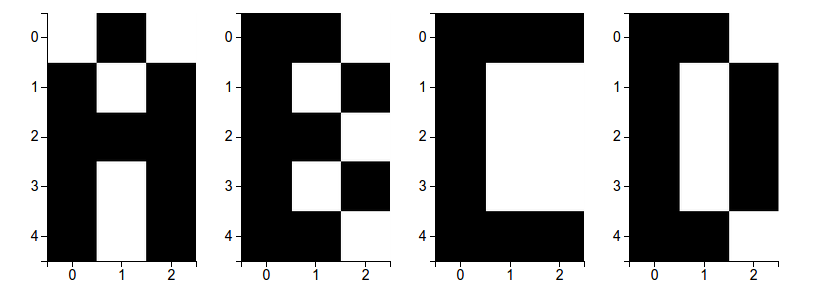Check out some of the latest results at this link .
See the bottom of this document for file descriptions and organization of the project.
from wikipedia: "Spiking neural networks (SNNs) fall into the third generation of neural network models, increasing the level of realism in a neural simulation. In addition to neuronal and synaptic state, SNNs also incorporate the concept of time into their operating model.
In practice, there is a major difference between the theoretical power of spiking neural networks and what has been demonstrated. They have proved useful in neuroscience, but not (yet) in engineering. As a result there has been little application of large scale spiking neural networks to solve computational tasks of the order and complexity that are commonly addressed using rate coded (second generation) neural networks. In addition it can be difficult to adapt second generation neural network models into real time, spiking neural networks (especially if these network algorithms are defined in discrete time). It is relatively easy to construct a spiking neural network model and observe its dynamics. It is much harder to develop a model with stable behavior that computes a specific function. "
We are trying to make the firsts steps to change that, by using a SNN to learn a very simple dataset which is compose by only 4 characters, described by 5 x 3 pixels.
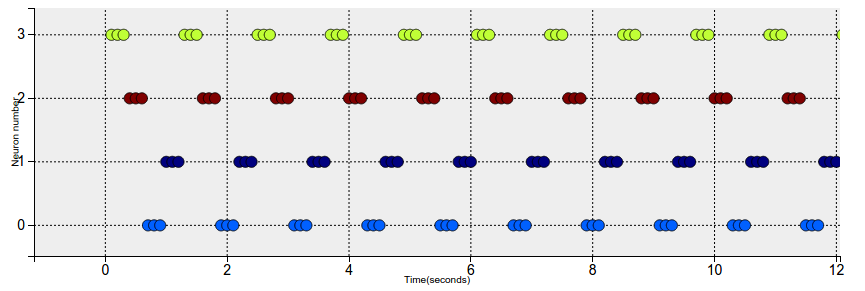
We input the image as a constant current to the first layer, which contains 15 nuerons. The neurons of the first layer recive a constant current, making them fire about 3 times, while each character is shown. The second layer contains 4 neurons, if the trainning is succesfull each neuron will be able to learn to represent one character, spiking 3 times when the character is shown, as the image below.
====== Authors:
- Nate Sutton
- Ignacio Tartavull
This is a work in progress and if you find this project interesting please join us and help out.
====== Getting Started
- The project is based on this paper. We use a clock-driven simulator for spiking neural networks called Brian. Users should have a Python environment with Brian2 installed. Anaconda is suggested and can install Brian2 through:
$ conda install brian2
-
Clone the project and run it in your Python environment. For instance, Sublime Text can be used with a buildfile such as this example. gupta_paper_further_formulas.py is the main file to run to start the main project code.
-
After the software has completed running graphical plots will be created that show the results. Command line output also will report statistics on the simulation. An example of training and then testing the simulation can be run by executing the shell script trainTestSim.sh in the base project directory.
-
Some notebooks have been created to illustrate the design of the experiments. These notebooks include: general overview - introduction.ipynb, simulation code - simulation.ipynb, performance analyses - analysis.ipynb, and others in the /notebooks folder. These notebooks may not be updated with the main project code and should only be be used for explanatory purposes; their code should not be used to run the main project code.
====== File descriptions and organization
/gupta_paper_further_formulas.py main file for project
/FFSSN.ipynb ipython notebook overviewing work
/experimentalComponents code exploring new functionality for possible use in the project
/furtherFormulas modules used in the main file
/img images
/notebooks notebooks to describe the project (not code for use with the main project)
/originalVersion initial version of the work, the new version is in gupta_paper_further_formulas.py
/utilities programs used for processing files to prepare them for use in the project