A Python utility for managing package versions with an interactive CLI interface. This tool helps you monitor, update, and backup your Python packages, whether they're project-specific or globally installed.
Want to get started quickly? Here's what you need to know:
- Install the tool:
pip install python-pvm- Run it:
python-pvm- Common Tasks:
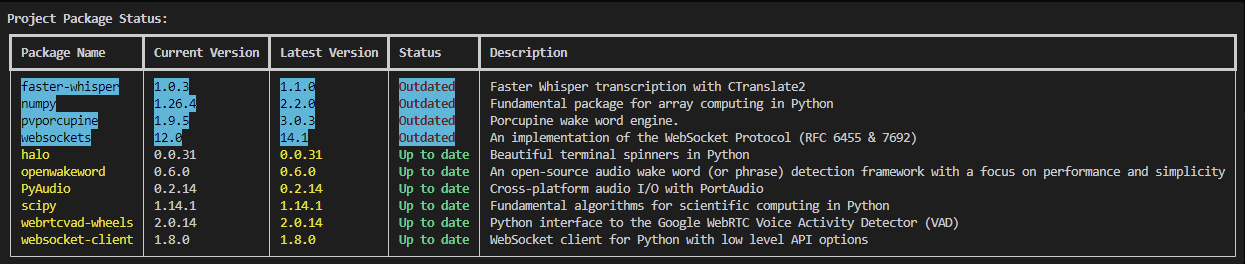
- Check for Updates: Look for packages highlighted in cyan - these need updates
- Update Packages: Choose "Update all packages" (don't worry, it creates automatic backups)
- Restore if Needed: Use "Restore from backup" if something goes wrong
That's it! Keep reading for more detailed information.
- 📊 Interactive CLI with rich terminal formatting
- 🔍 Check both project-specific and global package versions
- 🔄 Detect and update outdated packages
- 💾 Backup and restore package versions
- 📈 Progress tracking with visual indicators
- 🎨 Color-coded status display
- ⚡ Parallel processing for package information retrieval
- Python 3.12 or higher
- Required packages (automatically installed):
- rich
- inquirer
- packaging
pip install python-pvmgit clone https://github.com/workingwheel/python-package-version-manager.git
cd python-package-version-manager
pip install -e .Run the tool using:
python-pvmThe interactive menu will guide you through the following options:
-
Choose scope:
- Project Libraries (checks packages in requirements.txt)
- Global Libraries (checks all installed packages)
-
Available actions:
- Update all packages
- Create backup only
- Restore from backup
- Exit
Package Status Display
- Shows package name, current version, latest version, and description
- Color-coded status indicators:
- Green: Up to date
- Red: Outdated
- Cyan highlight: Outdated packages
- Sorted display with outdated packages shown first
Backup System
- Automatic backup creation before updates
- Manual backup creation option
- Restore from previous backups
- Backups stored in
package_backupsdirectory with timestamps
Progress Tracking
- Visual progress bars for updates and restores
- Time elapsed tracking
- Spinner animations for ongoing processes
Main Functions
main() The entry point of the application. Handles the interactive menu and orchestrates the overall flow of the program.
check_project_packages(console, requirements_file) Analyzes packages listed in a requirements file.
- Parameters:
console: Rich console instance for outputrequirements_file: Path to requirements.txt
check_global_packages(console) Analyzes globally installed packages.
- Parameters:
console: Rich console instance for output
Utility Functions
get_package_descriptions_parallel(packages, max_workers=10) Fetches package descriptions concurrently for better performance.
- Parameters:
packages: List of package dictionariesmax_workers: Maximum number of concurrent workers (default: 10)
update_packages(outdated_packages, console, global_packages=True) Updates outdated packages with progress tracking.
- Parameters:
outdated_packages: List of packages to updateconsole: Rich console instanceglobal_packages: Boolean for global/local scope
create_backup(packages) Creates a timestamped backup of current package versions.
- Parameters:
packages: List of package information to backup
restore_packages(backup_file, console) Restores packages from a backup file.
- Parameters:
backup_file: Path to backup JSON fileconsole: Rich console instance
The script includes comprehensive error handling for:
- File operations
- Package management operations
- User interruptions
- JSON parsing
- Network-related issues
- Always create a backup before updating packages
- Review the status table before proceeding with updates
- Keep track of backup files for version control
- Use project-specific checking for isolated environments
- PyPI Package: python-pvm
- GitHub Repository: python-package-version-manager
Feel free to submit issues and enhancement requests!
This project is open source and available under the MIT License.