-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
Zynq Support
Shuta Kimura edited this page Aug 24, 2019
·
1 revision
TinyThreads (since v1.5) supports ARM Cortex-A9 on Xilinx Zynq-7000 series. TinyThreads can be integrated with Xilinx SDK.
- Tested on Xilinx Vivado 2018.3
- Confirm location of your Xilinx SDK. For example,
C:\Xilinx\SDK\2018.3on Windows. - Download zip or tarball from Release page and unpack on
<SDK_location>/data/embeddedsw/ThirdParty/bsp/ - If your Xilinx SDK already running, please quit and relaunch.
- When you creates a new Application Project or Board Support Package Project, choose tinythreads from OS platform list.
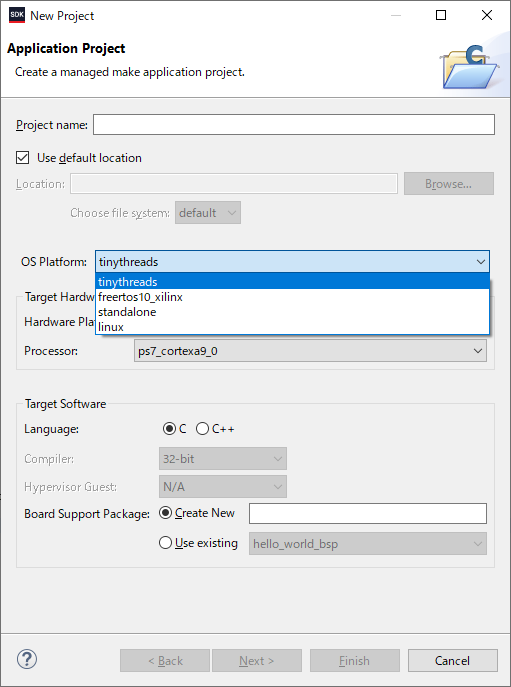

- Then, you can customize settings in tinythreads group in BSP Settings window.

| Group | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| features | enable_cond | Enable condition variable APIs (pthread_cond_*) |
| features | enable_mutex | Enable mutex APIs (pthread_mutex_*) |
| features | enable_sem | Enable semaphore APIs (sem_*) |
| features | enable_once | Enable once control APIs (pthread_once_*) |
| features | enable_rwlock | Ignored. Currently reader-writer lock is not supported. |
| features | enable_spin | Ignored. Currently spinlock is not supported. |
| features | enable_sleep | Enable sleep APIs (sleep, usleep) |
| features | enable_profile | Enable task-switch counting (for debugging) |
| features | enable_name | Enable thread name APIs (pthread_{get,set}name_np) (for debugging) |
| others | min_stack_size | Specify default size of stacks in bytes. |
| others | strict_check | Enable more assertions to detect invalid state |
| others | thread_safe_newlib | Enable thread-safe newlib. If disabled, RAM usage will be reduced but some newlib APIs are unsafe in multi-threaded environment. |
| others | enable_vfp_switch | Enable VFP context switching |
| scheduling | preemption_enabled | Enable preemption |
| scheduling | preemption_interval | Specify interval of preemption in milliseconds |
| scheduling | priority_max | Specify maximum value of priority (means lowest priority). Valid range is 1 to 255. |
| scheduling | priority_min | Specify minimum value of priority (means highest priority). Valid range is 1 to 255. |
| scheduling | priority_default | Specify default priority. Valid range is priority_min to priority_max. |
| scheduling | policy_default_fifo | If enabled, FIFO will be used as the default scheduling policy. If disabled, Round-robin will be used. |
- Instruction mode
- Only ARM mode supported. Thumb mode is not supported.
- API usage in ISR (interrupt handlers)
- Only
sem_post()can be used in ISR. - If other APIs are used in ISR, behavior is unpredictable.
- Only
- Interrupt usage in your application
- TinyThreads has an instance of XScuGic internally to use tick interrupts.
- If you want to access XScuGic, you can get a pointer to XScuGic by
tth_get_xcsugic_instance()function.// Example #include "bspconfig.h" /* For tth_get_xscugic_instance */ #include "xscugic.h" /* For XScuGic_xxx APIs */ void setup_interrupts() { XScuGic *InstancePtr = (XScuGic *)tth_get_xscugic_instance(); XScuGic_Connect(InstancePtr, ...); }
- Newlib thread safety
- If you disabled
thread_safe_newlib,_impure_ptrin newlib will not be managed by TinyThreads. In this case, newlib functions may be unsafe when they are called from multiple threads.
- If you disabled
- VFP usage in ISR
- You cannot use VFP (Floating point and Advanced SIMD) in ISR. If they are used, undefined exception occurs.
- VFP usage in threads
- If
enable_vfp_switchis enabled, each thread has own VFP registers. (TinyThreads manages VFP context on demand)- VFP context switch needs a lot of memory copy and time, so it will be delayed until each thread accesses VFP registers.
- If
enable_vfp_switchis disabled, all threads shares VFP registers.
- If