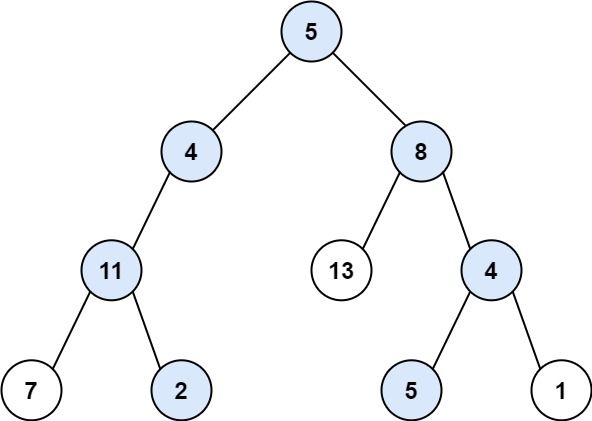
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
方法一:DFS
我们从根节点开始,递归遍历所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径,并记录路径和。当遍历到叶子节点时,如果此时路径和等于 targetSum,则将此路径加入答案。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
def dfs(root, s):
if root is None:
return
s += root.val
t.append(root.val)
if root.left is None and root.right is None and s == targetSum:
ans.append(t[:])
dfs(root.left, s)
dfs(root.right, s)
t.pop()
ans = []
t = []
dfs(root, 0)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root, targetSum);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int s) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
s -= root.val;
t.add(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && s == 0) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(t));
}
dfs(root.left, s);
dfs(root.right, s);
t.remove(t.size() - 1);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> t;
function<void(TreeNode*, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, int s) {
if (!root) return;
s -= root->val;
t.emplace_back(root->val);
if (!root->left && !root->right && s == 0) ans.emplace_back(t);
dfs(root->left, s);
dfs(root->right, s);
t.pop_back();
};
dfs(root, targetSum);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) (ans [][]int) {
t := []int{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, s int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
s -= root.Val
t = append(t, root.Val)
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil && s == 0 {
cp := make([]int, len(t))
copy(cp, t)
ans = append(ans, cp)
}
dfs(root.Left, s)
dfs(root.Right, s)
t = t[:len(t)-1]
}
dfs(root, targetSum)
return
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
fn dfs(
root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
paths: &mut Vec<i32>,
mut target_sum: i32,
res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>,
) {
if let Some(node) = root {
let mut node = node.borrow_mut();
target_sum -= node.val;
paths.push(node.val);
if node.left.is_none() && node.right.is_none() {
if target_sum == 0 {
res.push(paths.clone());
}
} else {
if node.left.is_some() {
Self::dfs(node.left.take(), paths, target_sum, res);
}
if node.right.is_some() {
Self::dfs(node.right.take(), paths, target_sum, res);
}
}
paths.pop();
}
}
pub fn path_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut res = vec![];
let mut paths = vec![];
Self::dfs(root, &mut paths, target_sum, &mut res);
res
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} targetSum
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var pathSum = function (root, targetSum) {
const ans = [];
const t = [];
function dfs(root, s) {
if (!root) return;
s -= root.val;
t.push(root.val);
if (!root.left && !root.right && s == 0) ans.push([...t]);
dfs(root.left, s);
dfs(root.right, s);
t.pop();
}
dfs(root, targetSum);
return ans;
};