- Kubernetes (For this example we are using Kind)
- Kustomize
- Docker
- ArgoCD
- Go
Greetings and welcome to our GitOps Proof of Concept documentation. This proof of concept aims to showcase the potential of GitOps in automating CI/CD process and deploying a Go application to a Kubernetes cluster.
We have implemented a continuous delivery pipeline that uses GitOps as the deployment methodology. Kustomize and ArgoCD are utilized to customize our Kubernetes manifest files based on our environment and automatically deploy our applications when changes are made in the repository.
The Go application we will be using in this proof of concept is a simple web server that displays a message on the screen. However, the primary objective of this project is to demonstrate how GitOps can be utilized to automate the deployment process and ensure that our application is always up-to-date and available in our Kubernetes cluster.
To build our Docker image, we use a GitHub action that is triggered when a push is made to the repository. This action builds the Docker image and updates the SHA tag in our Kustomize file. Argo CD then deploys our updated image automatically to our Kubernetes cluster.
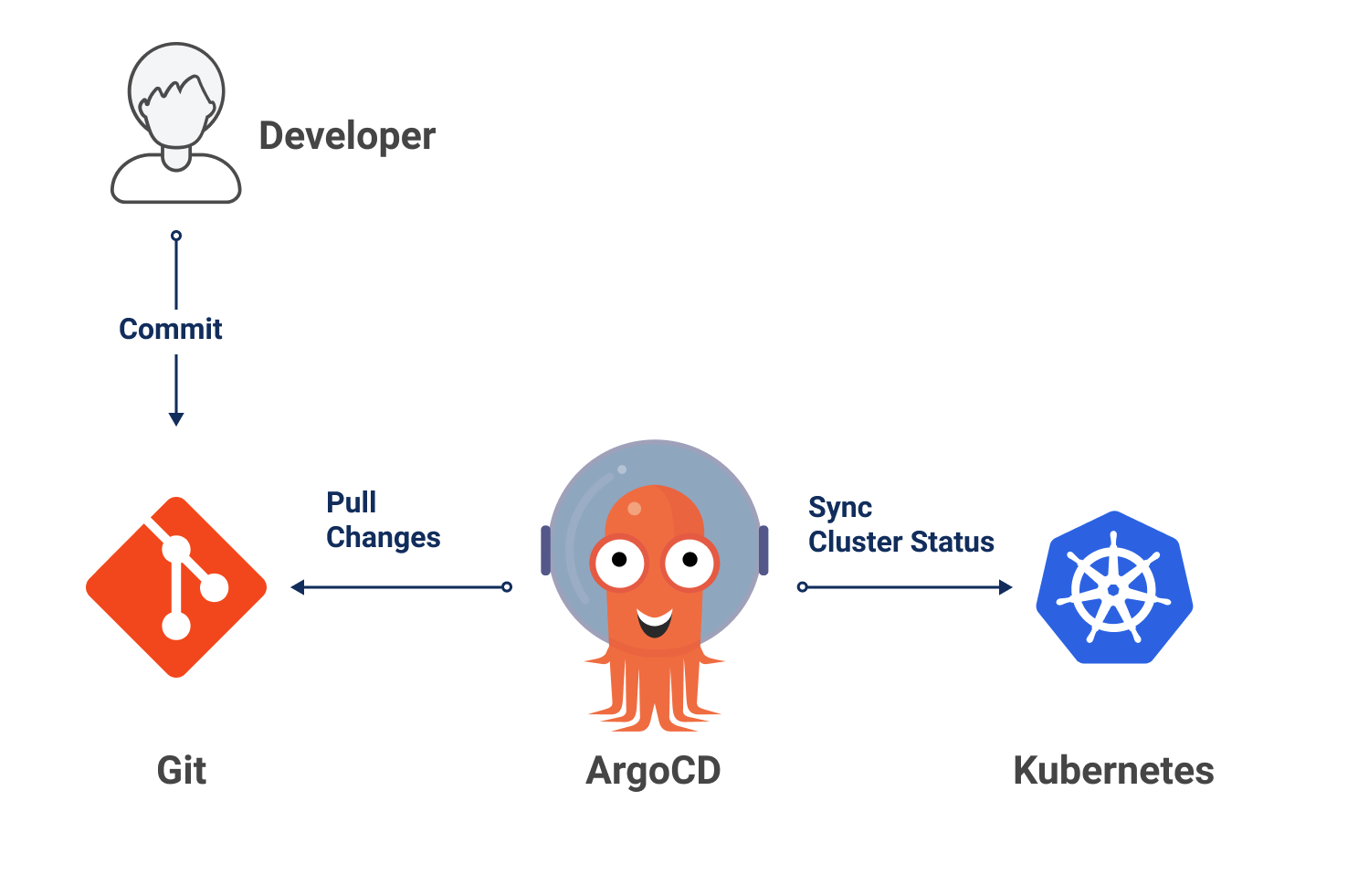
ArgoCD is a GitOps tool that monitors a Git repository for changes to a specific Kubernetes configuration and automatically deploys those changes to the cluster.
In the context of a Go application that uses Kustomize to manage Kubernetes resources and DockerHub to host the Docker image of the application, the update flow of ArgoCD is as follows:
- A code change is made in the Go application.
- The developer pushes the code to the Git repository.
- A CI/CD action is triggered to build the Docker image of the application and send it to DockerHub.
- Kustomize is configured to use the SHA of the Docker image in DockerHub as the image tag in the Kubernetes configuration.
- The Bot (via GithubActions) pushes the Kustomize changes to the Git repository.
- ArgoCD monitors the Git repository to identify changes in the Kubernetes configuration.
- When a change is identified, ArgoCD downloads the new configurations, compares them with the current state of the Kubernetes cluster, and applies the necessary changes.
Therefore, ArgoCD periodically searches for changes in the SHA of the Docker image in DockerHub and updates it in the Kustomize file to ensure that the Kubernetes configuration is always updated with the latest image.
Install a tool for managing a local Kubernetes cluster, such as Minikube or Kind. Use the tool to create a new Kubernetes cluster on your local machine.
1 - Create a new namespace in your Kubernetes cluster for ArgoCD:
kubectl create namespace argocd
2 - Apply the latest ArgoCD manifests from the official ArgoCD site.
In conclusion, this documentation provided a overview of how GitOps can be utilized to automate the CI/CD process and deploy a Go application to a Kubernetes cluster. By using Kustomize and ArgoCD, the Kubernetes manifest files can be customized based on the environment, and changes in the repository can automatically deploy the application. The documentation also explained the GitOps and ArgoCD flow and how it ensures that the application is always up-to-date and available in the Kubernetes cluster. Lastly, the documentation provided information on how to set up a local Kubernetes cluster, install ArgoCD in the cluster, and deploy the Go application. With the help of this documentation, users can easily deploy their applications to Kubernetes clusters using GitOps and ArgoCD.