链表是空节点,或者有一个值和一个指向下一个链表的指针,因此很多链表问题可以用递归来处理。
链表节点:
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}链表工具类:
public class LinkedListUtils {
//根据数组创建链表
public static ListNode createLinkedList(int[] arr){
if(arr.length==0){
return null;
}
ListNode head=new ListNode(arr[0]);
ListNode curNode=head;
for(int i=1;i<arr.length;i++){
curNode.next=new ListNode(arr[i]);
curNode=curNode.next;
}
return head;
}
//打印链表
public static void printList(ListNode head){
ListNode curNode=head;
while(curNode!=null){
System.out.print(curNode.val+"-->");
curNode=curNode.next;
}
System.out.println("NULL");
}
}206. Reverse Linked List (Easy)
//思路:
//1、准备三个指针,指向pre指向当前节点的前一个节点、cur指向当前节点、next指向当前节点的后一个节点
//2、要实现链表的反转,则 cur 指向 pre,同时 pre、cur、next都要相应的指向下一个位置。//写法一:非递归方式
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur ;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
@Test
public void test(){
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
ListNode head = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(arr);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
head = reverseList(head);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}//写法二:递归方式
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return head;
}
// last 节点就是以 head.next 为头结点的链表翻转后得到的最后一个节点
ListNode last = head.next;
//翻转后 head 是最后一个节点
head.next = null;
//以 head.next 为头结点的链表翻转后得到的新链表,头节点是 newHead
ListNode newHead = reverseList(last);
last.next = head;
return newHead;
}
@Test
public void test(){
int[] arr = {5,4,3,2,1};
ListNode head = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(arr);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
head = reverseList(head);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
// m,n 表示的是第m,n个节点
if(m >= n){ //不需要翻转
return head;
}
//TODO:引入虚拟头结点,是方便处理 m=1,即头结点无前驱节点的情况
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummyHead; // pre 用于定位 m 节点的前驱节点
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){ //注意是(m-1)次
pre=pre.next;
}
ListNode mnode = pre.next;
//进行(m-n)交换,即可实现反转
for(int i=0;i<(n-m);i++){
//实现将 mnode 的后继节点 mnext 插入到 pre 的下一个节点位置
//进行 (n-m) 次交换即可 (画个草图)
ListNode mnodeNext = mnode.next; // mnext 始终是 m 节点的后继节点
mnode.next = mnodeNext.next;
mnodeNext.next = pre.next;
pre.next = mnodeNext;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
@Test
public void test(){
int[] arr ={1,2,3,4,5};
int m=2,n=4;
ListNode head = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(arr);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
head = reverseBetween(head,m,n);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List (Easy)
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head ==null || head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
if(next!=null && cur.val == next.val){
cur.next = next.next;
}else{
cur = next;
}
}
return head;
}
@Test
public void test(){
//int[] arr={1,1,2};
int[] arr={1,1,2,3,3};
ListNode head = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(arr);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
head=deleteDuplicates(head);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummyHead; // pre 指向待删除元素的前一个节点
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==val){
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = pre.next;
}else{
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
@Test
public void test(){
// 1->2->6->3->4->5->6, val = 6
int[] nums={1,2,6,3,4,5,6};
//int val =6;
int val =2;
ListNode head = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums);
head=removeElements(head,val);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}//思路:
//两个链表是逆序的,结果链表也是逆序的,则使用尾插法来在结果链表中插入新元素
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null){
return l2;
}
if(l2==null){
return l1;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tail = dummyHead;
int c=0;
while(l1!=null || l2!=null){
if(l1!=null){
c += l1.val;
l1 = l1.next;
}
if(l2!=null){
c += l2.val;
l2 = l2.next;
}
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(c%10);
tail.next = newNode;
tail = newNode;
c /= 10;
}
if(c==1){
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(1);
tail.next = newNode;
tail = newNode;
}
tail.next = null; //注意尾插法
