Secure Azure Virtual WAN traffic with Palo Alto Networks VM-Series firewalls. Please see the Deployment Guide for more information.
This build illustrates how to secure Azure Virtual WAN traffic with VM-Series scale sets. The build is broken down into 5 Parts. Depending on existing Azure resources, certain parts may not be required.
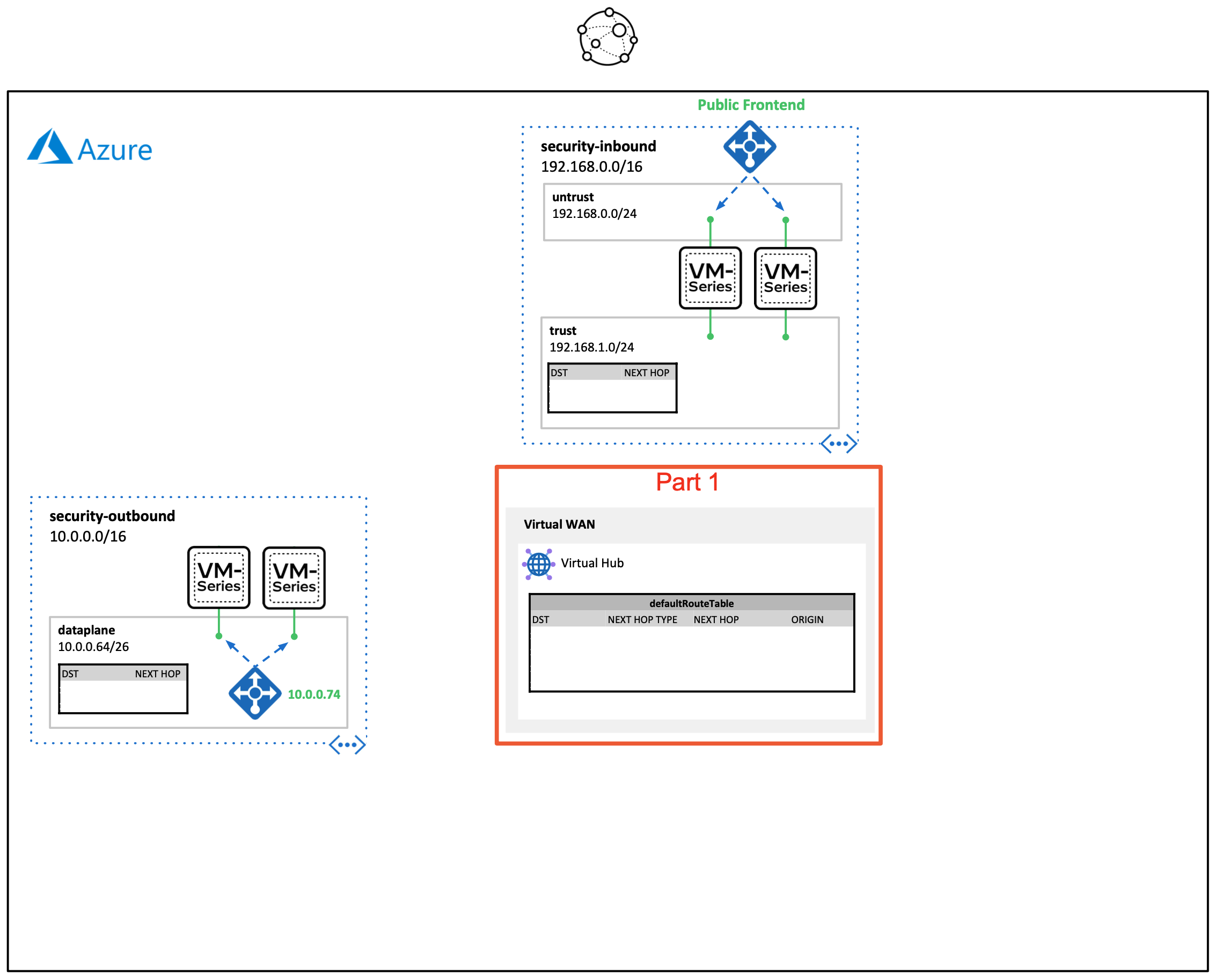
- Part 1. Create Virtual WAN & Virtual Hub
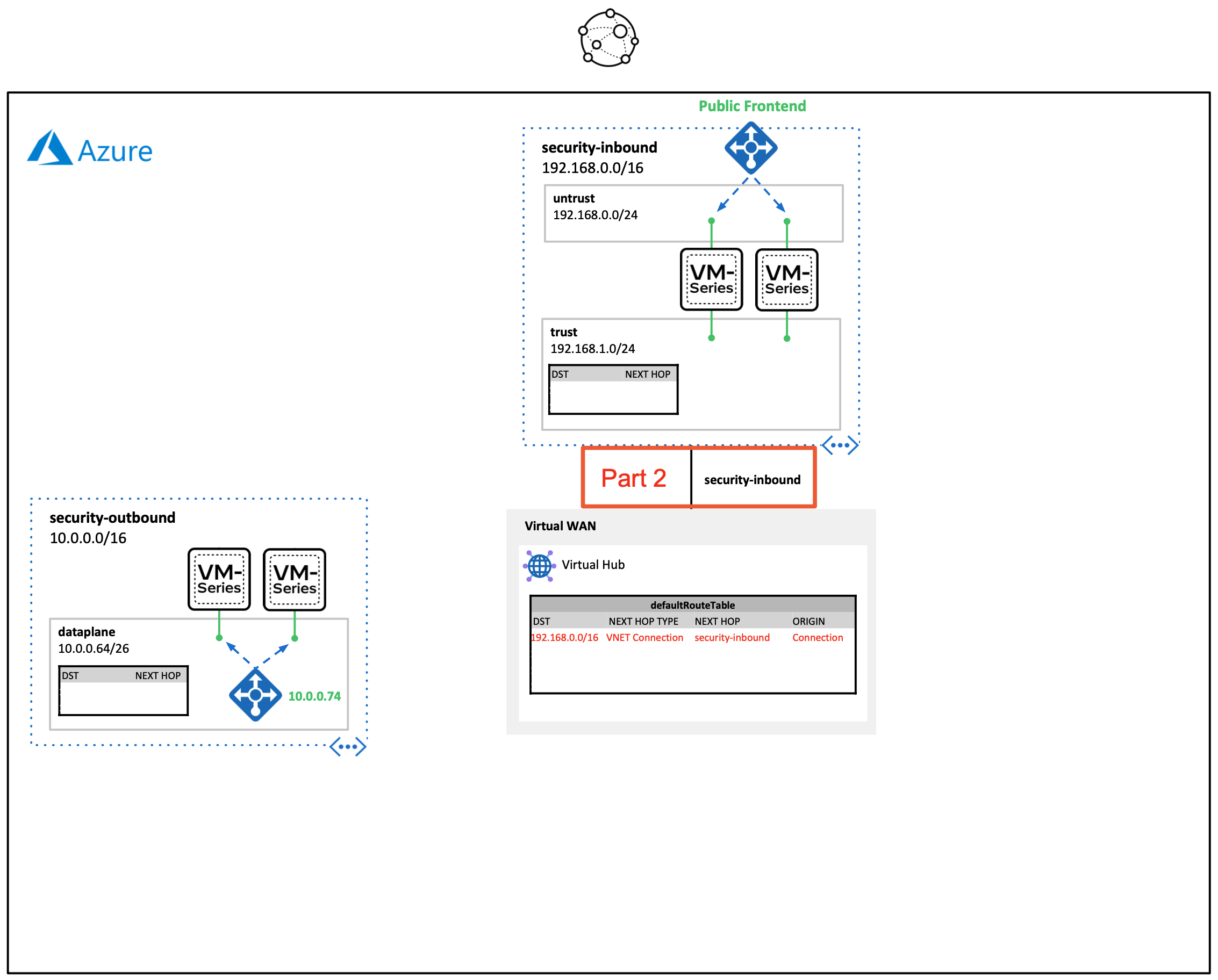
- Part 2. Connect VM-Series Inbound Scale Set to the Virtual Hub
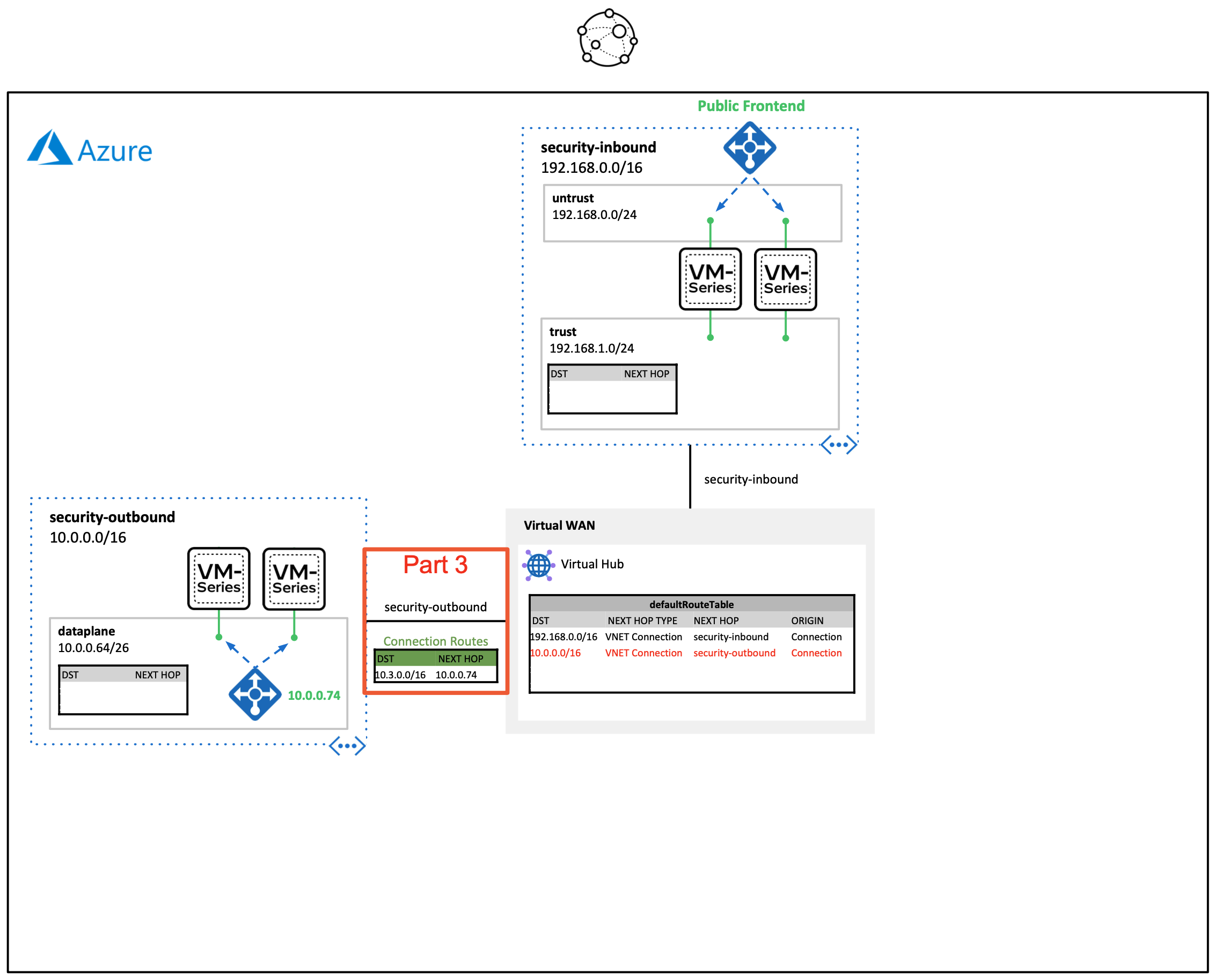
- Part 3. Connect VM-Series Outbound Scale Set to the Virtual Hub
