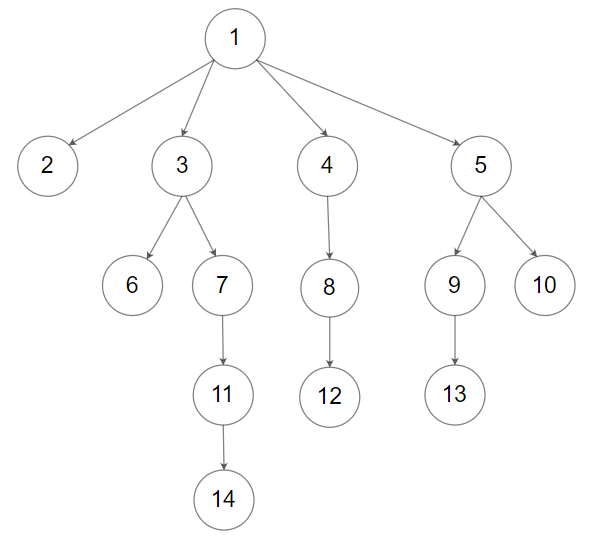
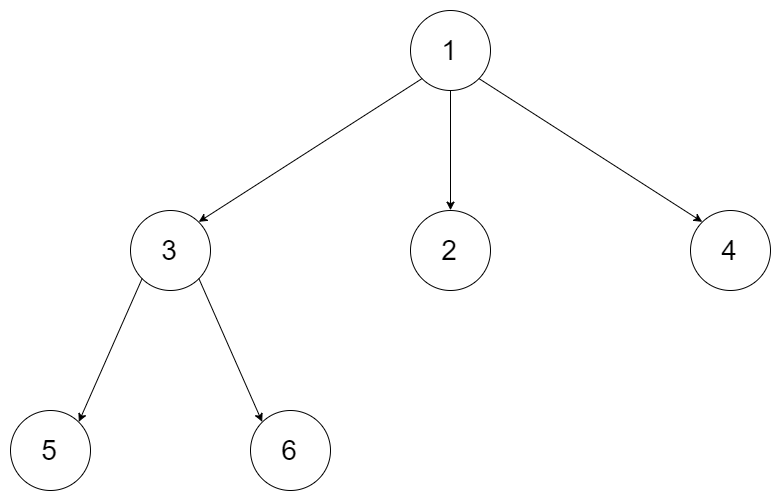
给定一棵 N 叉树 的所有节点在一个数组 Node[] tree 中,树中每个节点都有 唯一的值 。
找到并返回 N 叉树的 根节点 。
自定义测试:
N 叉树的输入序列为其层序遍历序列,每组子节点用 null 分隔(见示例)。
上图中的 N 叉树的序列化描述为 [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] 。
测试将以下列方式进行:
- 输入数据的形式为树的序列化描述。
- 驱动程序代码将根据序列化的输入数据构造树,并以任意顺序将每个
Node对象放入一个数组中。 - 驱动程序代码将把数组传递给
findRoot,你所编写的函数应该在数组中查找并返回根Node对象。 - 驱动程序代码将接受返回的
Node对象并对其进行序列化。如果序列化的结果和输入数据 相同 ,则测试 通过 。
示例 1:
输入:tree = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] 输出:[1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] 解释:来自输入数据的树如上所示。 驱动程序代码创建树,并以任意顺序向 findRoot 提供 Node 对象。 例如,传递的数组可以是 [Node(5),Node(4),Node(3),Node(6),Node(2),Node(1)] 或 [Node(2),Node(6),Node(1),Node(3),Node(5),Node(4)] 。 findRoot 函数应该返回根 Node(1) ,驱动程序代码将序列化它并与输入数据进行比较。 输入数据和序列化的 Node(1) 相同,因此测试通过。
示例 2:
输入:tree = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] 输出:[1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
提示:
- 节点的总个数在
[1, 5*10^4]之间。 - 每个节点都有唯一的值。
进阶:
- 你可以使用 O(1) 额外内存空间且 O(n) 时间复杂度的算法来找到该树的根节点吗?
方法一:位运算
对于一棵 N 叉树的节点,如果该节点是根节点,那么该节点只会出现一次在数组 tree 中;而如果该节点不是根节点,那么该节点会出现两次,一次在数组 tree 中,一次在该节点的父节点的 children 数组中。
因此,我们可以遍历数组 tree,计算每个节点的值以及其所有子节点的值的异或和,记录在变量
接下来,我们再遍历数组 tree,找到值为
时间复杂度 tree 的长度。
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children if children is not None else []
"""
class Solution:
def findRoot(self, tree: List['Node']) -> 'Node':
x = 0
for node in tree:
x ^= node.val
for child in node.children:
x ^= child.val
return next(node for node in tree if node.val == x)/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {
children = new ArrayList<Node>();
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
children = new ArrayList<Node>();
}
public Node(int _val,ArrayList<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node findRoot(List<Node> tree) {
int x = 0;
for (Node node : tree) {
x ^= node.val;
for (Node child : node.children) {
x ^= child.val;
}
}
for (int i = 0;; ++i) {
if (tree.get(i).val == x) {
return tree.get(i);
}
}
}
}/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* findRoot(vector<Node*> tree) {
int x = 0;
for (Node* node : tree) {
x ^= node->val;
for (Node* child : node->children) {
x ^= child->val;
}
}
for (int i = 0;; ++i) {
if (tree[i]->val == x) {
return tree[i];
}
}
}
};/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Children []*Node
* }
*/
func findRoot(tree []*Node) *Node {
x := 0
for _, node := range tree {
x ^= node.Val
for _, child := range node.Children {
x ^= child.Val
}
}
for i := 0; ; i++ {
if tree[i].Val == x {
return tree[i]
}
}
}/**
* Definition for Node.
* class Node {
* val: number
* children: Node[]
* constructor(val?: number, children?: Node[]) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.children = (children===undefined ? [] : children)
* }
* }
*/
function findRoot(tree: Node[]): Node | null {
let x = 0;
for (const node of tree) {
x ^= node.val;
for (const child of node.children) {
x ^= child.val;
}
}
return tree.find(node => node.val === x) || null;
}