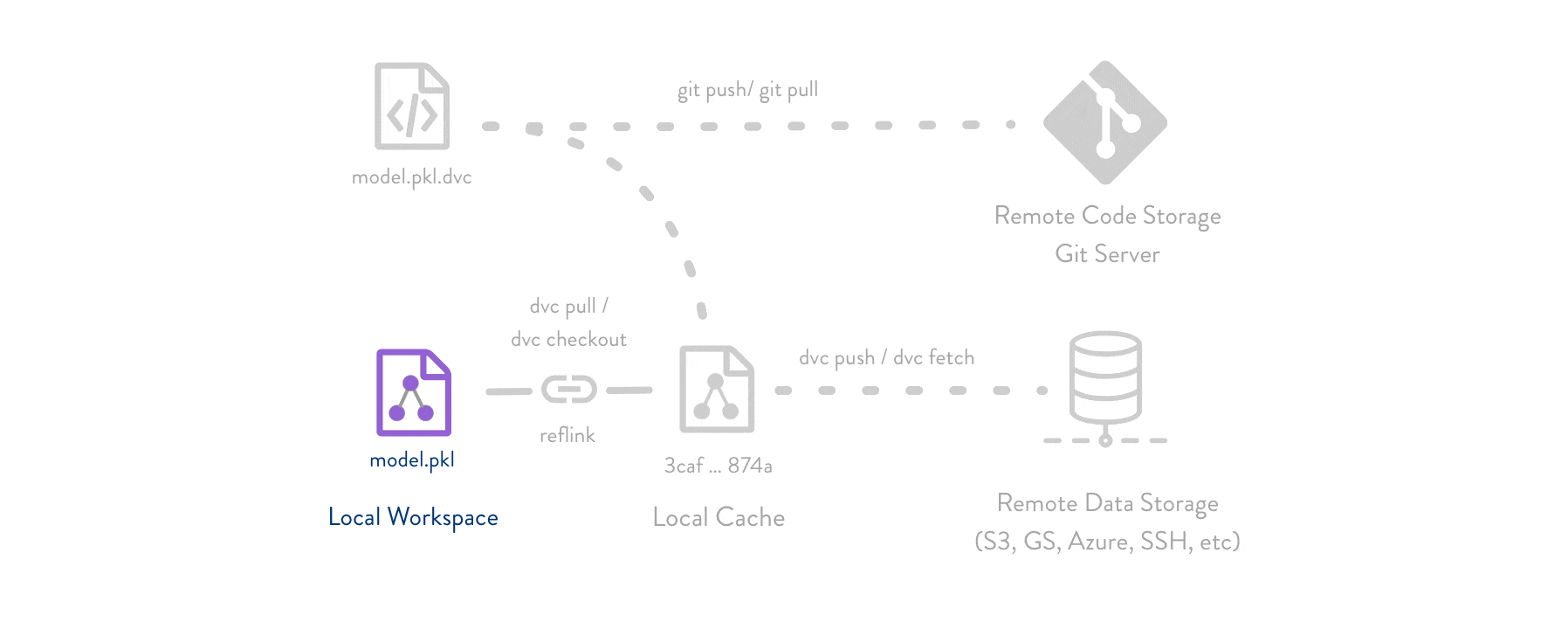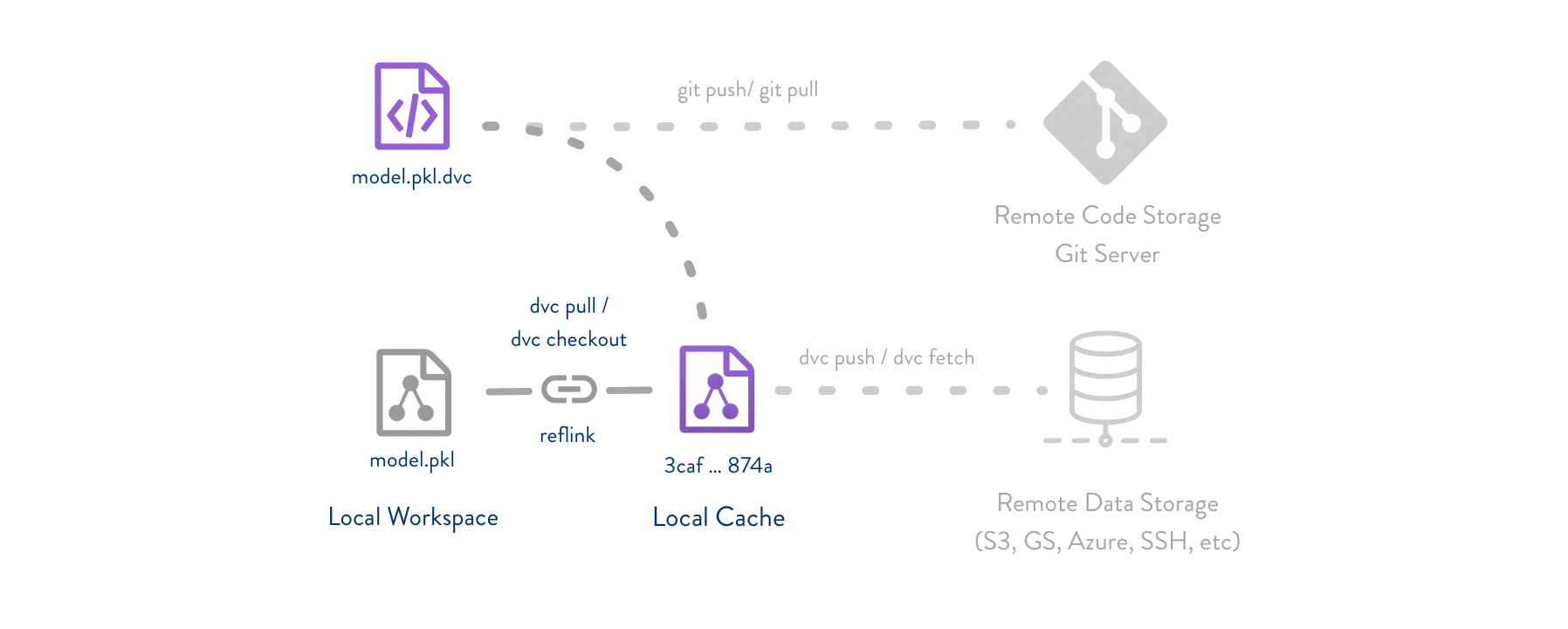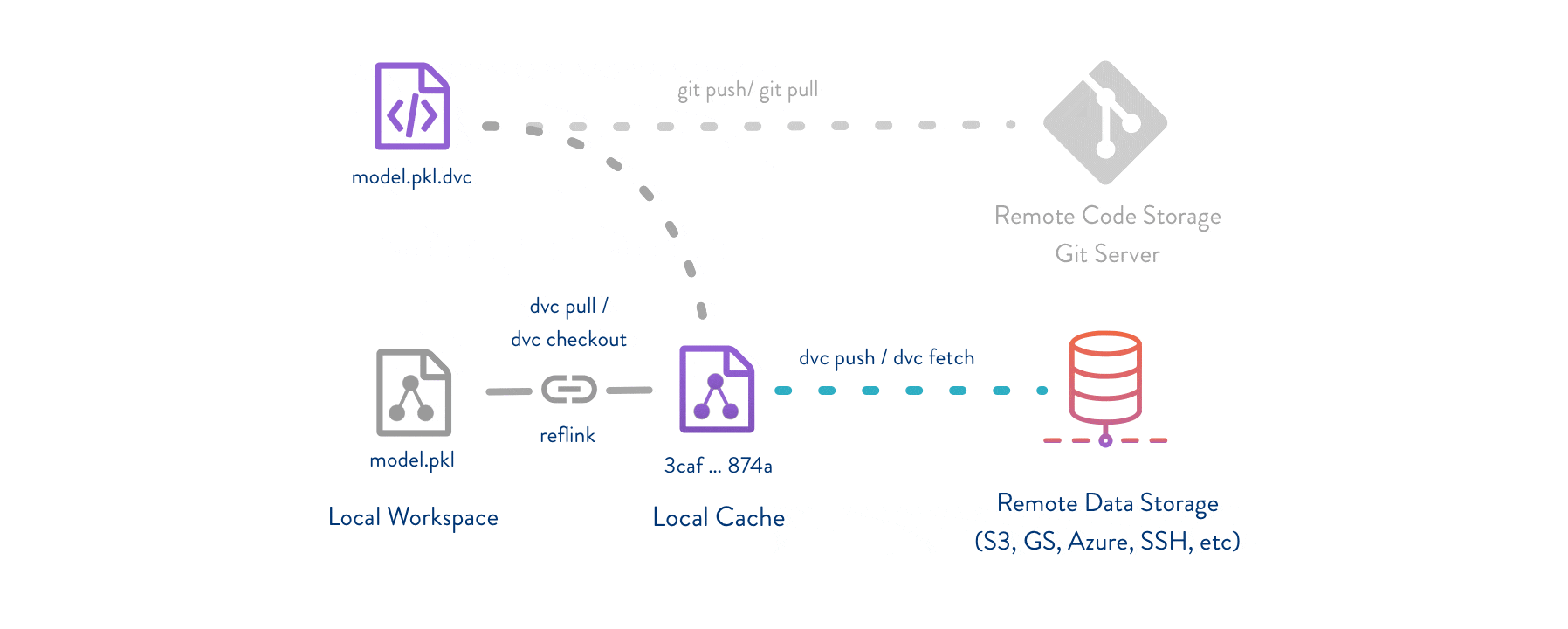