BFS, DFS(Recursive & Iterative), Dijkstra, Greedy, & A* Algorithms. These algorithms are used to search the tree and find the shortest path from starting node to goal node in the tree.
Blind search algorithms such as breadth-first and depth-first exhaust all possibilities; starting from the given node, they iterate over all possible paths until they reach the goal node. These algorithms run in O(V+E), or linear time, where V is the number of vertices, and E is the number of edges between vertices.
However, it is not necessary to examine all possible paths. Algorithms such as Greedy, Dijkstra’s algorithm, and A* eliminate paths either using educated guesses(heuristics) or distance from source to node V to find the optimal path. By eliminating impossible paths, these algorithms can achieve time complexities as low as O(E log(V)).
The Breadth First Search (BFS) traversal is an algorithm, which is used to visit all of the nodes of a given graph. In this traversal algorithm one node is selected and then all of the adjacent nodes are visited one by one. After completing all of the adjacent vertices, it moves further to check another vertices and checks its adjacent vertices again.
To implement this algorithm, we need to use the Queue data structure. All the adjacent vertices are added into the queue, when all adjacent vertices are completed, one item is removed from the queue and start traversing through that vertex again.
In Graph sometimes, we may get some cycles, so we will use an array to mark when a node is visited already or not.
It starts at the root and explores all of it’s children in the next level(neighbors) before moving to each of the root children, and then, it explores the children of the root children, and so on. The algorithm uses a queue to perform the BFS.
- Add root node to the queue, and mark it as visited(already explored).
- Loop on the queue as long as it's not empty.
- Get and remove the node at the top of the queue(current).
- For every non-visited child of the current node, do the following:
- Mark it as visited.
- Check if it's the goal node, If so, then return it.
- Otherwise, push it to the queue.
- If queue is empty, then goal node was not found!
It starts at the root and explores one of it’s children’s sub tree, and then move to the next child’s sub tree, and so on. It uses stack, or recursion to perform the DFS.
