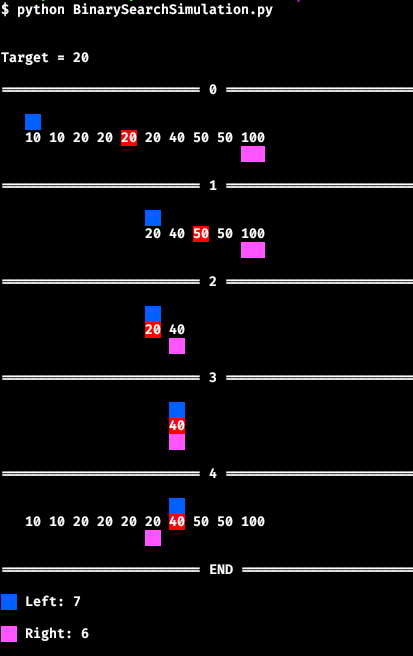
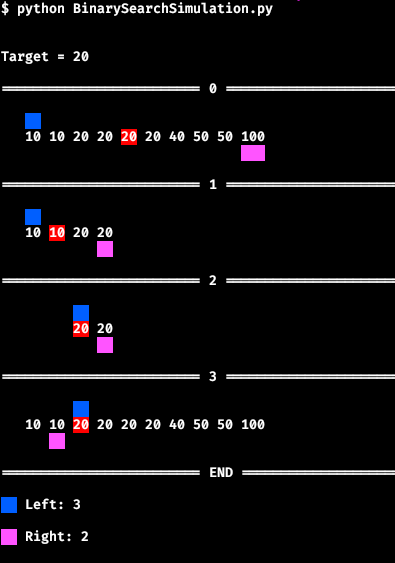
Python program to visualize the behavior of upper_bound and lower_bound binary searches.
pip install binarysearchsimulation
| Upper Bound |
Lower Bound |
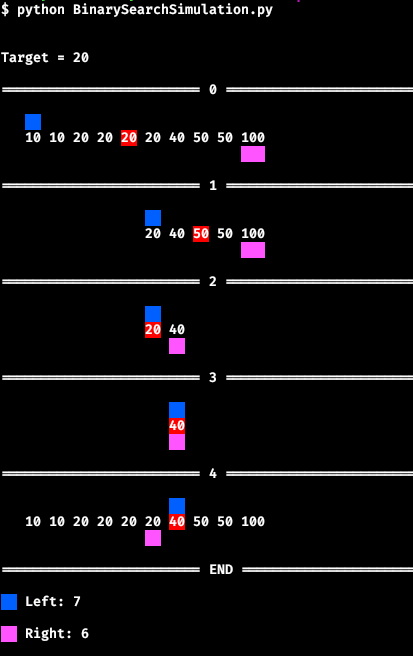
|
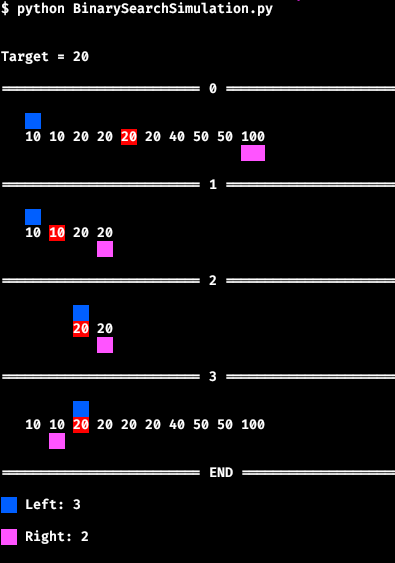
|
| Intuitive Binary Search |
| Upper Bound |
Lower Bound |
int upperBound(vector<int> &array, int target) {
// array should be sorted in non-decreasing
// order from left to right
int l = 0, r = array.size() - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (target < array[mid]) {
r = m - 1;
} else {
l = m + 1;
}
}
return l;
} |
int lowerBound(vector<int> &array, int target) {
// array should be sorted in non-decreasing
// order from left to right
int l = 0, r = array.size() - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (target <= array[mid]) {
r = m - 1;
} else {
l = m + 1;
}
}
return l;
} |
| Binary Search Variation (works optimally for non-integer spaces) |
| Upper Bound |
Lower Bound |
int upperBound(vector<int> &array, int target) {
// array should be sorted in non-decreasing
// order from left to right
int l = -1, r = array.size();
while (l + 1 < r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (target < array[mid]) {
r = m;
} else {
l = m;
}
}
return r;
} |
int lowerBound(vector<int> &array, int target) {
// array should be sorted in non-decreasing
// order from left to right
int l = -1, r = array.size();
while (l + 1 < r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (target <= array[mid]) {
r = m;
} else {
l = m;
}
}
return r;
} |