In this installation guide, we cover the step-by-step process of installing the ETSO famework on Ubuntu 16.04. We need to have an Opendayligh node that manages the service function chains. Next we will show how to install on Ubuntu 16.04 an Opendaylight who will play the role of an SFC controller. Then we will provide a description of the steps followed to install the ETSO and to create an SFC on OpenStack and OpenDaylight.
Authors:
Copyright (C) Marouane Mechteri & Chaima Ghribi
Contents
Installation of openjdk 8 and unzip:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jre sudo apt-get install unzip
Edit /etc/environment with JAVA_HOME variable:
sudo vi /etc/environment JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/
Download the OpenDaylight Boron release:
wget https://nexus.opendaylight.org/content/repositories/opendaylight.release/org/opendaylight/integration/distribution-karaf/0.5.1-Boron-SR1/distribution-karaf-0.5.1-Boron-SR1.zip unzip distribution-karaf-0.5.1-Boron-SR1.zip
Load JAVA_HOME variable:
logout and login again
Installation of SFC features:
cd distribution-karaf-0.5.1-Boron-SR1/ ./bin/karaf feature:install odl-sfc-model odl-sfc-provider odl-sfc-provider-rest odl-sfc-netconf odl-sfc-ovs odl-sfc-scf-openflow odl-sfc-openflow-renderer odl-sfclisp odl-sfc-sb-rest odl-sfc-ui
To build the ETSO framework you need to install the following additional libraries and tools:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get -y upgrade sudo apt-get -y install python-setuptools python-dateutil python-pip git openjdk-8-jre python-packaging
Installation of python clients of OpenStack services:
sudo apt-get -y install python-openstackclient python-ceilometerclient python-heatclient
Clone this git repository in your ETSO VM:
git clone https://github.com/MarouenMechtri/ETSO.git -b ETSO_v2
Adding trusted root certificates to the ETSO VM:
# Copy your CA to dir /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/: sudo cp openstack_https.crt /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/openstack_https.crt # Update the CA store: sudo update-ca-certificates
To customize the ETSO framework to your cloud environement, you should specify:
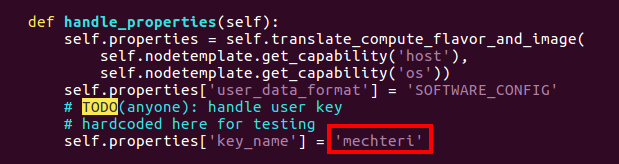
key pair that you are using in the OpenStack:
vi ETSO/SFC-orchestrator/Tosca-parser/toscaparser/sfc/tosca/tosca_compute.py
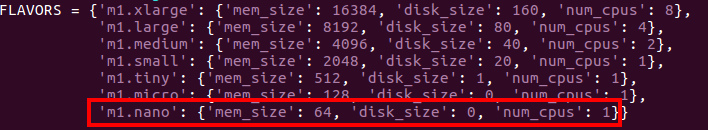
flavors that you are using by adding new element as depicted in the figure:
vi ETSO/SFC-orchestrator/Tosca-parser/toscaparser/sfc/tosca/tosca_compute.py
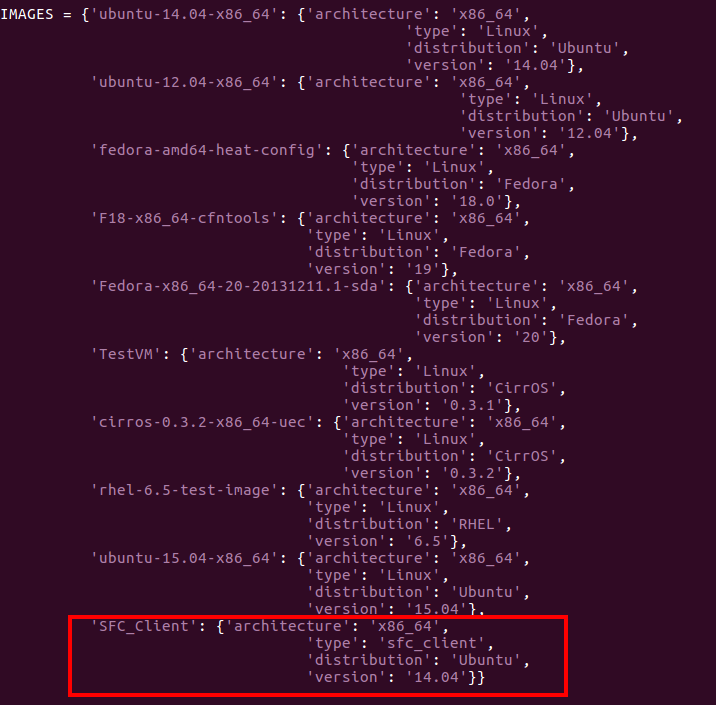
images available in your cloud by adding new element as depicted in the figure:
vi ETSO/SFC-orchestrator/Tosca-parser/toscaparser/sfc/tosca/tosca_compute.py
Install ETSO services:
cd ETSO sudo ./install.sh
Update ODL plugin with the OpenDaylight address, port, username and password:
vi SFC-manager/plugins/config.json { "ODL" : "192.168.111.36", "ODL_PORT" : 8181, "ODL_USERNAME" : "admin", "ODL_PASSWORD" : "admin" }Update credentials.py file with credentials of the OpenStack selected to host the requested SFC, VMs, and stacks:
vi SFC-orchestrator/credentials.py USERNAME="username" PASSWORD="password" TENANT_NAME="tenant_name" TENANT_ID="tenant_uuid" ENDPOINT="https://OPENSTACK_ADDRESS:5000/v2.0" SERVICE="compute" REGION="RegionOne" VERSION=2 HEAT_URL="https://OPENSTACK_ADDRESS:8004/v1/tenant_id" OS_CACERT="/etc/ssl/certs/openstack_https.pem"
Before creating your first SFC, you need to start the ETSO services.
