QCA is an abstract quantum computational nanotechnology based on field-coupled arrays of finite-state automata. Each QCA device “cell” consists of a bi-stable or tri-stable semiconductor (molecular) structure of quantum dots. The computational basis is defined as two fully polarized configurations of the cell.
This project focuses on solving the general Hamiltonian of two kinds of QCA circuits. The general hamiltonian takes into account the interactions between the all the cells with the driver(s), all the cells with each other, and all the cells with the environment.
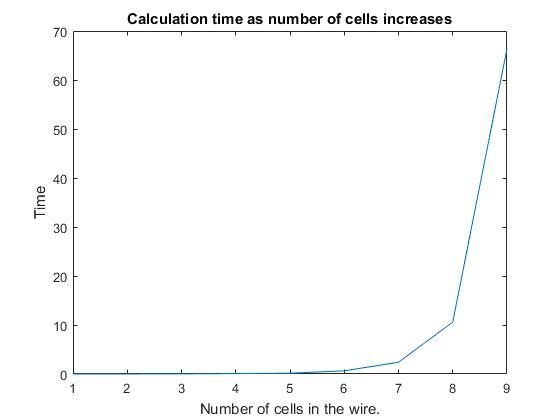
The first kind of circuit that we look at is a modular sized wire. The modularWire.m file creates and solves the general hamiltonian of a wire containing n cells. The timer_for_wire.m uses the modularWire.m file to measure how long in seconds it takes to process different lengths of wire. An example of findings is below:
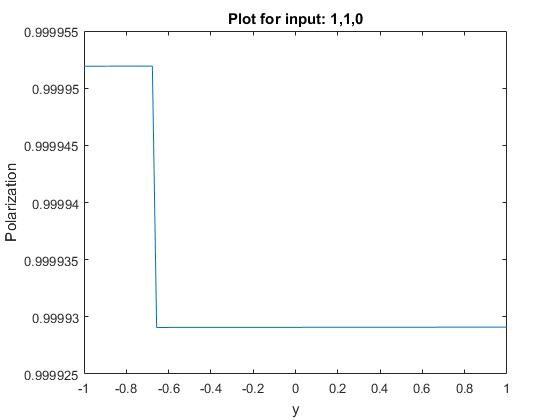
The second kind of circuit is a majority gate. The output (steady state) depends on the whether the three inputs have a majority of 1 or -1. The generalHamiltonian.m file creates and solves the general hamiltonian for this circuit shape. The checking_outputs.m plots the polarization of the majority gate output as the potential of the circuit moves the system to steady state.