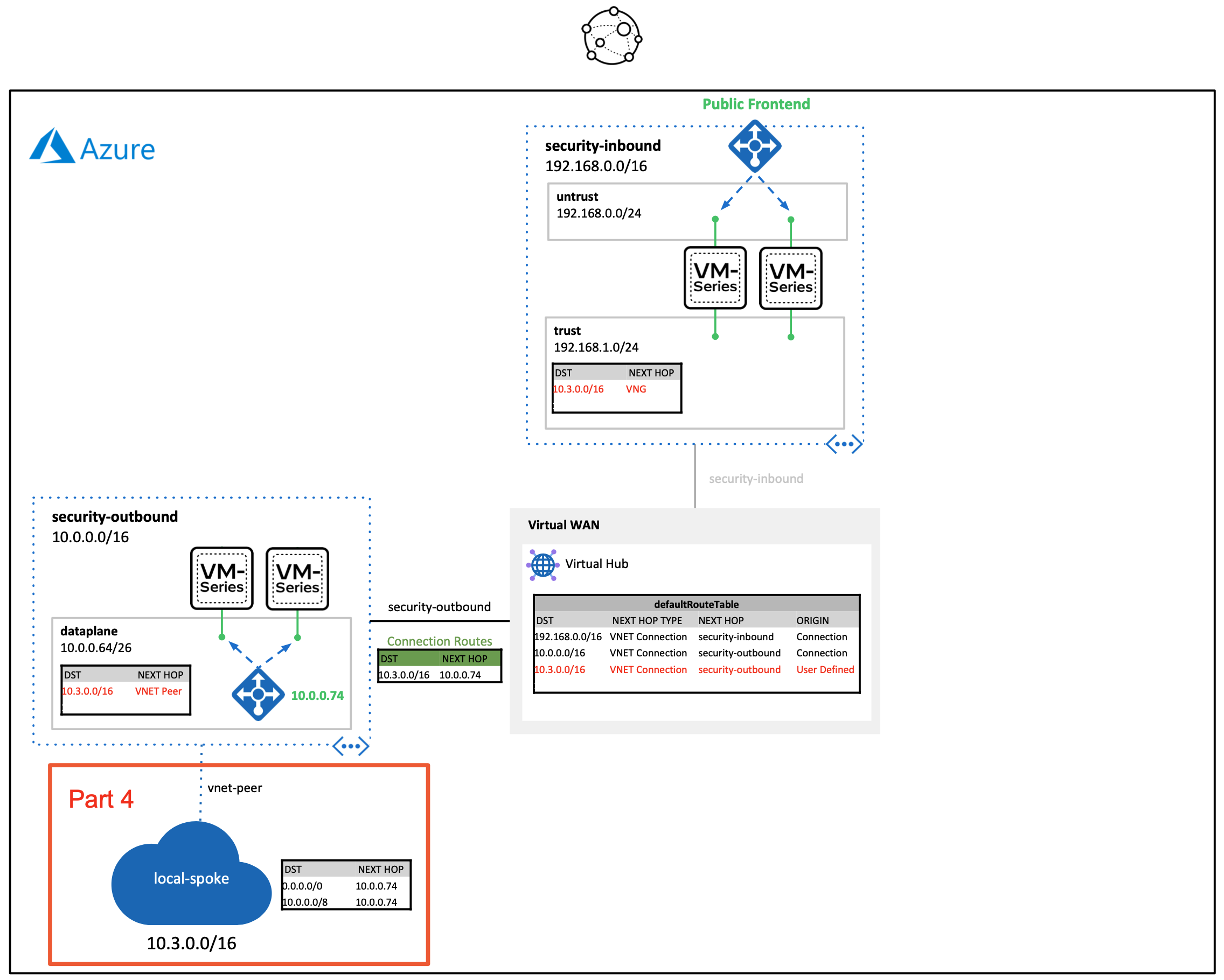
- Part 4. Peer Local VNET to VM-Series Outbound VNET
- Part 5. Connect Spoke VNET to Virtual Hub
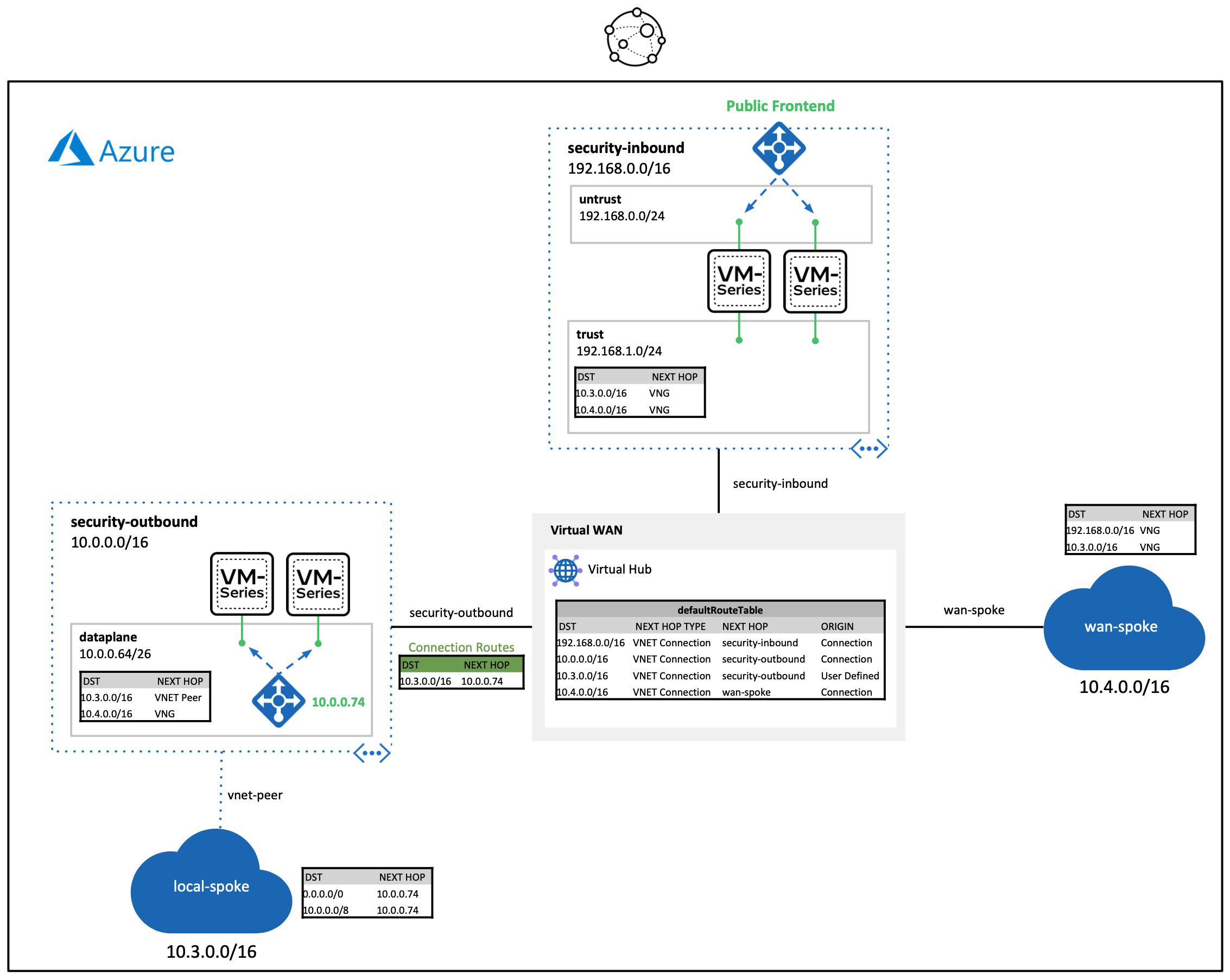
The build shows two types of traffic flows through a Virtual WAN hub.
- Internet inbound traffic through a VM-Series scale set to directly connected hub virtual network (vwan-spoke)
- Additional scale sets can be added throughout different Azure regions to achieve a globally scalable inbound security edge.
- East-West traffic through a VM-Series scale set from a vwan-spoke to a locally peered virtual network