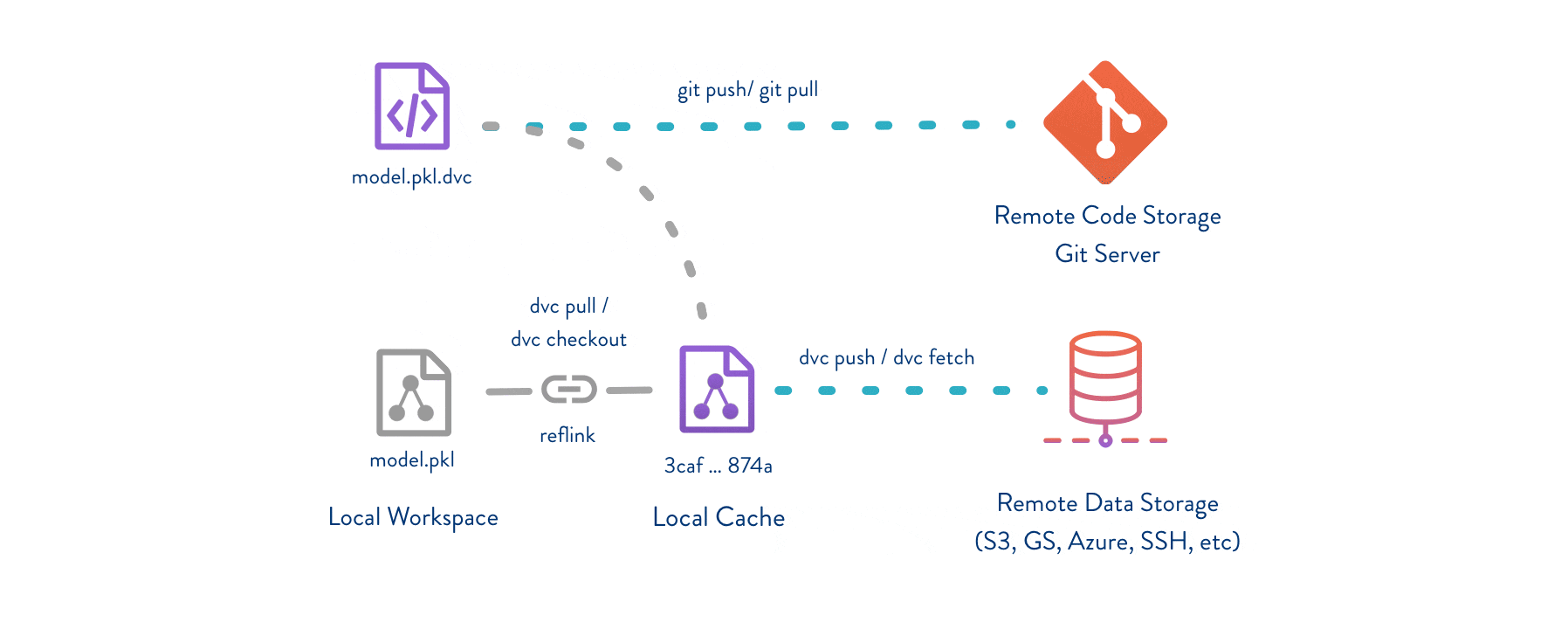
Git/Git-LFSpart - DVC helps store and share data artifacts and models, connecting them with a Git repository.Makefiles part - DVC describes how one data or model artifact was built from other data and code.
