This library implements a heuristic-based approach to normalize paths encoded with the Google Polyline Format.
The goal of this project is to "clean up" existing polyline data to match real-world roadway segments.
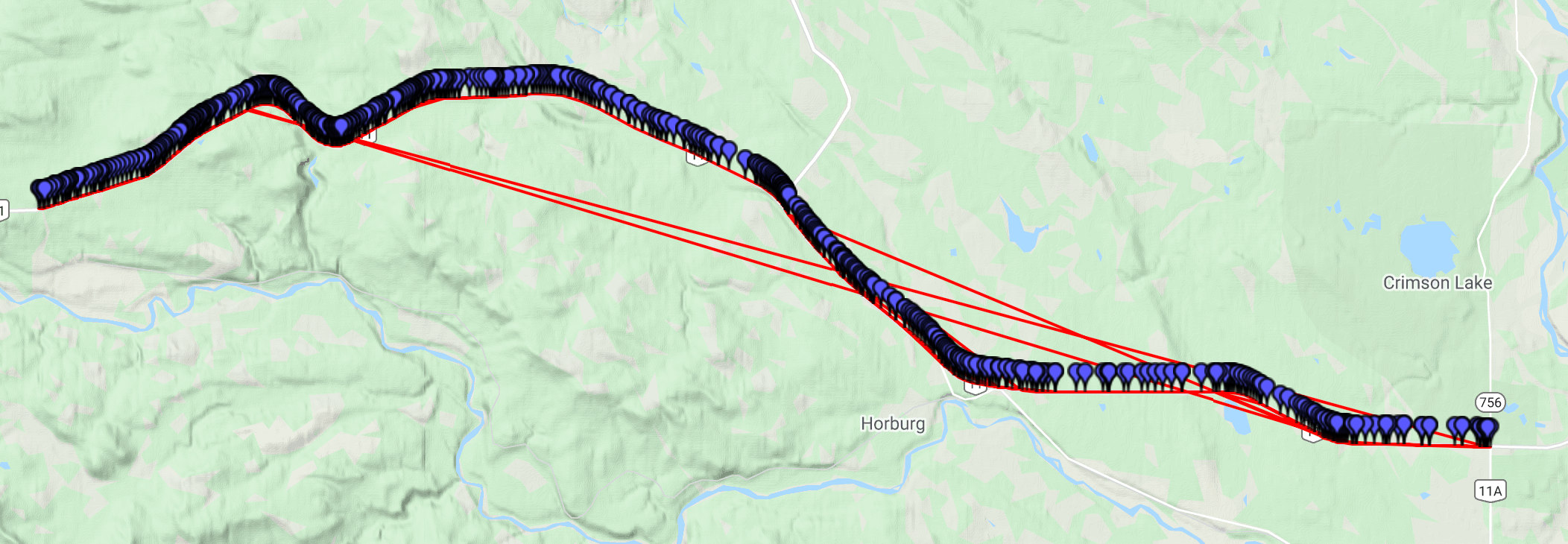
For example, we want to take a polyline that looks something like:
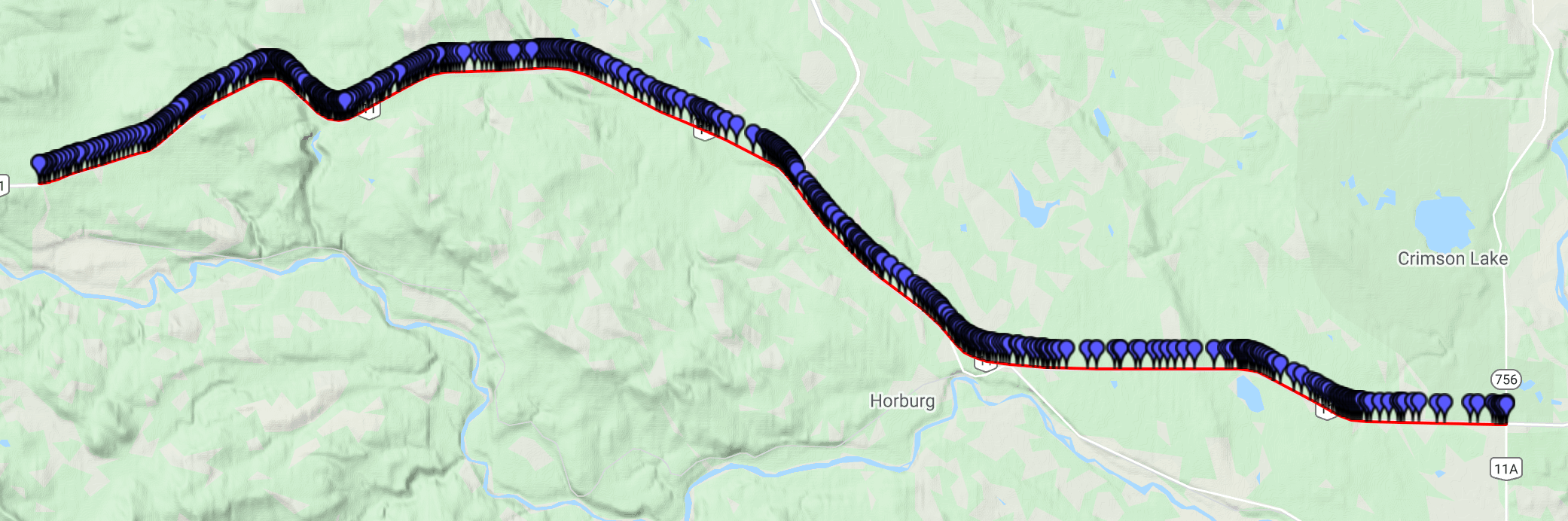
and produce an output line that looks like this:
The algorithm attempts to order the points encoded in the polyline by closest geodesic distance to one another. This approach may produce sub-optimal output if a polyline contains points that vary greatly in direction, yet are close to one another.
Add this line to your application's Gemfile:
gem 'polyline-normalizer'And then execute:
$ bundle install
Or install it yourself as:
$ gem install polyline-normalizer
To normalize an encoded polyline, simply do the following:
require 'polyline-normalizer'
encoded_polyline = 'kjrlHlbjvTa`@A...'
Polyline::Normalizer::RoadSegment.new(encoded_polyline).normalize # => returns a string representing the normalized encoded polylineAfter checking out the repo, run bin/setup to install dependencies. Then, run rake spec to run the tests. You can also run bin/console for an interactive prompt that will allow you to experiment.
To install this gem onto your local machine, run bundle exec rake install. To release a new version, update the version number in version.rb, and then run bundle exec rake release, which will create a git tag for the version, push git commits and the created tag, and push the .gem file to rubygems.org.
Bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub at https://github.com/amaabca/polyline-normalizer. This project is intended to be a safe, welcoming space for collaboration, and contributors are expected to adhere to the code of conduct.
The gem is available as open source under the terms of the MIT License.
Everyone interacting in the Polyline::Normalizer project's codebases, issue trackers, chat rooms and mailing lists is expected to follow the code of conduct.