The thief has found himself a new place for his thievery again. There is only one entrance to this area, called root.
Besides the root, each house has one and only one parent house. After a tour, the smart thief realized that all houses in this place form a binary tree. It will automatically contact the police if two directly-linked houses were broken into on the same night.
Given the root of the binary tree, return the maximum amount of money the thief can rob without alerting the police.
Example 1:
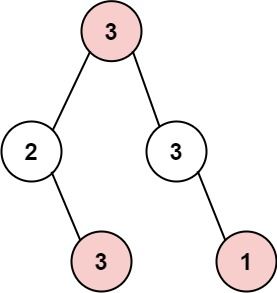
Input: root = [3,2,3,null,3,null,1] Output: 7 Explanation: Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 3 + 3 + 1 = 7.
Example 2:
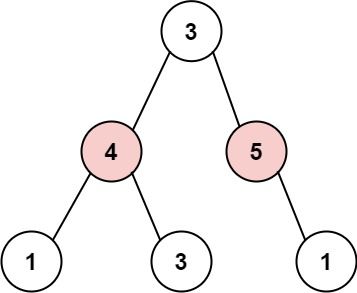
Input: root = [3,4,5,1,3,null,1] Output: 9 Explanation: Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 4 + 5 = 9.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. 0 <= Node.val <= 104
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rob(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
@cache
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return 0
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
return root.val
a = dfs(root.left) + dfs(root.right)
b = root.val
if root.left:
b += dfs(root.left.left) + dfs(root.left.right)
if root.right:
b += dfs(root.right.left) + dfs(root.right.right)
return max(a, b)
return dfs(root)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private Map<TreeNode, Integer> memo;
public int rob(TreeNode root) {
memo = new HashMap<>();
return dfs(root);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (memo.containsKey(root)) {
return memo.get(root);
}
int a = dfs(root.left) + dfs(root.right);
int b = root.val;
if (root.left != null) {
b += dfs(root.left.left) + dfs(root.left.right);
}
if (root.right != null) {
b += dfs(root.right.left) + dfs(root.right.right);
}
int res = Math.max(a, b);
memo.put(root, res);
return res;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> memo;
int rob(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root);
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
if (memo.count(root)) return memo[root];
int a = dfs(root->left) + dfs(root->right);
int b = root->val;
if (root->left) b += dfs(root->left->left) + dfs(root->left->right);
if (root->right) b += dfs(root->right->left) + dfs(root->right->right);
int res = max(a, b);
memo[root] = res;
return res;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func rob(root *TreeNode) int {
memo := make(map[*TreeNode]int)
var dfs func(root *TreeNode) int
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
if _, ok := memo[root]; ok {
return memo[root]
}
a := dfs(root.Left) + dfs(root.Right)
b := root.Val
if root.Left != nil {
b += dfs(root.Left.Left) + dfs(root.Left.Right)
}
if root.Right != nil {
b += dfs(root.Right.Left) + dfs(root.Right.Right)
}
res := max(a, b)
memo[root] = res
return res
}
return dfs(root)
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}