return dummyHead.next;
}
@Test
public void test(){
int[] nums1={2,4,3};
int[] nums2={5,6,4};
ListNode l1 = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums1);
ListNode l2 = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums2);
ListNode head = addTwoNumbers(l1,l2);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}//思路:
//两个链表是顺序的,需要先将两个链表进行逆序处理
//结果链表也是顺序的,则使用头插法来在结果链表中插入新元素
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null){
return l2;
}
if(l2==null){
return l1;
}
//将两个链表进行逆序处理
l1 = reverse(l1);
l2 = reverse(l2);
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
int c=0;
while(l1!=null || l2!=null){
if(l1!=null){
c += l1.val;
l1=l1.next;
}
if(l2!=null){
c += l2.val;
l2=l2.next;
}
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(c%10);
newNode.next = dummyHead.next;
dummyHead.next = newNode;
c/=10;
}
if(c==1){
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(1);
newNode.next = dummyHead.next;
dummyHead.next = newNode;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
//将链表逆序处理
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head){
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur; //注意:pre、cur 的先后顺序
cur = next;
}
//最中 pre 就是头结点
return pre;
}
@Test
public void test(){
int[] nums1={7,2,4,3};
int[] nums2={5,6,4};
ListNode l1 = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums1);
ListNode l2 = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums2);
ListNode head = addTwoNumbers(l1,l2);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummyHead;
ListNode cur = head;
//head 链表至少有 1 个节点,cur 不为 null
while(cur.next!=null){
if(cur.val != cur.next.val){ //相邻元素的值不相同,但是还不能说明 cur 不是重复元素,需要进一步判断
if(pre.next == cur){ //cur是 pre 的后一个元素,就说明该 cur元素不是重复元素
pre = cur;
}else{ //该cur元素是重复元素(cur此时指向了该值的重复元素的最后一个节点)
pre.next = cur.next;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
//TODO:cur此时指向最后一个元素,这是一种特殊的情况
//比如 1->2->2->2 ,需要特殊处理: pre指向元素1,后面的元素都被删除了,
//此时只需要将pre.next设置成null即可
//该cur此时指向了该值的重复元素的最后一个节点
if(pre.next!=cur){
pre.next=null;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
@Test
public void test(){
//1->2->3->3->4->4->5
//int[] nums = {1,2,3,3,4,4,5};
//1->1->1->2->3
//int[] nums = {1,1,1,2,3};
int[] nums = {1,2,2,2};
ListNode head = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums);
head = deleteDuplicates(head);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}//思路:
//设 A 的长度为 a + c,B 的长度为 b + c,其中 c 为尾部公共部分长度,
//可知 (a + c) + b = (b + c) + a。
//当访问 A 链表的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 B 的头部开始访问链表 B;
//同样地,当访问 B 链表的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 A 的头部开始访问链表 A。
//这样就能控制访问 A 和 B 两个链表的指针能同时访问到交点。
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode l1=headA;
ListNode l2=headB;
while(l1!=l2){
if(l1==null){
l1 = headB;
}else{
l1=l1.next;
}
if(l2==null){
l2 = headA;
}else{
l2=l2.next;
}
}
return l1;
}
@Test
public void test(){
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(8);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode node6 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode node7 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode node8 = new ListNode(1);
node1.next=node2;
node2.next=node3;
node3.next=node4;
node4.next=node5;
ListNode headA = node1;
node6.next=node7;
node7.next=node8;
node8.next=node3;
ListNode headB = node6;
ListNode head = getIntersectionNode(headA,headB);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}21. Merge Two Sorted Lists (Easy)
//思路:
//类似合并两个有序数组
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null){
return l2;
}
if(l2==null){
return l1;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tail = dummyHead;
while(l1!=null && l2!=null){
if(l1.val < l2.val){ //将l1中数据加入新链表
tail.next = l1;
tail = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
tail.next = l2;
tail = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
if(l1!=null){
tail.next = l1;
}
if(l2!=null){
tail.next = l2;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
@Test
public void test(){
//1->2->4, 1->3->4
int[] nums1={1,2,4};
int[] nums2={1,3,4};
ListNode head1 = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums1);
