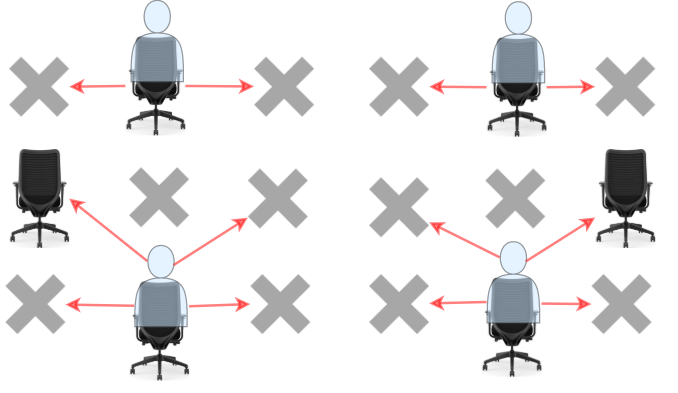
给你一个 m * n 的矩阵 seats 表示教室中的座位分布。如果座位是坏的(不可用),就用 '#' 表示;否则,用 '.' 表示。
学生可以看到左侧、右侧、左上、右上这四个方向上紧邻他的学生的答卷,但是看不到直接坐在他前面或者后面的学生的答卷。请你计算并返回该考场可以容纳的一起参加考试且无法作弊的最大学生人数。
学生必须坐在状况良好的座位上。
示例 1:
输入:seats = [["#",".","#","#",".","#"], [".","#","#","#","#","."], ["#",".","#","#",".","#"]] 输出:4 解释:教师可以让 4 个学生坐在可用的座位上,这样他们就无法在考试中作弊。
示例 2:
输入:seats = [[".","#"], ["#","#"], ["#","."], ["#","#"], [".","#"]] 输出:3 解释:让所有学生坐在可用的座位上。
示例 3:
输入:seats = [["#",".",".",".","#"], [".","#",".","#","."], [".",".","#",".","."], [".","#",".","#","."], ["#",".",".",".","#"]] 输出:10 解释:让学生坐在第 1、3 和 5 列的可用座位上。
提示:
seats只包含字符'.' 和'#'m == seats.lengthn == seats[i].length1 <= m <= 81 <= n <= 8
方法一:状态压缩 + 记忆化搜索
我们注意到,每个座位有两种状态:可选和不可选。因此,我们可以使用二进制数来表示每一行的座位状态,其中
接下来,我们设计一个函数
我们可以枚举第
- 状态
$mask$ 不能选择$seat$ 之外的座位; - 状态
$mask$ 不能选择相邻的座位。
如果满足条件,我们求出当前行选择的座位个数
最后,我们将
为了避免重复计算,我们可以使用记忆化搜索,将函数
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def maxStudents(self, seats: List[List[str]]) -> int:
def f(seat: List[str]) -> int:
mask = 0
for i, c in enumerate(seat):
if c == '.':
mask |= 1 << i
return mask
@cache
def dfs(seat: int, i: int) -> int:
ans = 0
for mask in range(1 << n):
if (seat | mask) != seat or (mask & (mask << 1)):
continue
cnt = mask.bit_count()
if i == len(ss) - 1:
ans = max(ans, cnt)
else:
nxt = ss[i + 1]
nxt &= ~(mask << 1)
nxt &= ~(mask >> 1)
ans = max(ans, cnt + dfs(nxt, i + 1))
return ans
n = len(seats[0])
ss = [f(s) for s in seats]
return dfs(ss[0], 0)class Solution {
private Integer[][] f;
private int n;
private int[] ss;
public int maxStudents(char[][] seats) {
int m = seats.length;
n = seats[0].length;
ss = new int[m];
f = new Integer[1 << n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (seats[i][j] == '.') {
ss[i] |= 1 << j;
}
}
}
return dfs(ss[0], 0);
}
private int dfs(int seat, int i) {
if (f[seat][i] != null) {
return f[seat][i];
}
int ans = 0;
for (int mask = 0; mask < 1 << n; ++mask) {
if ((seat | mask) != seat || (mask & (mask << 1)) != 0) {
continue;
}
int cnt = Integer.bitCount(mask);
if (i == ss.length - 1) {
ans = Math.max(ans, cnt);
} else {
int nxt = ss[i + 1];
nxt &= ~(mask << 1);
nxt &= ~(mask >> 1);
ans = Math.max(ans, cnt + dfs(nxt, i + 1));
}
}
return f[seat][i] = ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maxStudents(vector<vector<char>>& seats) {
int m = seats.size();
int n = seats[0].size();
vector<int> ss(m);
vector<vector<int>> f(1 << n, vector<int>(m, -1));
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (seats[i][j] == '.') {
ss[i] |= 1 << j;
}
}
}
function<int(int, int)> dfs = [&](int seat, int i) -> int {
if (f[seat][i] != -1) {
return f[seat][i];
}
int ans = 0;
for (int mask = 0; mask < 1 << n; ++mask) {
if ((seat | mask) != seat || (mask & (mask << 1)) != 0) {
continue;
}
int cnt = __builtin_popcount(mask);
if (i == m - 1) {
ans = max(ans, cnt);
} else {
int nxt = ss[i + 1];
nxt &= ~(mask >> 1);
nxt &= ~(mask << 1);
ans = max(ans, cnt + dfs(nxt, i + 1));
}
}
return f[seat][i] = ans;
};
return dfs(ss[0], 0);
}
};func maxStudents(seats [][]byte) int {
m, n := len(seats), len(seats[0])
ss := make([]int, m)
f := make([][]int, 1<<n)
for i, seat := range seats {
for j, c := range seat {
if c == '.' {
ss[i] |= 1 << j
}
}
}
for i := range f {
f[i] = make([]int, m)
for j := range f[i] {
f[i][j] = -1
}
}
var dfs func(int, int) int
dfs = func(seat, i int) int {
if f[seat][i] != -1 {
return f[seat][i]
}
ans := 0
for mask := 0; mask < 1<<n; mask++ {
if (seat|mask) != seat || (mask&(mask<<1)) != 0 {
continue
}
cnt := bits.OnesCount(uint(mask))
if i == m-1 {
ans = max(ans, cnt)
} else {
nxt := ss[i+1] & ^(mask >> 1) & ^(mask << 1)
ans = max(ans, cnt+dfs(nxt, i+1))
}
}
f[seat][i] = ans
return ans
}
return dfs(ss[0], 0)
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}