- Mark the current node as visited(initially current node is the root node)
- Check if current node is the goal, If so, then return it.
- Iterate over children nodes of current node, and do the following:
- Check if a child node is not visited.
- If so, then, mark it as visited.
- Go to it's sub tree recursively until you find the goal node(In other words, do the same steps here passing the child node as the current node in the next recursive call).
- If the child node has the goal node in this sub tree, then, return it.
- If goal node is not found, then goal node is not in the tree!
- Add root node to the stack.
- Loop on the stack as long as it's not empty.
- Get the node at the top of the stack(current), mark it as visited, and remove it.
- For every non-visited child of the current node, do the following:
- Check if it's the goal node, If so, then return this child node.
- Otherwise, push it to the stack.
- If stack is empty, then goal node was not found!
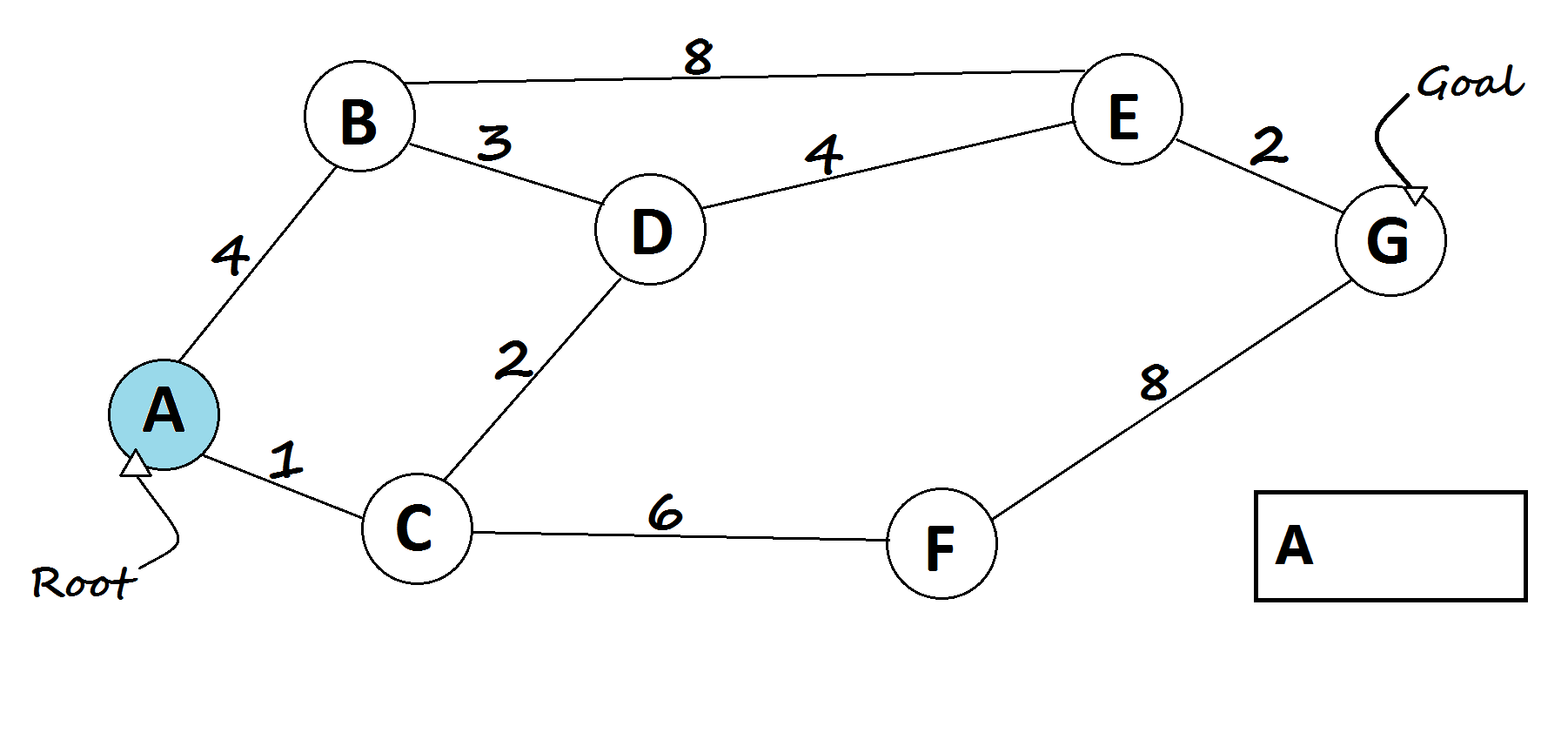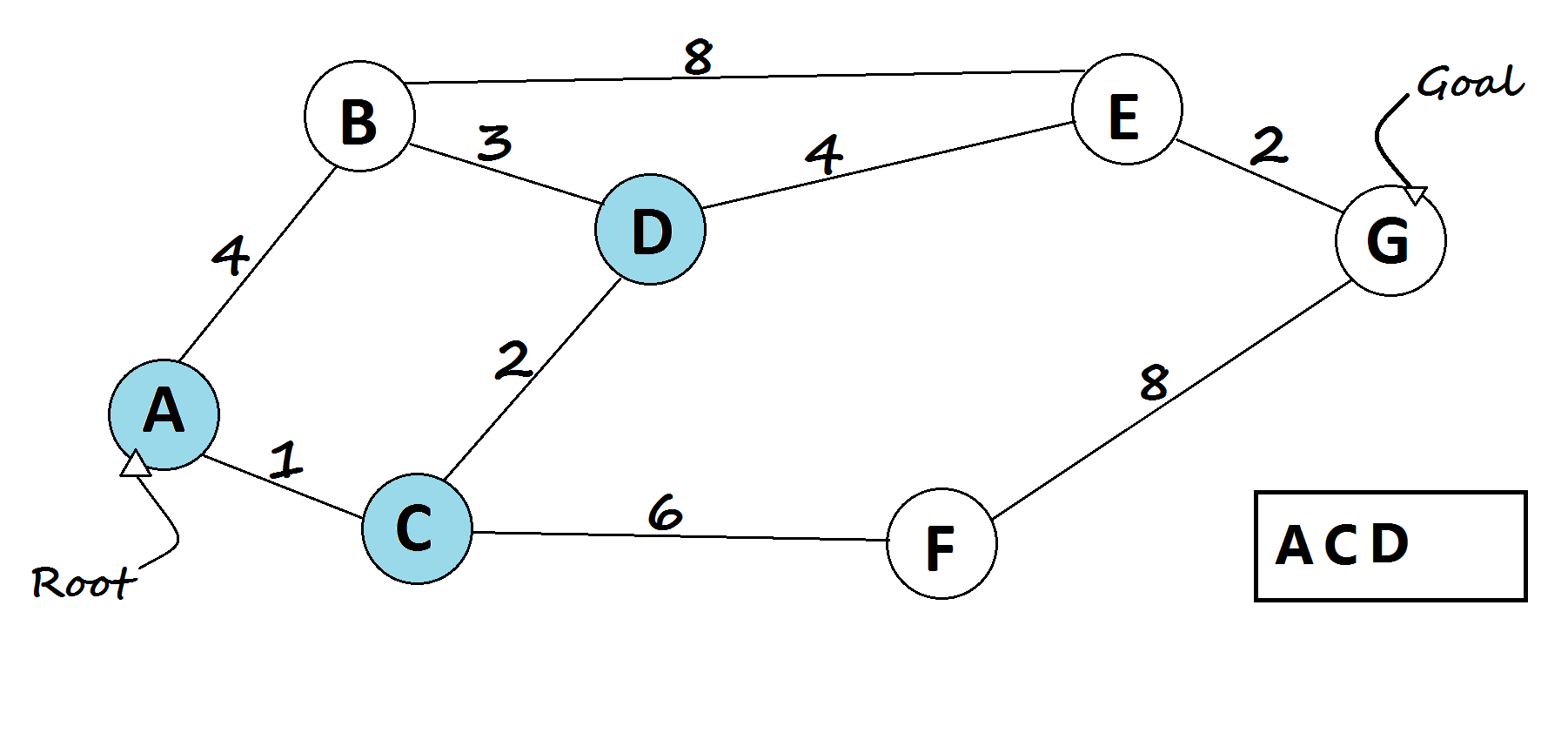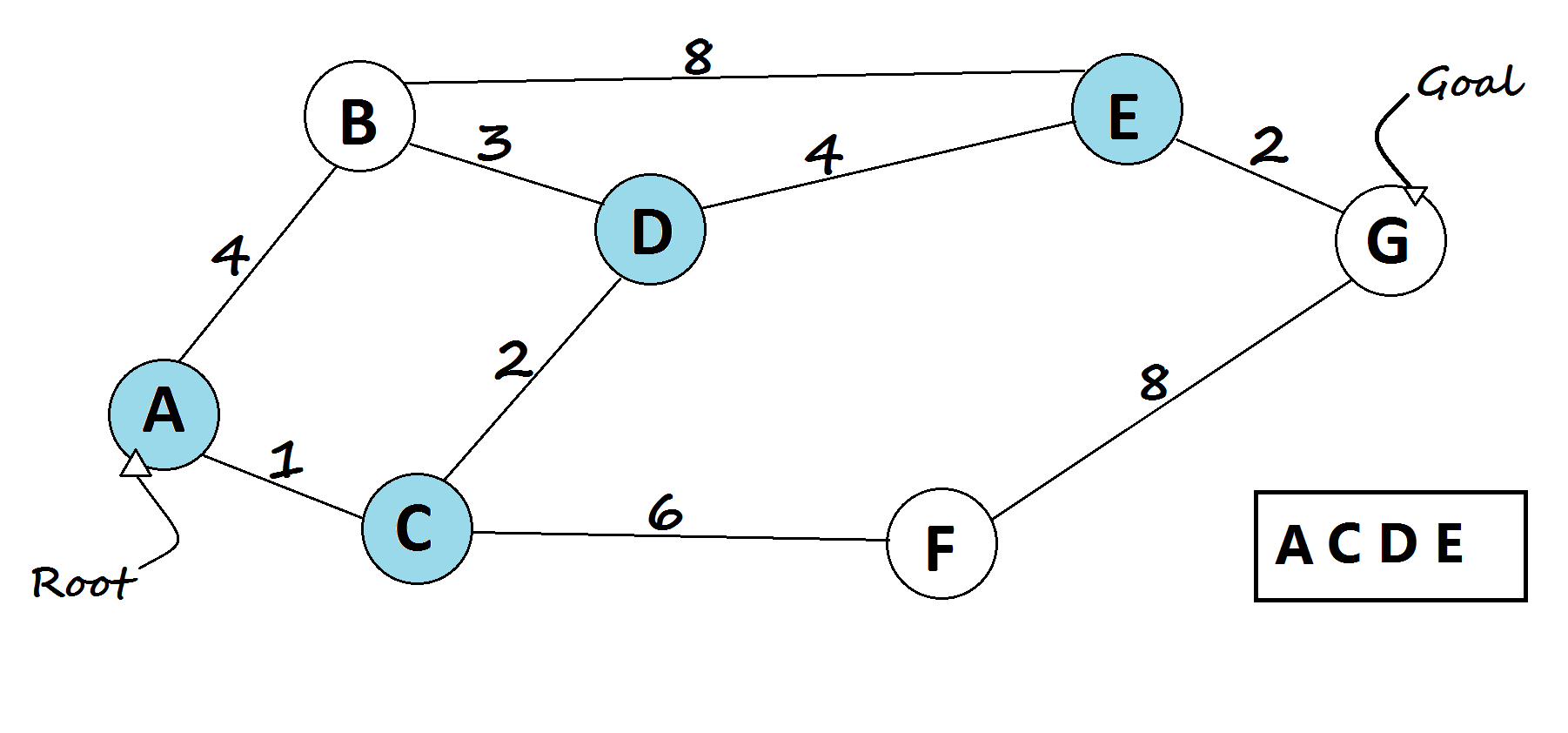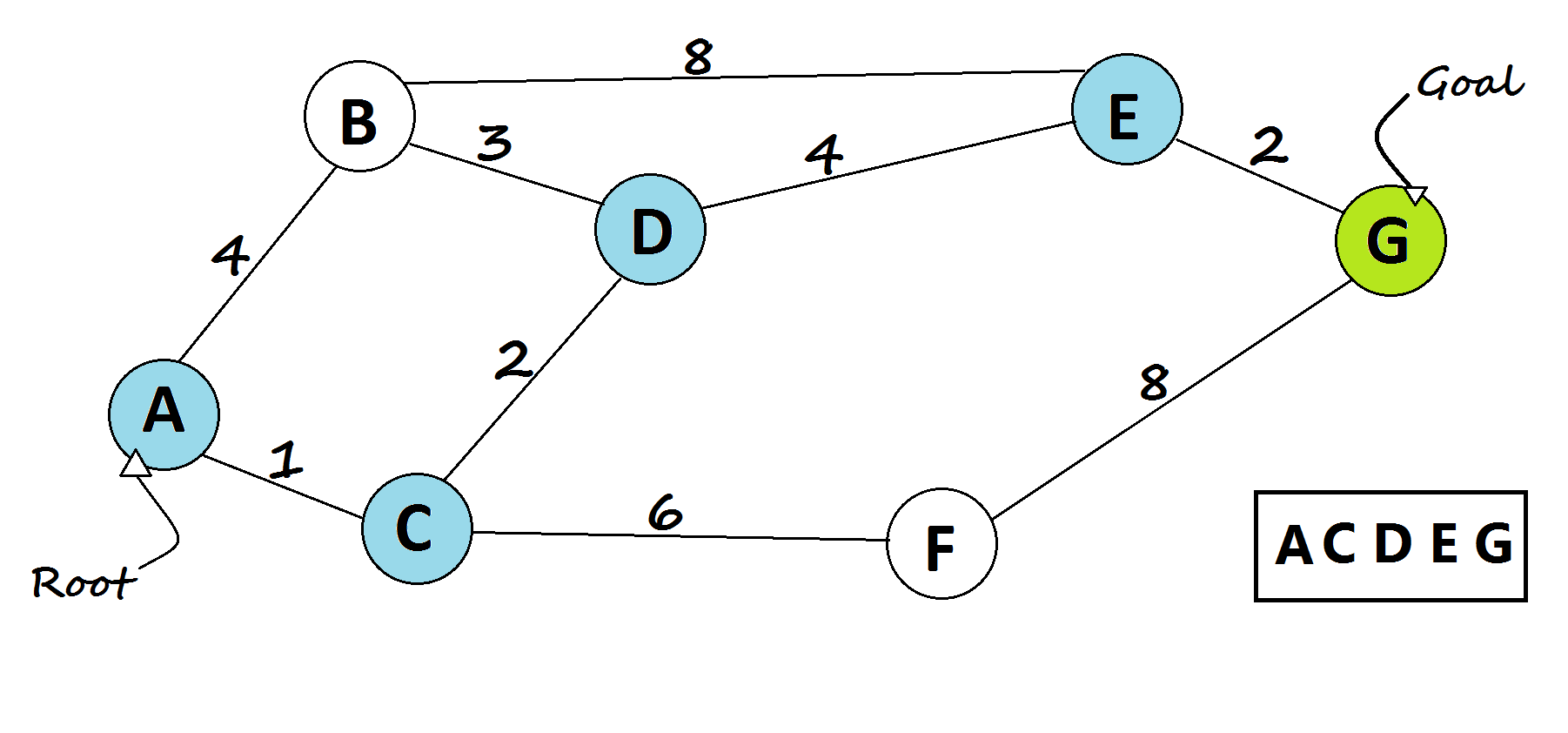
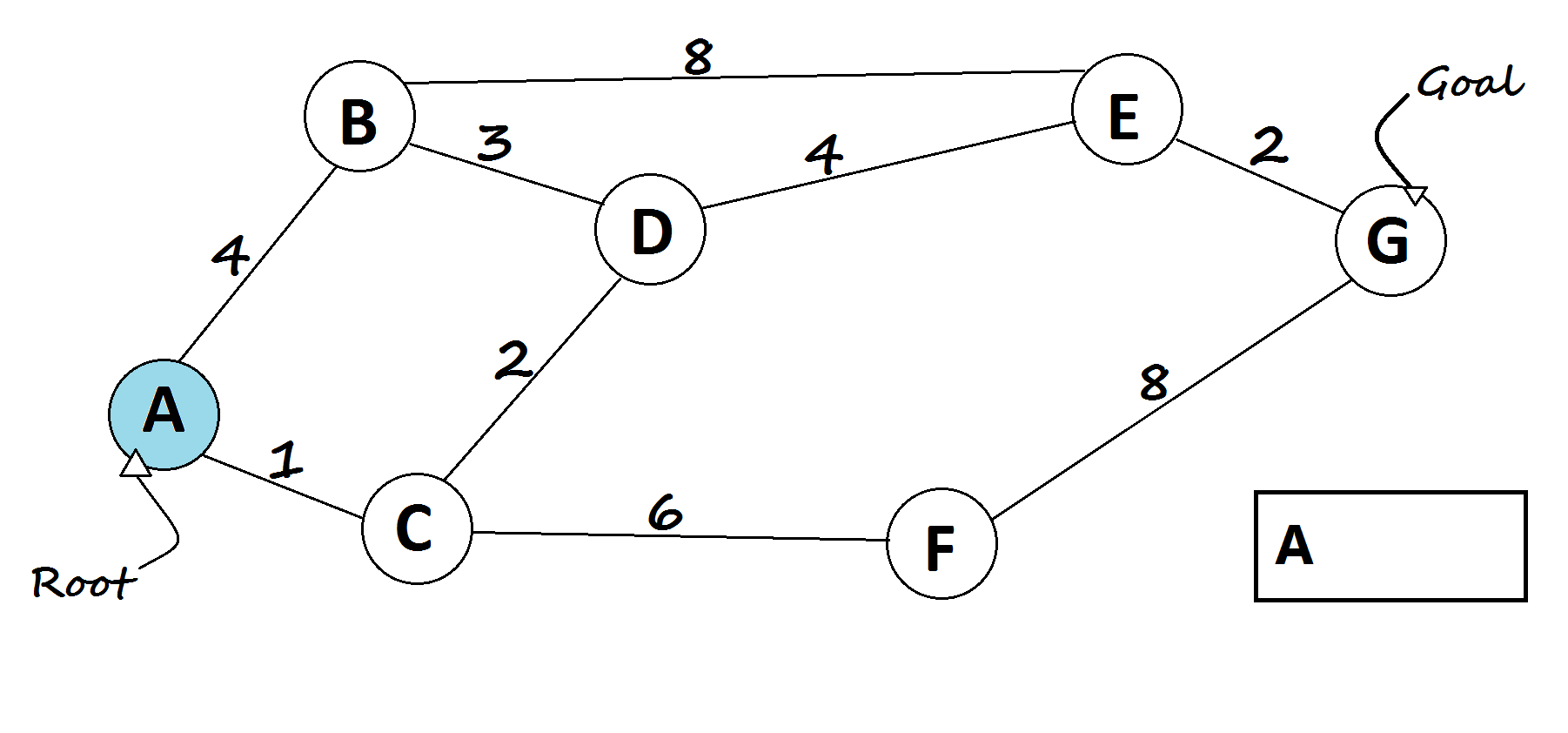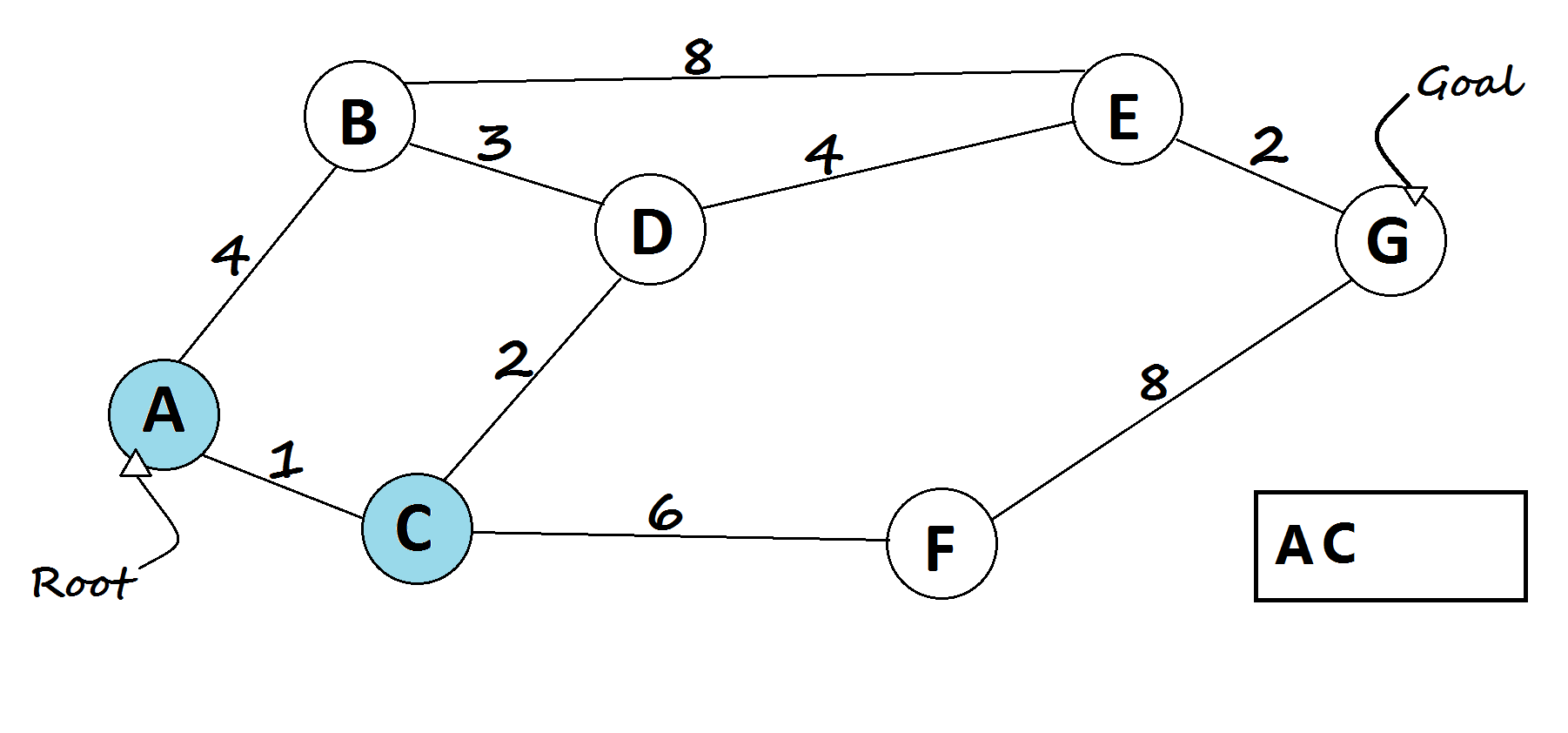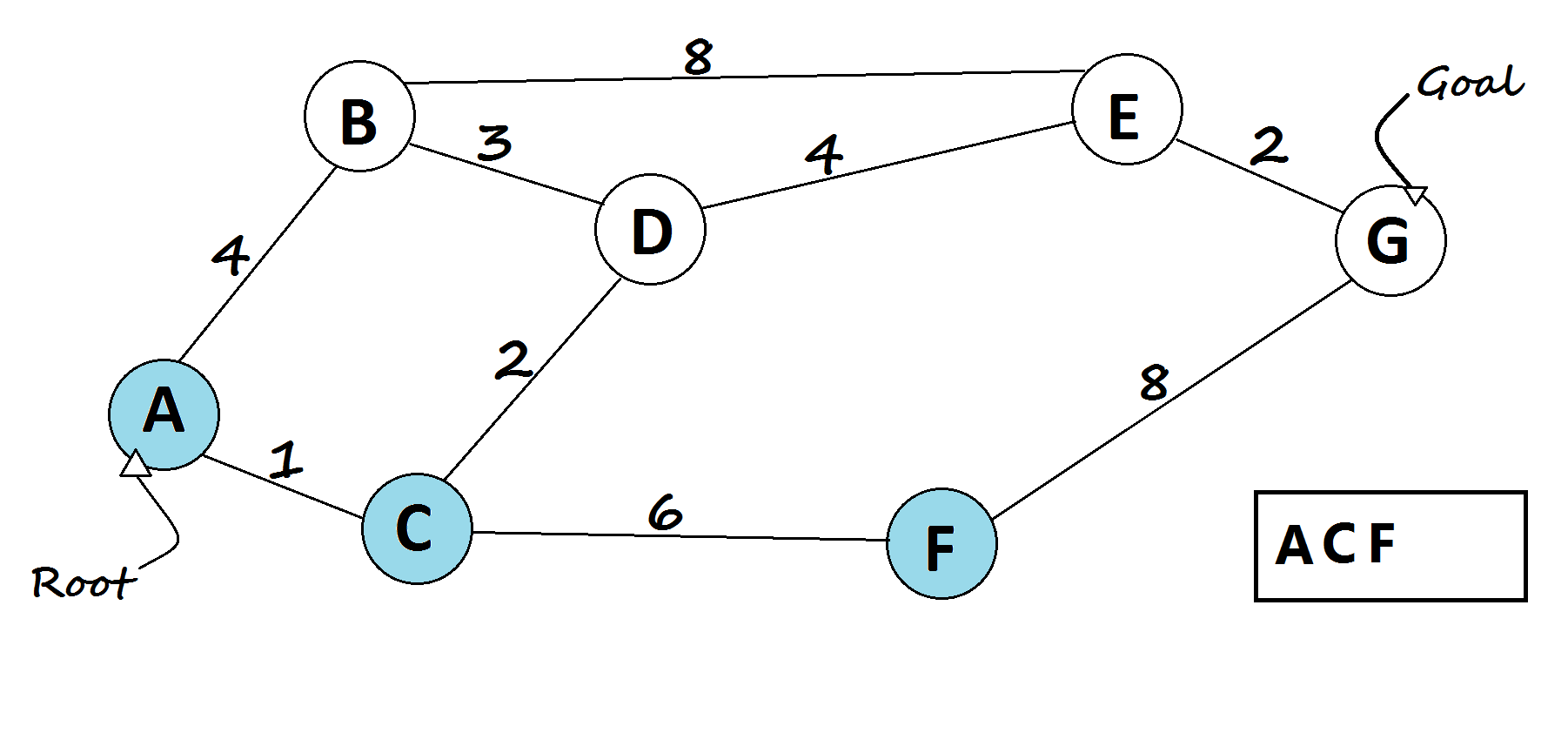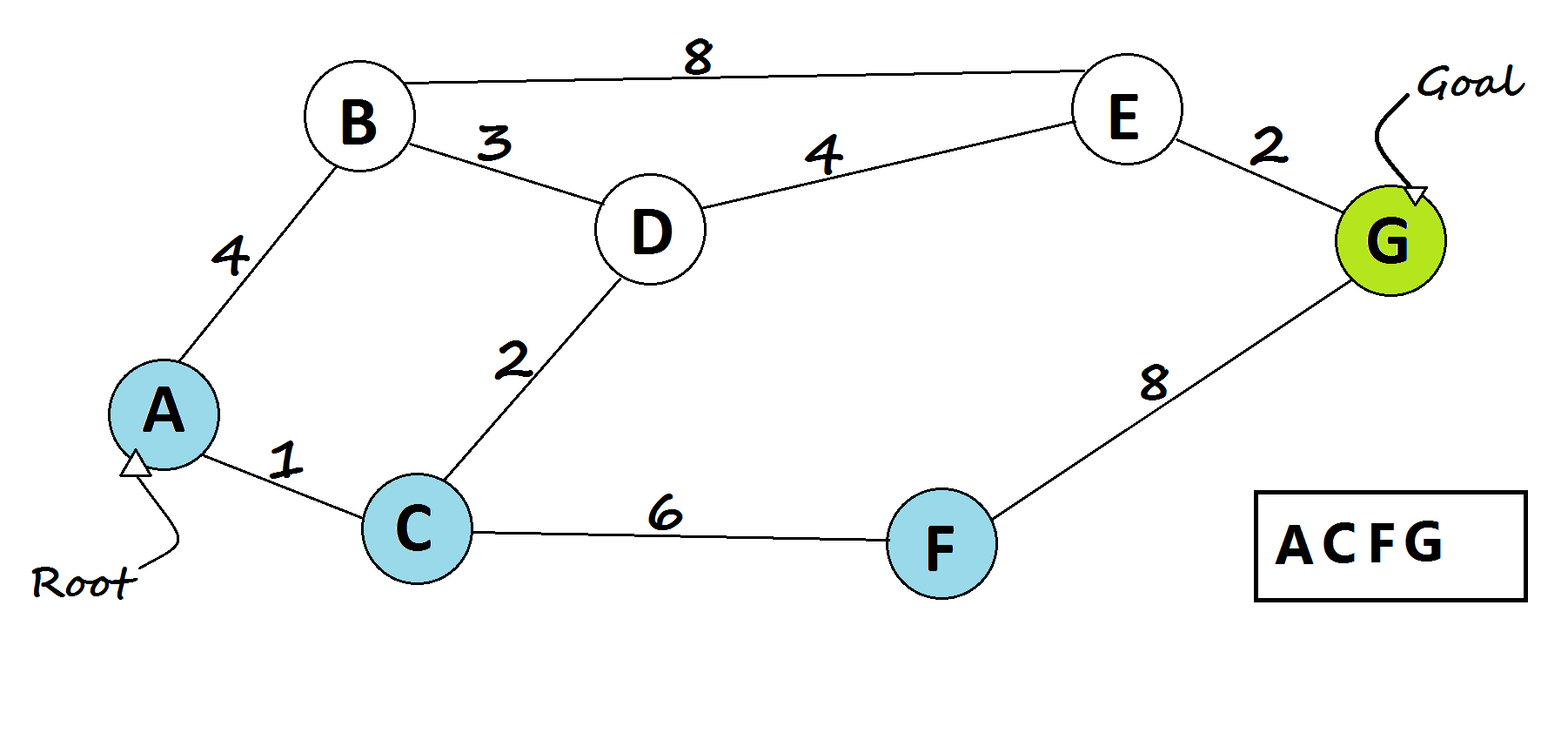
Dijkstra’s algorithm tries to find the shortest path from the starting(root) node to every node, hence we can get the shortest path from the starting node to the goal.