ListNode head2 = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums2);
ListNode head = mergeTwoLists(head1,head2);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}//思路二:使用递归
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}//思路:
//难点在于算法的空间复杂度应为 O(1),时间复杂度应为 O(nodes),nodes 为节点总数。
//要求要一次循环,就可以处理问题,根据经验,就要使用多个指针
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return head;
}
//前面的判断保证了链表至少有 2 个节点
ListNode odd = head; //奇数节点
ListNode even = head.next; //偶数节点
ListNode evenHead = even;
//记录偶数节点的开始位置,因为对链表进行遍历后
//odd 会指向最后一个奇数节点 和 even 会指向最后一个偶数节点
while (even!=null && even.next!=null){
//如果链表长度为奇数,则 even != null 是循环终止条件
//如果链表长度为偶数,则 even.next != null 是循环终止条件
odd.next = even.next;
odd = even.next;
even.next = odd.next;
even = odd.next;
}
odd.next = evenHead;
//空间复杂度要求是 O(1),只能改变链表结构,但是不能创建新链表
return head;
}
@Test
public void test(){
int[] nums={1,2,3,4,5};
//int[] nums={2,1,3,5,6,4,7};
ListNode head = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
head = oddEvenList(head);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}public ListNode[] splitListToParts(ListNode root, int k) {
ListNode cur = root;
//统计该链表长度
int len=0;
while(cur!=null){
len++;
cur=cur.next;
}
int size = len/k;
int mod = len%k;
//所谓 k 个链表就是:
//mod 个 (size+1) 长度的链表,(k-m) 个 size 长度的链表
ListNode[] res = new ListNode[k];
cur = root;
for(int i=0;cur!=null && i<k;i++){ //TODO:访问链表结束,循环就结束了
res[i] = cur;
//mod 个 (size+1) 长度的链表,(k-m) 个 size 长度的链表
int newSize = size + (mod-->0?1:0);
for(int j=1;j<newSize;j++){
//res[i] = cur; 中 cur 已经是该链表的头结点了,所以 j 从 1 开始
cur=cur.next;
}
// cur 此时指向本链表的最后一个元素了,需要断开连接
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = null; //断开连接
cur = next;
}
return res;
}
@Test
public void test(){
int[] nums={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int k = 3;
ListNode root = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums);
ListNode[] res = splitListToParts(root,k);
for(ListNode l : res){ LinkedListUtils.printList(l);
}
}//思路:
//准备两个指针 p 和 q:
//q 先走(n+1)个节点,则 p 和 q 之间的差距就是(n+1)个节点;
//然后 p 和 q 一起走,一直到 q 走到链表结尾,此时 p 和 q 之间的差距仍然是(n+1)个节点
//p 的下一个节点就是待删除的节点
//注意:n 是从1开始的,p 指向倒数 n 个节点的前一个节点,方便删除目标节点。public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
//p 最终指向倒数 n 个节点的前一个节点
ListNode p = dummyHead;
//q 先走(n+1)个节点
ListNode q = dummyHead;
for(int i=0;i<(n+1);i++){
if(q==null){ //q 可能已经走到链表末尾了
break;
}
q=q.next;
}
while(q!=null){
p=p.next;
q=q.next;
}
//此时,p 指向倒数 n 个节点的前一个节点
//删除目标节点
ListNode delNode = p.next;
p.next = delNode.next;
return dummyHead.next;
}
@Test
public void test(){
//1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2.
int[] nums={1,2,3,4,5};
ListNode head = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
int n=2;
head=removeNthFromEnd(head,n);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}//思路:
// 1、链表为空,就直接返回
// 2、k==0 || k==n*len 时,链表是不变的。
// 所以当判断条件是 k%len==0时,直接返回原来的链表。
// 3、旋转 k 和旋转 k = k % 链表长度 的效果实际上相同的。
// 比如:0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
// 向右旋转 4 步: 2->0->1->NULL
// 和向右旋转 4%3=1 步:2->0->1->NULL 是一样的。
// 4、这里的旋转实际上就是子链表的平移
// 比如:1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
// 就是将 4->5 连接到1->2->3的前面
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return head;
}
int len = 0; //统计该链表长度
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
len++;
cur=cur.next;
}
//旋转 k 和旋转 k = k % 链表长度 的效果实际上相同的。
k %= len;
if(k==0){
return head;
}
//此时确定倒数第 k 个位置元素,然后平移即可 --> 参考 19 题
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode p = dummyHead;
ListNode q = dummyHead;
//改进:preq 始终指向 q 的前一个节点,最终 preq 指向链表的尾节点
ListNode preq = null;
for(int i=0;i<(k+1);i++){
if(q==null){
break;
}
preq = q;
q=q.next;
}
while(q!=null){
p=p.next;
preq=q;
q=q.next;
}
//preq 指向原来链表的尾节点
//对链表进行平移:
//nodeK 作为新的头节点
//p就是尾节点
ListNode nodeK = p.next;
p.next = null;
preq.next = head;
return nodeK;
}
@Test
public void test(){
int[] nums={1,2,3,4,5};
int k=2;
//int[] nums={0,1,2};
//int k=4;
ListNode head=LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
head = rotateRight(head,k);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}//思路:
//要求时间复杂度是 O(n)
//将该链表进行折半处理,然后反转后半部分链表
//比较这两部分的链表中的数组
