给你一棵有 n 个节点的无向树,节点编号为 0 到 n-1 ,它们中有一些节点有苹果。通过树上的一条边,需要花费 1 秒钟。你从 节点 0 出发,请你返回最少需要多少秒,可以收集到所有苹果,并回到节点 0 。
无向树的边由 edges 给出,其中 edges[i] = [fromi, toi] ,表示有一条边连接 from 和 toi 。除此以外,还有一个布尔数组 hasApple ,其中 hasApple[i] = true 代表节点 i 有一个苹果,否则,节点 i 没有苹果。
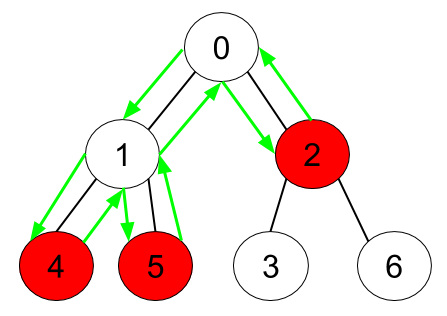
示例 1:
输入:n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], hasApple = [false,false,true,false,true,true,false] 输出:8 解释:上图展示了给定的树,其中红色节点表示有苹果。一个能收集到所有苹果的最优方案由绿色箭头表示。
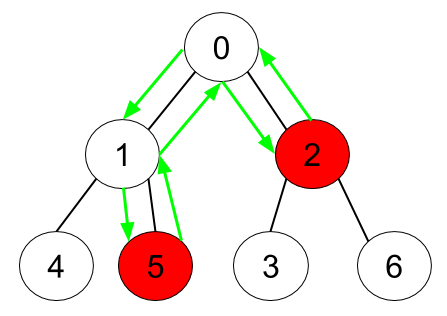
示例 2:
输入:n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], hasApple = [false,false,true,false,false,true,false] 输出:6 解释:上图展示了给定的树,其中红色节点表示有苹果。一个能收集到所有苹果的最优方案由绿色箭头表示。
示例 3:
输入:n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], hasApple = [false,false,false,false,false,false,false] 输出:0
提示:
1 <= n <= 10^5edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai < bi <= n - 1hasApple.length == n
方法一:DFS
class Solution:
def minTime(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], hasApple: List[bool]) -> int:
def dfs(u, cost):
if vis[u]:
return 0
vis[u] = True
nxt_cost = 0
for v in g[u]:
nxt_cost += dfs(v, 2)
if not hasApple[u] and nxt_cost == 0:
return 0
return cost + nxt_cost
g = defaultdict(list)
for u, v in edges:
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
vis = [False] * n
return dfs(0, 0)class Solution {
public int minTime(int n, int[][] edges, List<Boolean> hasApple) {
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
List<Integer>[] g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
g[u].add(v);
g[v].add(u);
}
return dfs(0, 0, g, hasApple, vis);
}
private int dfs(int u, int cost, List<Integer>[] g, List<Boolean> hasApple, boolean[] vis) {
if (vis[u]) {
return 0;
}
vis[u] = true;
int nxtCost = 0;
for (int v : g[u]) {
nxtCost += dfs(v, 2, g, hasApple, vis);
}
if (!hasApple.get(u) && nxtCost == 0) {
return 0;
}
return cost + nxtCost;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int minTime(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<bool>& hasApple) {
vector<bool> vis(n);
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (auto& e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
return dfs(0, 0, g, hasApple, vis);
}
int dfs(int u, int cost, vector<vector<int>>& g, vector<bool>& hasApple, vector<bool>& vis) {
if (vis[u]) return 0;
vis[u] = true;
int nxt = 0;
for (int& v : g[u]) nxt += dfs(v, 2, g, hasApple, vis);
if (!hasApple[u] && !nxt) return 0;
return cost + nxt;
}
};func minTime(n int, edges [][]int, hasApple []bool) int {
vis := make([]bool, n)
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
u, v := e[0], e[1]
g[u] = append(g[u], v)
g[v] = append(g[v], u)
}
var dfs func(int, int) int
dfs = func(u, cost int) int {
if vis[u] {
return 0
}
vis[u] = true
nxt := 0
for _, v := range g[u] {
nxt += dfs(v, 2)
}
if !hasApple[u] && nxt == 0 {
return 0
}
return cost + nxt
}
return dfs(0, 0)
}