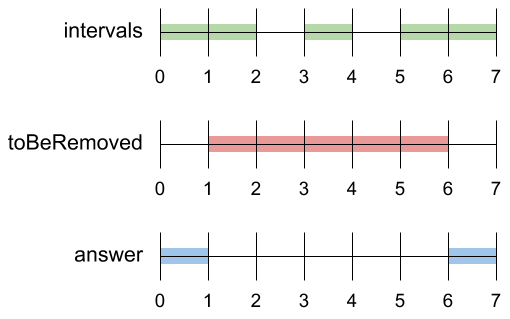
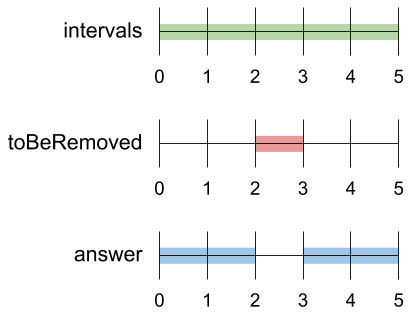
A set of real numbers can be represented as the union of several disjoint intervals, where each interval is in the form [a, b). A real number x is in the set if one of its intervals [a, b) contains x (i.e. a <= x < b).
You are given a sorted list of disjoint intervals intervals representing a set of real numbers as described above, where intervals[i] = [ai, bi] represents the interval [ai, bi). You are also given another interval toBeRemoved.
Return the set of real numbers with the interval toBeRemoved removed from intervals. In other words, return the set of real numbers such that every x in the set is in intervals but not in toBeRemoved. Your answer should be a sorted list of disjoint intervals as described above.
Example 1:
Input: intervals = [[0,2],[3,4],[5,7]], toBeRemoved = [1,6] Output: [[0,1],[6,7]]
Example 2:
Input: intervals = [[0,5]], toBeRemoved = [2,3] Output: [[0,2],[3,5]]
Example 3:
Input: intervals = [[-5,-4],[-3,-2],[1,2],[3,5],[8,9]], toBeRemoved = [-1,4] Output: [[-5,-4],[-3,-2],[4,5],[8,9]]
Constraints:
1 <= intervals.length <= 104-109 <= ai < bi <= 109
class Solution:
def removeInterval(self, intervals: List[List[int]], toBeRemoved: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
x, y = toBeRemoved
ans = []
for a, b in intervals:
if a >= y or b <= x:
ans.append([a, b])
else:
if a < x:
ans.append([a, x])
if b > y:
ans.append([y, b])
return ansclass Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> removeInterval(int[][] intervals, int[] toBeRemoved) {
int x = toBeRemoved[0], y = toBeRemoved[1];
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (var e : intervals) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
if (a >= y || b <= x) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(a, b));
} else {
if (a < x) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(a, x));
}
if (b > y) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(y, b));
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> removeInterval(vector<vector<int>>& intervals, vector<int>& toBeRemoved) {
int x = toBeRemoved[0], y = toBeRemoved[1];
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for (auto& e : intervals) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
if (a >= y || b <= x) {
ans.push_back(e);
} else {
if (a < x) {
ans.push_back({a, x});
}
if (b > y) {
ans.push_back({y, b});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func removeInterval(intervals [][]int, toBeRemoved []int) (ans [][]int) {
x, y := toBeRemoved[0], toBeRemoved[1]
for _, e := range intervals {
a, b := e[0], e[1]
if a >= y || b <= x {
ans = append(ans, e)
} else {
if a < x {
ans = append(ans, []int{a, x})
}
if b > y {
ans = append(ans, []int{y, b})
}
}
}
return
}