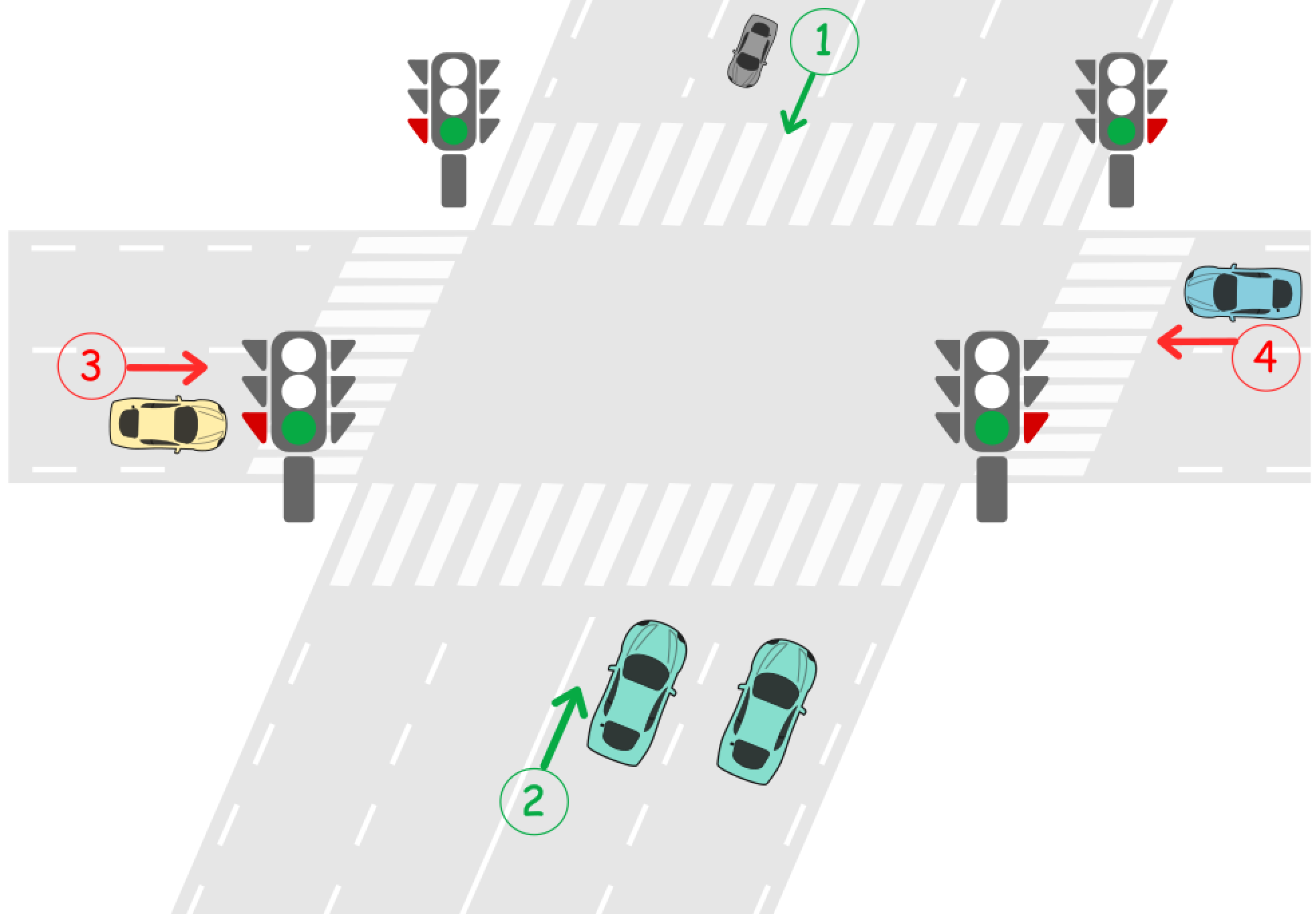
这是两条路的交叉路口。第一条路是 A 路,车辆可沿 1 号方向由北向南行驶,也可沿 2 号方向由南向北行驶。第二条路是 B 路,车辆可沿 3 号方向由西向东行驶,也可沿 4 号方向由东向西行驶。
每条路在路口前都有一个红绿灯。红绿灯可以亮起红灯或绿灯。
- 绿灯表示两个方向的车辆都可通过路口。
- 红灯表示两个方向的车辆都不可以通过路口,必须等待绿灯亮起。
两条路上的红绿灯不可以同时为绿灯。这意味着,当 A 路上的绿灯亮起时,B 路上的红灯会亮起;当 B 路上的绿灯亮起时,A 路上的红灯会亮起.
