You are given an undirected graph. You are given an integer n which is the number of nodes in the graph and an array edges, where each edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between ui and vi.
A connected trio is a set of three nodes where there is an edge between every pair of them.
The degree of a connected trio is the number of edges where one endpoint is in the trio, and the other is not.
Return the minimum degree of a connected trio in the graph, or -1 if the graph has no connected trios.
Example 1:
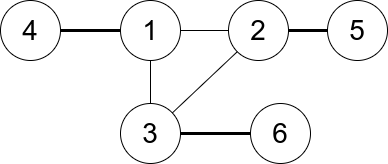
Input: n = 6, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[3,2],[4,1],[5,2],[3,6]] Output: 3 Explanation: There is exactly one trio, which is [1,2,3]. The edges that form its degree are bolded in the figure above.
Example 2:
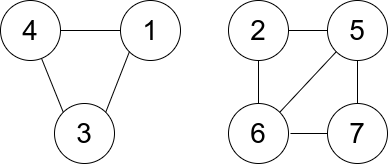
Input: n = 7, edges = [[1,3],[4,1],[4,3],[2,5],[5,6],[6,7],[7,5],[2,6]] Output: 0 Explanation: There are exactly three trios: 1) [1,4,3] with degree 0. 2) [2,5,6] with degree 2. 3) [5,6,7] with degree 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 400edges[i].length == 21 <= edges.length <= n * (n-1) / 21 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi- There are no repeated edges.
class Solution:
def minTrioDegree(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
g = [[False] * n for _ in range(n)]
deg = [0] * n
for u, v in edges:
u, v = u - 1, v - 1
g[u][v] = g[v][u] = True
deg[u] += 1
deg[v] += 1
ans = inf
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
if g[i][j]:
for k in range(j + 1, n):
if g[i][k] and g[j][k]:
ans = min(ans, deg[i] + deg[j] + deg[k] - 6)
return -1 if ans == inf else ansclass Solution {
public int minTrioDegree(int n, int[][] edges) {
boolean[][] g = new boolean[n][n];
int[] deg = new int[n];
for (var e : edges) {
int u = e[0] - 1, v = e[1] - 1;
g[u][v] = true;
g[v][u] = true;
++deg[u];
++deg[v];
}
int ans = 1 << 30;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (g[i][j]) {
for (int k = j + 1; k < n; ++k) {
if (g[i][k] && g[j][k]) {
ans = Math.min(ans, deg[i] + deg[j] + deg[k] - 6);
}
}
}
}
}
return ans == 1 << 30 ? -1 : ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int minTrioDegree(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
bool g[n][n];
memset(g, 0, sizeof g);
int deg[n];
memset(deg, 0, sizeof deg);
for (auto& e : edges) {
int u = e[0] - 1, v = e[1] - 1;
g[u][v] = g[v][u] = true;
deg[u]++, deg[v]++;
}
int ans = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (g[i][j]) {
for (int k = j + 1; k < n; ++k) {
if (g[j][k] && g[i][k]) {
ans = min(ans, deg[i] + deg[j] + deg[k] - 6);
}
}
}
}
}
return ans == INT_MAX ? -1 : ans;
}
};func minTrioDegree(n int, edges [][]int) int {
g := make([][]bool, n)
deg := make([]int, n)
for i := range g {
g[i] = make([]bool, n)
}
for _, e := range edges {
u, v := e[0]-1, e[1]-1
g[u][v], g[v][u] = true, true
deg[u]++
deg[v]++
}
ans := 1 << 30
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
if g[i][j] {
for k := j + 1; k < n; k++ {
if g[i][k] && g[j][k] {
ans = min(ans, deg[i]+deg[j]+deg[k]-6)
}
}
}
}
}
if ans == 1<<30 {
return -1
}
return ans
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}