Starting the ETSO services:
./start.py
To test the ETSO framework, we provided some examples of template in this folder. The ETSO framework handles two types of templates:
- Network Service Descriptor (NSD) templates in TOSCA/yaml format which containt the NCT (Network Connectivity Template) part and the SFC (Service Function Chain) part. Here is some exmaples.
- Templates in TOSCA/yaml which contain a set of cloud resources (VMs, network, subnet, port...). These templates do not contain an SFC part. Here is some exmaples.
The ETSO framework can be invoked with several methods.
For example, you can use the curl command line tool:
curl -X POST --data-binary @SFC-orchestrator/ETSO_templates/templates_with_SFC/nsd_with_3vfns_on_existingNet.yaml -H "Content-type: text/x-yaml" http://ETSO_IP_ADDRESS:8181/deploy_template
You can use GUI plateform like postman tool. In this case you should specify:
The type of request (POST, GET, DELETE...)
POST
The ETSO URL:
http://ETSO_IP_ADDRESS:8181/deploy_template
The body contains the TOSCA/yaml request:
tosca_definitions_version: tosca_simple_yaml_1_0 description: example for a NSD with existing network. imports: topology_template: inputs: network_name: type: string default: admin_internal_net node_templates: VM1: type: tosca.nodes.Compute capabilities: # Host container properties host: properties: num_cpus: 2 disk_size: 10 GB mem_size: 512 MB # Guest Operating System properties os: properties: # host Operating System image properties architecture: x86_64 type: sfc_client distribution: ubuntu version: 14.04 VM2: type: tosca.nodes.Compute capabilities: # Host container properties host: properties: num_cpus: 2 disk_size: 10 GB mem_size: 512 MB # Guest Operating System properties os: properties: # host Operating System image properties architecture: x86_64 type: sfc_client distribution: ubuntu version: 14.04 VM3: type: tosca.nodes.Compute capabilities: # Host container properties host: properties: num_cpus: 2 disk_size: 10 GB mem_size: 512 MB # Guest Operating System properties os: properties: # host Operating System image properties architecture: x86_64 type: sfc_client distribution: ubuntu version: 14.04 my_network: type: tosca.nodes.network.Network properties: network_name: { get_input: network_name } my_port1: type: tosca.nodes.network.Port requirements: - binding: node: VM1 - link: node: my_network my_port2: type: tosca.nodes.network.Port requirements: - binding: node: VM2 - link: node: my_network my_port3: type: tosca.nodes.network.Port requirements: - binding: node: VM3 - link: node: my_network VNF1: type: tosca.nodes.nfv.VNF properties: attributes: type: dpi address: 10.100.0.105 port: 40000 nsh_aware: true requirements: - host: VM1 CP11: #endpoints of VNF1 linked to VL1 type: tosca.nodes.nfv.CP properties: attributes: IP_address: 10.100.0.105 interface: ens3 port: 30000 requirements: - virtualBinding: VNF1 - virtualLink: VL1 VNF2: type: tosca.nodes.nfv.VNF properties: attributes: type: firewall address: 10.100.0.106 port: 40000 nsh_aware: true requirements: - host: VM2 CP21: #endpoints of VNF2 linked to VL1 type: tosca.nodes.nfv.CP properties: attributes: IP_address: 10.100.0.106 interface: ens3 port: 30000 requirements: - virtualBinding: VNF2 - virtualLink: VL1 VNF3: type: tosca.nodes.nfv.VNF properties: attributes: type: napt44 address: 10.100.0.107 port: 40000 nsh_aware: true requirements: - host: VM3 CP31: #endpoints of VNF3 linked to VL2 type: tosca.nodes.nfv.CP properties: attributes: IP_address: 10.100.0.107 port: 30000 interface: ens3 requirements: - virtualBinding: VNF3 - virtualLink: VL1 VL1: type: tosca.nodes.nfv.VL properties: vendor: HP attributes: type: ip transport_type: vxlan-gpe Forwarding_path1: type: tosca.nodes.nfv.FP description: the path (CP11->CP21->CP31) properties: policy: requirements: - forwarder: CP11 - forwarder: CP21 - forwarder: CP31 ################################################# # VNF Forwarding Graph nodes and the associated # Network Forwarding Paths ################################################# groups: VNF_FG1: type: tosca.groups.nfv.VNFFG description: VNF forwarding graph properties: vendor: version: connection_point: [ CP11, CP21, CP31 ] dependent_virtual_link: [ VL1 ] constituent_vnfs: [ VNF1, VNF2, VNF3 ] members: [ Forwarding_path1 ] outputs: vnf1_ip: description: The private IP address of the VNF container1. value: { get_attribute: [VM1, private_address] } vnf2_ip: description: The private IP address of the VNF container2. value: { get_attribute: [VM2, private_address] } vnf3_ip: description: The private IP address of the VNF container3. value: { get_attribute: [VM3, private_address] }From the Horizon web interface, you can verify that the requested resources are instantiated:
https://OPENSTACK_IP/horizon/project/stacks/
Then, from the OpenDaylight web interface you can check that the service function chains (SFCs) are instantiated:
http://ODL_IP:8181/index.html#/sfc/serviceforwarder