开始时,A 路上的绿灯亮起,B 路上的红灯亮起。当一条路上的绿灯亮起时,所有车辆都可以从任意两个方向通过路口,直到另一条路上的绿灯亮起。不同路上的车辆不可以同时通过路口。
给这个路口设计一个没有死锁的红绿灯控制系统。
实现函数 void carArrived(carId, roadId, direction, turnGreen, crossCar) :
carId为到达车辆的编号。roadId为车辆所在道路的编号。direction为车辆的行进方向。turnGreen是一个函数,调用此函数会使当前道路上的绿灯亮起。crossCar是一个函数,调用此函数会允许车辆通过路口。
当你的答案避免了车辆在路口出现死锁,此答案会被认定为正确的。当路口已经亮起绿灯时仍打开绿灯,此答案会被认定为错误的。
示例 1:
输入: cars = [1,3,5,2,4], directions = [2,1,2,4,3], arrivalTimes = [10,20,30,40,50] 输出: [ "Car 1 Has Passed Road A In Direction 2", // A 路上的红绿灯为绿色,1 号车可通过路口。 "Car 3 Has Passed Road A In Direction 1", // 红绿灯仍为绿色,3 号车通过路口。 "Car 5 Has Passed Road A In Direction 2", // 红绿灯仍为绿色,5 号车通过路口。 "Traffic Light On Road B Is Green", // 2 号车在 B 路请求绿灯。 "Car 2 Has Passed Road B In Direction 4", // B 路上的绿灯现已亮起,2 号车通过路口。 "Car 4 Has Passed Road B In Direction 3" // 红绿灯仍为绿色,4 号车通过路口。 ]
示例 2:
输入: cars = [1,2,3,4,5], directions = [2,4,3,3,1], arrivalTimes = [10,20,30,40,40] 输出: [ "Car 1 Has Passed Road A In Direction 2", // A 路上的红绿灯为绿色,1 号车可通过路口。 "Traffic Light On Road B Is Green", // 2 号车在 B 路请求绿灯。 "Car 2 Has Passed Road B In Direction 4", // B 路上的绿灯现已亮起,2 号车通过路口。 "Car 3 Has Passed Road B In Direction 3", // B 路上的绿灯现已亮起,3 号车通过路口。 "Traffic Light On Road A Is Green", // 5 号车在 A 路请求绿灯。 "Car 5 Has Passed Road A In Direction 1", // A 路上的绿灯现已亮起,5 号车通过路口。 "Traffic Light On Road B Is Green", // 4 号车在 B 路请求绿灯。4 号车在路口等灯,直到 5 号车通过路口,B 路的绿灯亮起。 "Car 4 Has Passed Road B In Direction 3" // B 路上的绿灯现已亮起,4 号车通过路口。 ] 解释: 这是一个无死锁的方案。注意,在 A 路上的绿灯亮起、5 号车通过前让 4 号车通过,也是一个正确且可被接受的方案。
提示:
1 <= cars.length <= 20cars.length = directions.lengthcars.length = arrivalTimes.lengthcars中的所有值都是唯一的。1 <= directions[i] <= 4arrivalTimes是非递减的。
from threading import Lock
class TrafficLight:
def __init__(self):
self.lock = Lock()
self.road = 1
def carArrived(
self,
carId: int, # ID of the car
# ID of the road the car travels on. Can be 1 (road A) or 2 (road B)
roadId: int,
direction: int, # Direction of the car
# Use turnGreen() to turn light to green on current road
turnGreen: 'Callable[[], None]',
# Use crossCar() to make car cross the intersection
crossCar: 'Callable[[], None]'
) -> None:
self.lock.acquire()
if self.road != roadId:
self.road = roadId
turnGreen()
crossCar()
self.lock.release()class TrafficLight {
private int road = 1;
public TrafficLight() {
}
public synchronized void carArrived(int carId, // ID of the car
int roadId, // ID of the road the car travels on. Can be 1 (road A) or 2 (road B)
int direction, // Direction of the car
Runnable turnGreen, // Use turnGreen.run() to turn light to green on current road
Runnable crossCar // Use crossCar.run() to make car cross the intersection
) {
if (roadId != road) {
turnGreen.run();
road = roadId;
}
crossCar.run();
}
}