- This design can be integrated into larger infrastructures that have regional hub and spoke architectures. The VM-Series in each regional hub VNET, can secure ingress traffic coming from virtual WAN hubs.
- This can design can also be applied for traffic between ExpressRoute and VNET connections.
The following items are required prior to launching the build.
- A active Azure subscription with appropriate permissions and resource allocation quota.
- Panorama
- PAN-OS 10.0 or greater
- Azure Plugin 3.0 or greater
- Inbound & Outbound VM-Series scale set within a dedicated VNETs.
If you do not have the VM-Series deployed, please see Deployment Guide for how-to.
In this part, a Virtual WAN is created with a virtual hub. The hub will be used in Parts 2 and 3 to direct traffic from connected spokes to the security VNETs. If you already have a virtual hub, you can skip this step and proceed to part 2.

Connects an existing security VNET that contains a VM-Series inbound scale set to the virtual hub created in part 1.

Connects an existing security VNET that contains a VM-Series outbound scale set to the virtual hub created in part 1.

Creates a spoke VNET that is peered (via vNet Peering) to the outbound VM-Series VNET. A route table is created to direct all traffic from the spoke VNET to the outbound firewall's interal load balancer. A route is also added to the virtual hub's route table. This route will direct virtual WAN traffic destined to the spoke VNET through the outbound VM-Series VNET connection that was created in part 3.

Creates a spoke VNET that is directly connected to the virtual hub created in part 1. This VNET is used to demonstrate/test internet inbound traffic through the inbound VM-Series and also lateral traffic through the outbound VM-Series its local spoke.