- Assign dis[v] for all nodes = INT_MAX (distance from root node to every other node).
- Assign dis[root] = 0(distance from root node to itself).
- Add all nodes to a priority queue.
- Loop on the queue as long as it's not empty.
- In every loop, choose the node with the minimum distance from the root node in the queue(root node will be selected first).
- Remove the current chosen node from the queue (vis[current] = true).
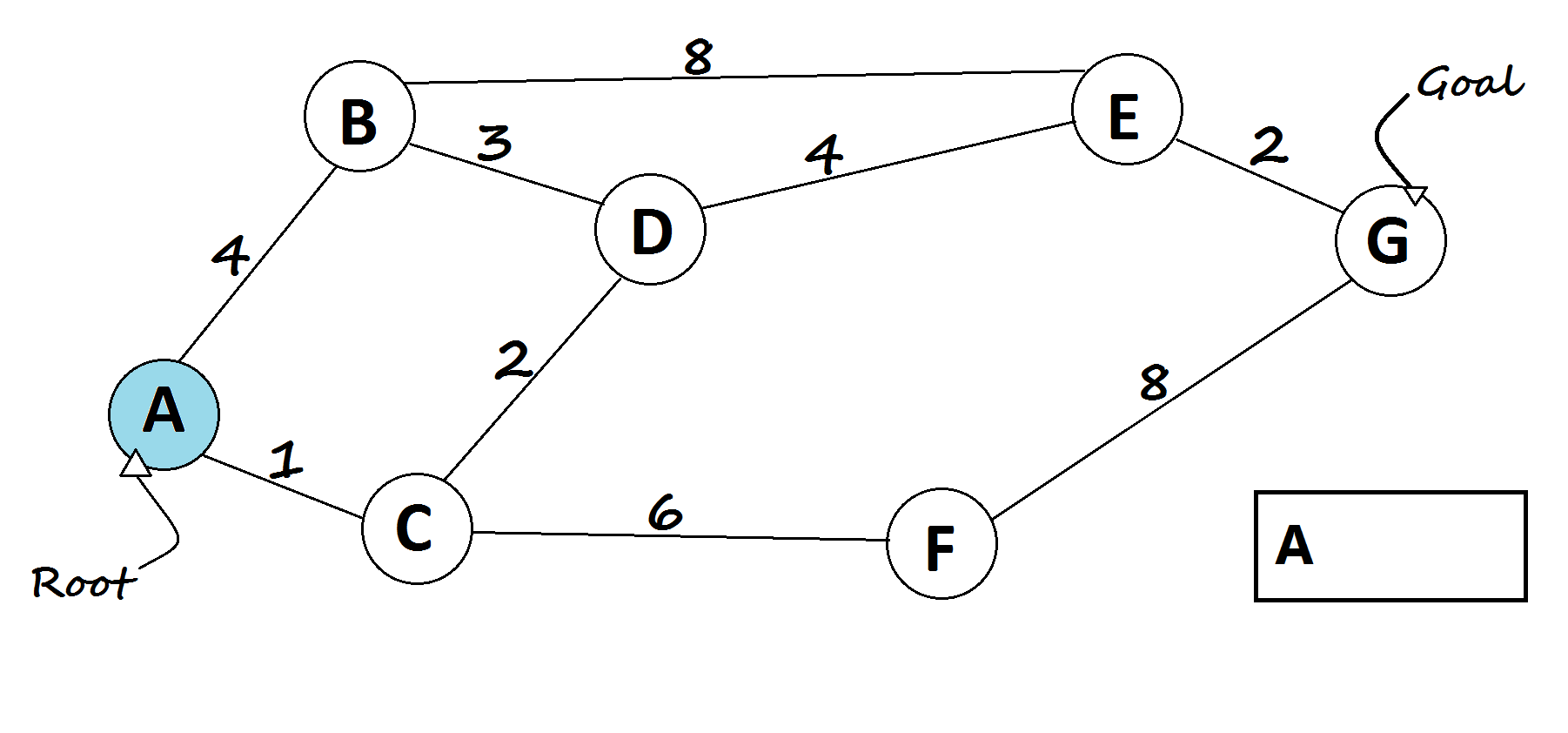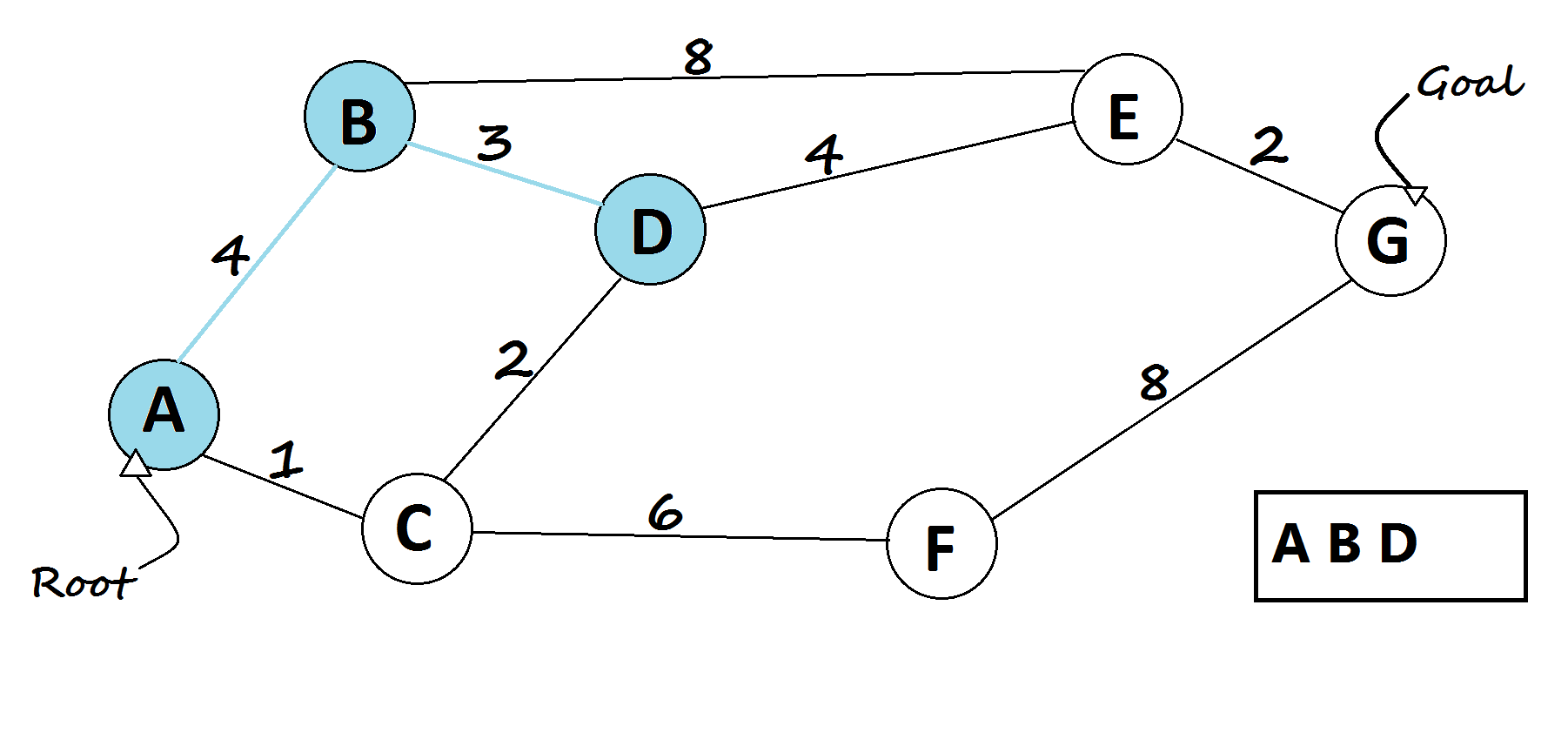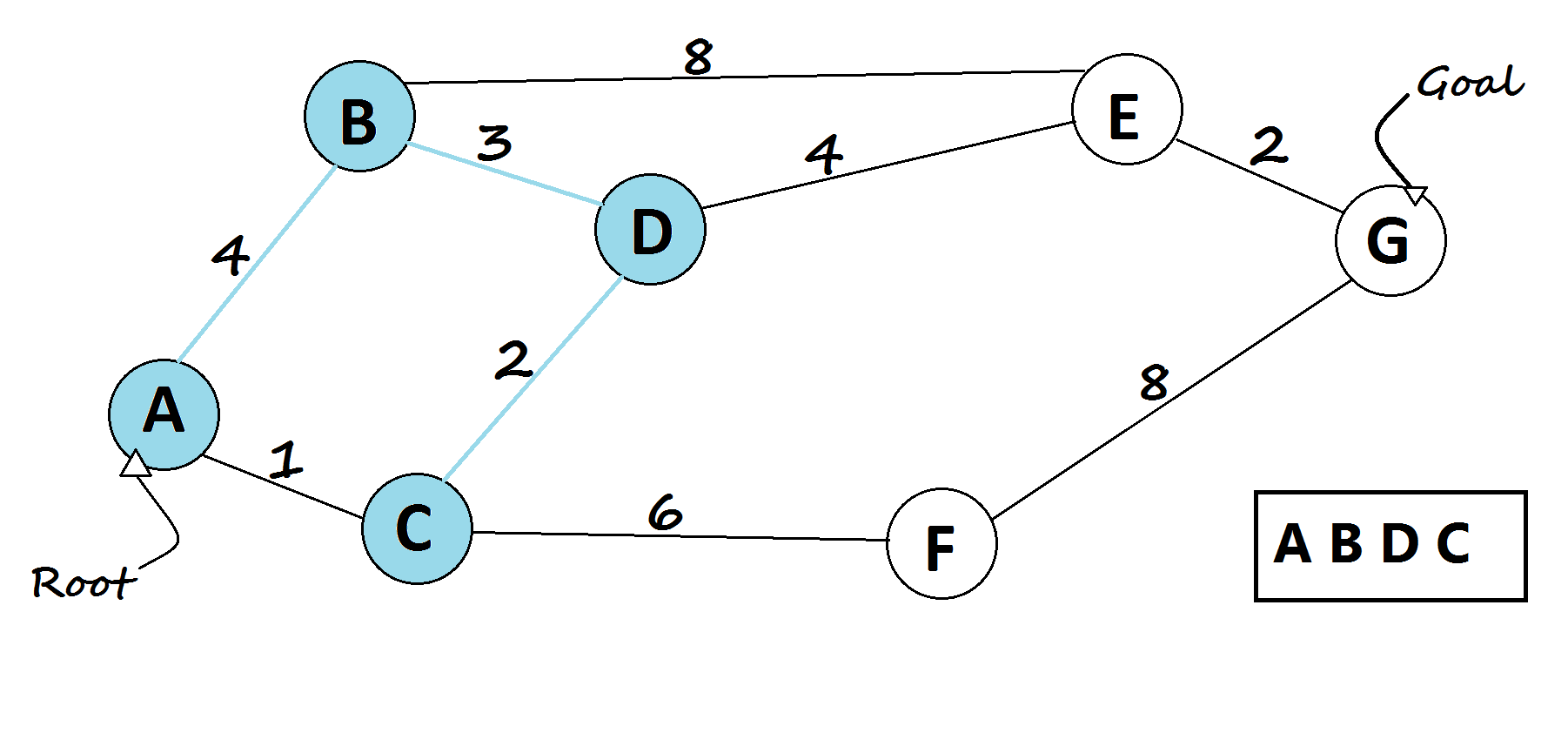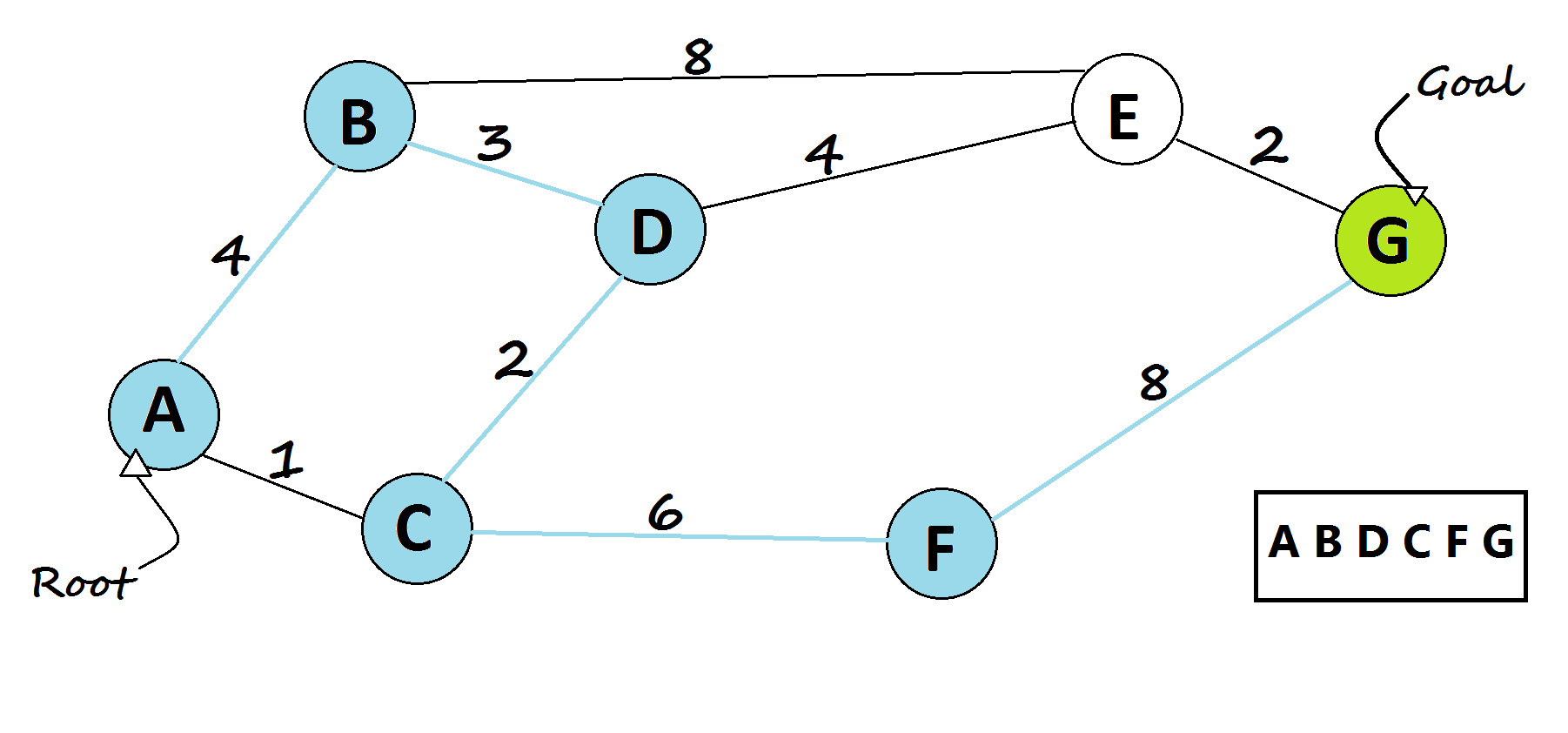
- If the current chosen node is the goal node, then return it.
- For every child of the current node, do the following:
- If child node is not already in the queue (already visited), then skip this iteration.
- Assign temp = dist[current] + distance from current to child node.
- If temp < dist[child], then, assign dist[child] = temp. This denotes a shorter path to child node has been found.
- If queue is empty, then goal node was not found!
