Given a binary tree where node values are digits from 1 to 9. A path in the binary tree is said to be pseudo-palindromic if at least one permutation of the node values in the path is a palindrome.
Return the number of pseudo-palindromic paths going from the root node to leaf nodes.
Example 1:
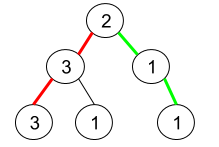
Input: root = [2,3,1,3,1,null,1] Output: 2 Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the red path [2,3,3], the green path [2,1,1], and the path [2,3,1]. Among these paths only red path and green path are pseudo-palindromic paths since the red path [2,3,3] can be rearranged in [3,2,3] (palindrome) and the green path [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 2:
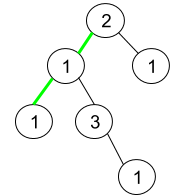
Input: root = [2,1,1,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,1] Output: 1 Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the green path [2,1,1], the path [2,1,3,1], and the path [2,1]. Among these paths only the green path is pseudo-palindromic since [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 3:
Input: root = [9] Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 9
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def pseudoPalindromicPaths(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return
nonlocal ans, counter
counter[root.val] += 1
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
if sum(1 for i in range(1, 10) if counter[i] % 2 == 1) < 2:
ans += 1
else:
dfs(root.left)
dfs(root.right)
counter[root.val] -= 1
ans = 0
counter = [0] * 10
dfs(root)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int ans;
private int[] counter;
public int pseudoPalindromicPaths(TreeNode root) {
ans = 0;
counter = new int[10];
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
++counter[root.val];
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (check(counter)) {
++ans;
}
} else {
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
--counter[root.val];
}
private boolean check(int[] counter) {
int n = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 10; ++i) {
if (counter[i] % 2 == 1) {
++n;
}
}
return n < 2;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int ans;
vector<int> counter;
int pseudoPalindromicPaths(TreeNode* root) {
ans = 0;
counter.resize(10);
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
++counter[root->val];
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
int n = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 10; ++i)
if (counter[i] % 2 == 1)
++n;
if (n < 2) ++ans;
} else {
dfs(root->left);
dfs(root->right);
}
--counter[root->val];
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func pseudoPalindromicPaths(root *TreeNode) int {
ans := 0
counter := make([]int, 10)
var dfs func(root *TreeNode)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
counter[root.Val]++
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
n := 0
for i := 1; i < 10; i++ {
if counter[i]%2 == 1 {
n++
}
}
if n < 2 {
ans++
}
} else {
dfs(root.Left)
dfs(root.Right)
}
counter[root.Val]--
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}