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return true;
}
//TODO:这段代码十分重要使用快慢指针切分链表
//=================================
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(slow!=null && fast.next!=null
&& fast.next.next!=null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//==================================
ListNode head1 = head;
ListNode head2 = slow.next;
slow.next=null;
head2 = reverse(head2);
while(head1!=null && head2!=null){
if(head1.val!=head2.val){
return false;
}
head1 = head1.next;
head2 = head2.next;
}
return true;
}
//反转链表
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head){
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur =head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre=cur;
cur=next;
}
return pre;
}
@Test
public void test(){
//int[] nums={1,2};
int[] nums={1,2,2,1};
ListNode head = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums);
System.out.println(isPalindrome(head));
}//思路:
//引入虚拟头结点
//pre 始终指向要交换的两个节点的前面一个节点 --> 方便两两遍历节点
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode pre =dummyHead;
while(pre.next!=null && pre.next.next!=null){
ListNode p = pre.next;
ListNode q = pre.next.next;
//交换 p、q 两个节点
ListNode next = q.next;
p.next = next;
q.next = p;
pre.next = q; // p、q 交换节点后,必须要保证链表是连接的
pre=p;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
@Test
public void test(){
int[] nums={1,2,3,4};
ListNode head = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
head = swapPairs(head);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
}//思路:
//先将该链表拆成两个部分:
// L0→L1→...→L(n/2) ==> head1
// L(n/2+1)→L1→...→L(n) ==> head2
// 实际上就是将 head2 逆序后得到的链表中节点插入到 head1 中。
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return;
}
//将链表切分为两个链表
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(slow!=null && fast.next!=null
&& fast.next.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
ListNode head1 = head;
ListNode head2 = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
head2 = reverse(head2);
//将 head2 中元素插入到 head1 中
ListNode p = head1;
ListNode q = head2;
while(p!=null && q!=null){
ListNode nextP = p.next;
ListNode nextQ = q.next;
p.next = q;
q.next = nextP;
p = nextP;
q = nextQ;
}
head = head1;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head){
ListNode pre=null;
ListNode cur =head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
@Test
public void test(){
//int[] nums={1,2,3,4};
int[] nums={1,2,3,4,5};
ListNode head = LinkedListUtils.createLinkedList(nums);
LinkedListUtils.printList(head);
reorderList(head);
}弗洛伊德(Floyd )使用了两个指针,一个慢指针(龟)每次前进一步,快指针(兔)指针每次前进两步(两步或多步效果是等价的,只要一个比另一个快就行。但是如果移动步数增加,算法的复杂度可能增加)。如果两者在链表头以外(不包含开始情况)的某一点相遇(即相等)了,那么说明链表有环,否则,如果(快指针)到达了链表的结尾(如果存在结尾,肯定无环),那么说明没环。
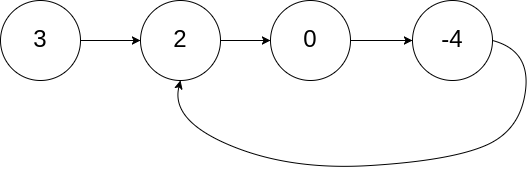
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
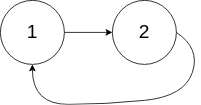
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
进阶:
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
//思路:Floyd 环检测算法
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){ // 空链表是无环的
return false;
}
if(head.next == null){
return false; // 链表只有一个节点,也是无环的
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(slow !=null && fast!=null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if(fast !=null){
fast = fast.next;
}
if(slow == fast){ //相遇,说明有环
return true;
}
}
return false;
}给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
**说明:**不允许修改给定的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:tail connects to node index 1
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:tail connects to node index 0
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:no cycle
解释:链表中没有环。
进阶: 你是否可以不用额外空间解决此题?
//思路:Floyd 环检测算法,尤其要注意后面 TODO: 部分
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
//空链表,或者只有一个节点的链表,返回 null
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(slow != null && fast != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if(fast != null){
fast = fast.next;
}
if(fast == slow){
break;
}
}
slow = head;
//TODO:判断是否有进行后面操作的必要,后面会涉及到 fast 、fast.next
if(fast == null || fast.next == null){
return null;
}
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}