给定一棵 N 叉树的根节点 root ,返回该树的深拷贝(克隆)。
N 叉树的每个节点都包含一个值( int )和子节点的列表( List[Node] )。
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
}
N 叉树的输入序列用层序遍历表示,每组子节点用 null 分隔(见示例)。
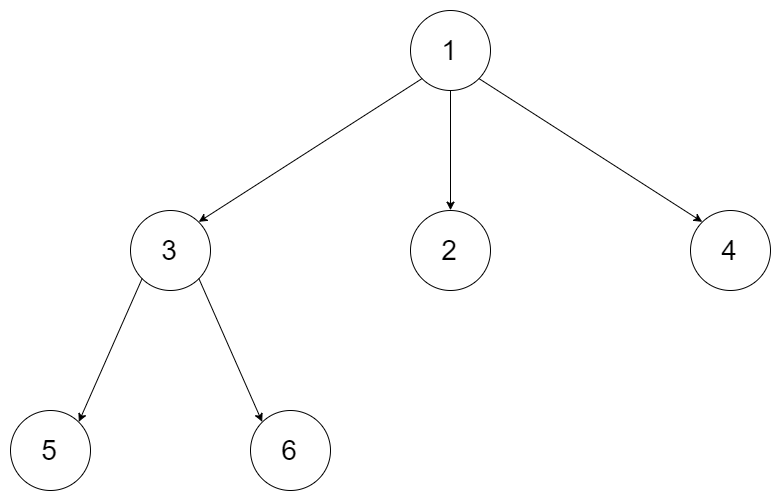
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] 输出:[1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
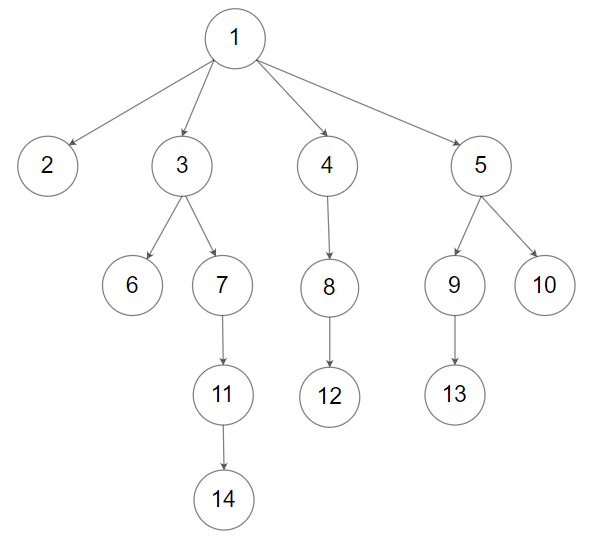
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] 输出:[1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
提示:
- 给定的 N 叉树的深度小于或等于
1000。 - 节点的总个数在
[0, 10^4]之间
进阶:你的解决方案可以适用于克隆图问题吗?
方法一:递归
我们可以用递归的方法来实现 N 叉树的深拷贝。
对于当前节点,如果为空,则返回空;否则,创建一个新节点,其值为当前节点的值,然后对当前节点的每个子节点递归调用该函数,将返回值作为新节点的子节点。最后返回新节点即可。
时间复杂度
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children if children is not None else []
"""
class Solution:
def cloneTree(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if root is None:
return None
children = [self.cloneTree(child) for child in root.children]
return Node(root.val, children)/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {
children = new ArrayList<Node>();
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
children = new ArrayList<Node>();
}
public Node(int _val,ArrayList<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node cloneTree(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
ArrayList<Node> children = new ArrayList<>();
for (Node child : root.children) {
children.add(cloneTree(child));
}
return new Node(root.val, children);
}
}/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneTree(Node* root) {
if (!root) {
return root;
}
vector<Node*> children;
for (Node* child : root->children) {
children.emplace_back(cloneTree(child));
}
return new Node(root->val, children);
}
};/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Children []*Node
* }
*/
func cloneTree(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
children := []*Node{}
for _, child := range root.Children {
children = append(children, cloneTree(child))
}
return &Node{root.Val, children}
}