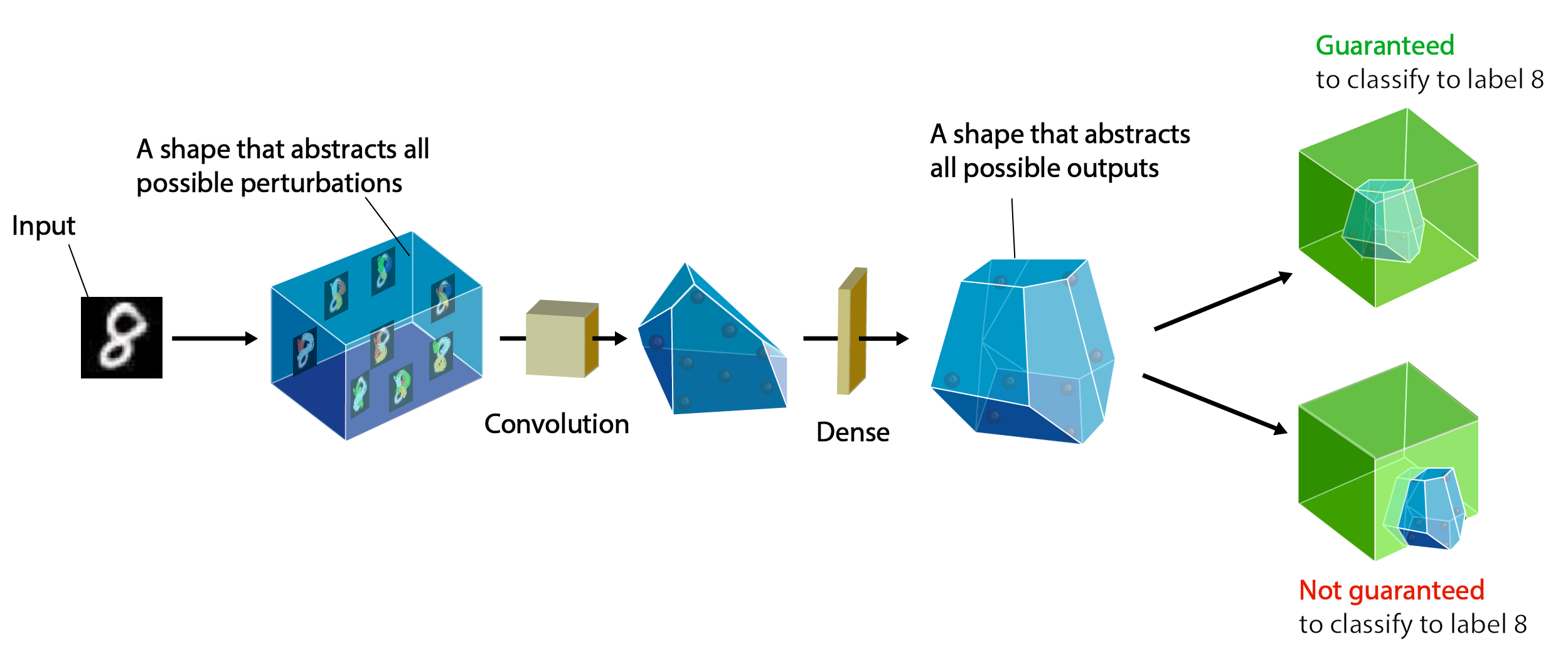The original ERAN system description is described below, this repo adds support of BatchNormalization layers in onnx model on top of ERAN system.
ETH Robustness Analyzer for Neural Networks (ERAN) is a state-of-the-art sound, precise, scalable, and extensible analyzer based on abstract interpretation for the complete and incomplete verification of MNIST, CIFAR10, and ACAS Xu based networks. ERAN produces state-of-the-art precision and performance for both complete and incomplete verification and can be tuned to provide best precision and scalability (see recommended configuration settings at the bottom). ERAN is developed at the SRI Lab, Department of Computer Science, ETH Zurich as part of the Safe AI project. The goal of ERAN is to automatically verify safety properties of neural networks with feedforward, convolutional, and residual layers against input perturbations (e.g., L∞-norm attacks, geometric transformations, vector field deformations, etc).
ERAN supports fully-connected, convolutional, and residual networks with ReLU, Sigmoid, Tanh, and Maxpool activations and is sound under floating point arithmetic. It employs custom abstract domains which are specifically designed for the setting of neural networks and which aim to balance scalability and precision. Specifically, ERAN supports the following four analysis:
-
DeepZ [NIPS'18]: contains specialized abstract Zonotope transformers for handling ReLU, Sigmoid and Tanh activation functions.
-
DeepPoly [POPL'19]: based on a domain that combines floating point Polyhedra with Intervals.
-
RefineZono [ICLR'19]: combines DeepZ analysis with MILP and LP solvers for more precision.
-
RefinePoly [NeurIPS'19]: combines DeepPoly analysis with MILP and k-ReLU framework for state-of-the-art precision while maintaining scalability.
All analysis are implemented using the ELINA library for numerical abstractions. More details can be found in the publications below.