Greedy is an algorithm which makes a choice based on educated guesses(heuristics) at each stage. The node with shortest heuristic distance from the goal node will be explored next.
- Assign dis[v] for all nodes = INT_MAX (distance from every node to goal node).
- Assign dis[root] = heuristics(root, goal) (distance from root node to goal).
- Add root node to priority queue.
- Loop on the queue as long as it's not empty.
- In every loop, choose the node with the minimum heuristic distance from the goal node in the queue(root node will be selected first).
- Remove the current chosen node from the queue (vis[current] = true).
- If the current chosen node is the goal node, then return it.
- For every child of the current node, do the following:
- If child node is already visited (previously removed from the queue), then skip this iteration.
- Assign dist[current] = heuristics(current, goal).
- Add child node to the queue.
- If queue is empty, then goal node was not found!
A* is a combination of Dijkstra and Greedy. It uses distance from the root node plus heuristics distance to the goal. The algorithm terminates when we find the goal node.
- Assign dis[v] for all nodes = INT_MAX (distance from root node + heuristics of every node).
- Assign dis[root] = 0 + heuristic(root, goal) (distance from root node to itself + heuristics).
- Add root node to priority queue.
- Loop on the queue as long as it's not empty.
- In every loop, choose the node with the minimum distance from the root node in the queue + heuristic (root node will be selected first).
- Remove the current chosen node from the queue (vis[current] = true).
- If the current node is the goal node, then return it.
- For every child of the current node, do the following:
- Assign temp = distance(root, current) + distance(current, child) + heuristic(child, goal).
- If temp < dis[child], then, assign dist[child] = temp. This denotes a shorter path to child node has been found.
- And, add child node to the queue if not already in the queue (thus, it's now marked as not visited again).
- If queue is empty, then goal node was not found!