DVC usually runs along with Git. Git is used as usual to store and version code (including DVC meta-files). DVC helps to store data and model files seamlessly out of Git, while preserving almost the same user experience as if they were stored in Git itself. To store and share the data cache, DVC supports multiple remotes - any cloud (S3, Azure, Google Cloud, etc) or any on-premise network storage (via SSH, for example).
The DVC pipelines (computational graph) feature connects code and data together. It is possible to explicitly specify all steps required to produce a model: input dependencies including data, commands to run, and output information to be saved. See the quick start section below or the Get Started tutorial to learn more.
Please read Get Started guide for a full version. Common workflow commands include:
| Step | Command |
|---|---|
| Track data | $ git add train.py$ dvc add images.zip |
| Connect code and data by commands | $ dvc run -n prepare -d images.zip -o images/ unzip -q images.zip$ dvc run -n train -d images/ -d train.py -o model.p python train.py |
| Make changes and reproduce | $ vi train.py$ dvc repro model.p.dvc |
| Share code | $ git add .$ git commit -m 'The baseline model'$ git push |
| Share data and ML models | $ dvc remote add myremote -d s3://mybucket/image_cnn$ dvc push |
To install version patched by lacmus, run:
pip install git+https://github.com/lacmus-foundation/dvc.git- Data Engineering tools such as AirFlow <https://airflow.apache.org/>, Luigi <https://github.com/spotify/luigi>, and others - in DVC data, model and ML pipelines represent a single ML project focused on data scientists' experience. Data engineering tools orchestrate multiple data projects and focus on efficient execution. A DVC project can be used from existing data pipelines as a single execution step.
- Git-annex - DVC uses the idea of storing the content of large files (which should not be in a Git repository) in a local key-value store, and uses file hardlinks/symlinks instead of copying/duplicating files.
- Git-LFS - DVC is compatible with many remote storage services (S3, Google Cloud, Azure, SSH, etc). DVC also uses reflinks or hardlinks to avoid copy operations on checkouts; thus handling large data files much more efficiently.
- Makefile (and analogues including ad-hoc scripts) - DVC tracks dependencies (in a directed acyclic graph).
- Workflow Management Systems - DVC is a workflow management system designed specifically to manage machine learning experiments. DVC is built on top of Git.
- DAGsHub - online service to host DVC projects. It provides a useful UI around DVC repositories and integrates other tools.
- DVC Studio - official online platform for DVC projects. It can be used to manage data and models, run and track experiments, and visualize and share results. Also, it integrates with CML (CI/CD for ML) <https://cml.dev/> for training models in the cloud or Kubernetes.
Contributions are welcome! Please see our Contributing Guide for more details. Thanks to all our contributors!
Want to stay up to date? Want to help improve DVC by participating in our occasional polls? Subscribe to our mailing list. No spam, really low traffic.
This project is distributed under the Apache license version 2.0 (see the LICENSE file in the project root).
By submitting a pull request to this project, you agree to license your contribution under the Apache license version 2.0 to this project.
Iterative, DVC: Data Version Control - Git for Data & Models (2020) DOI:10.5281/zenodo.012345.
Barrak, A., Eghan, E.E. and Adams, B. On the Co-evolution of ML Pipelines and Source Code - Empirical Study of DVC Projects , in Proceedings of the 28th IEEE International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution, and Reengineering, SANER 2021. Hawaii, USA.