标签(空格分隔): LeetCode
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/
题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-a-multilevel-doubly-linked-list/description/
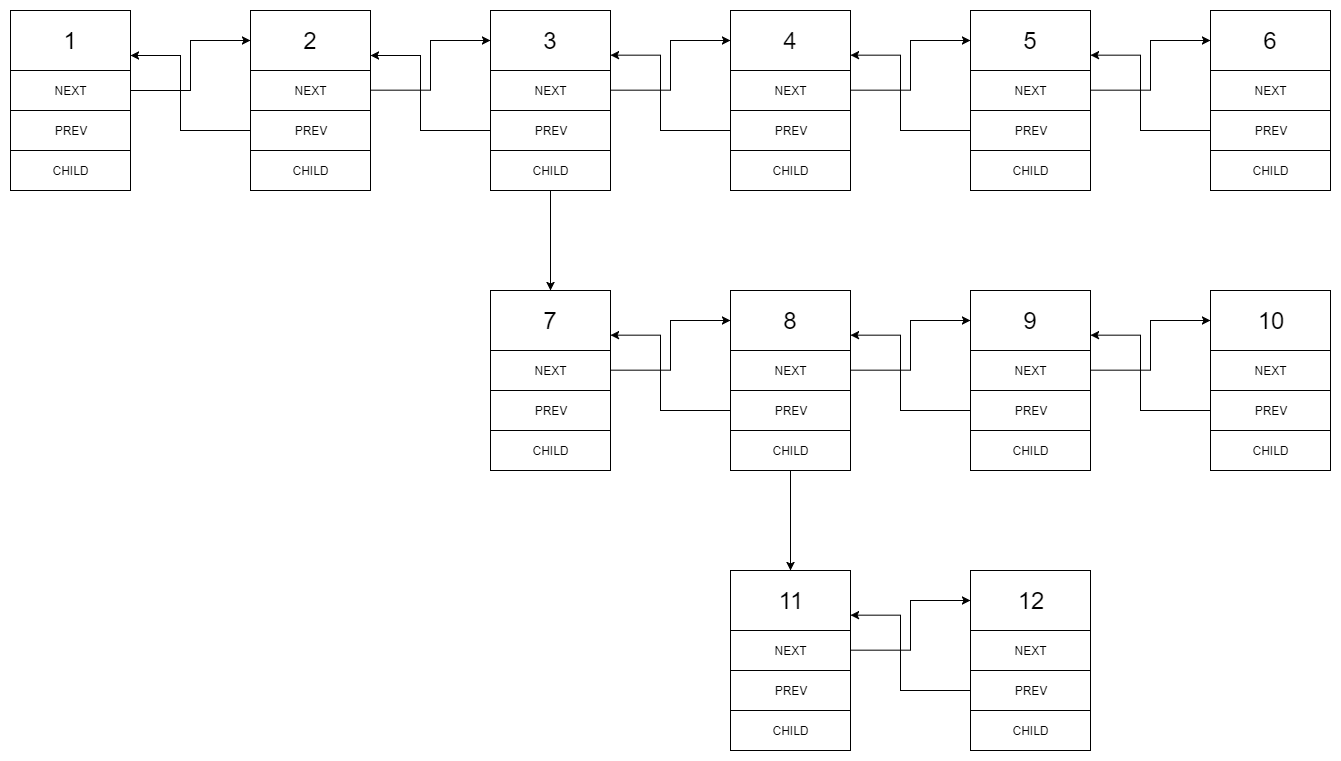
You are given a doubly linked list which in addition to the next and previous pointers, it could have a child pointer, which may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure, as shown in the example below.
Flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list. You are given the head of the first level of the list.
Example:
Input:
1---2---3---4---5---6--NULL
|
7---8---9---10--NULL
|
11--12--NULL
Output:
1-2-3-7-8-11-12-9-10-4-5-6-NULL
Explanation for the above example:
Given the following multilevel doubly linked list:
We should return the following flattened doubly linked list:
给出的是一个带有子节点的双向链表。要求把这个带有子节点的双向链表转化为一个不带子节点的双向链表,其规则是把子节点所有的节点都插入到该节点的后面。
看到把子节点插入到后面,就想到了我们应该使用的是DFS,这种搜索方式会让我们提前使用更深层次的节点,当更深层次的搜索结束之后再往上层返回。
现在的思路就是每次遇到child节点,就把这个节点作为当前node的next节点;并且要遍历child节点后面的所有节点,找到child链表最后面的节点,作为要插入的一整段链表最后的节点,即原node.next节点prev节点。
做法需要新定义一个函数,这个函数对每个child链表进行遍历,把整段的child链表插入到原链表中。
思路总结就是:DFS负责查找,新定义的函数负责插入。
代码如下:
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, prev, next, child):
self.val = val
self.prev = prev
self.next = next
self.child = child
"""
class Solution(object):
def flatten(self, head):
"""
:type head: Node
:rtype: Node
"""
if not head: return None
node = head
while node:
node_next = node.next
if node.child:
flattened = self.flatten(node.child)
node.child = None
nextNode = self.appendToList(node, flattened)
node = nextNode
else:
node = node.next
return head
def appendToList(self, node, listToAppendHead):
next_node = node.next
node.next = listToAppendHead
listToAppendHead.prev = node
while node.next:
node = node.next
node.next = next_node
if next_node:
next_node.prev = node
return next_node2018 年 8 月 23 日 ———— 疲惫说明在逆流而上