forked from rncarpio/linterp
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
/
params.json
1 lines (1 loc) · 10.4 KB
/
params.json
1
{"name":"Linterp","tagline":"N-dimensional linear interpolation on a rectangular grid in C++","body":"Project page: http://rncarpio.github.com/linterp\r\n\r\n### What is `linterp`?\r\n`linterp` is a C++ header-only library for N-dimensional linear interpolation on a rectangular grid, similar to Matlab's [interpn](http://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/interpn.html) command. For interpolation on unstructured data, take a look at [delaunay_linterp](http://rncarpio.github.com/delaunay_linterp/). Arbitrary dimensions are supported, but the number of dimensions must be specified as a template parameter at compile time. Two algorithms for computing the interpolated value are available:\r\n* Multilinear: This uses the values at the 2^N vertices of the N-dimensional hypercube containing the point. In two dimensions, this is equivalent to bilinear interpolation; in 3 dimensions, trilinear, etc. Each interpolation step is O(2^N).\r\n* Simplicial: This uses the values at the N+1 vertices of the N-dimensional simplex containing the point. Each hypercube of the rectangular grid is split into simplices; the simplex containing a point `x` is determined by sorting the coordinates of `x`. Each interpolation step is O(N log N). Compared to the multilinear algorithm, this becomes much faster in higher dimensions, at the cost of decreased accuracy (since less neighboring points are used to control the interpolated value). \r\n\r\nThe number type is user-specified as a template parameter. The underlying data may be shared or copied. If a reference-counting scheme is used for the memory containing the underlying data, an optional reference-counting type may be passed as a template parameter.\r\n\r\nRequires the [boost.multi_array](http://www.boost.org/libs/multi_array) library.\r\n\r\nFor a description of the two interpolation algorithms, see:\r\n* Weiser & Zarantonello (1988), \"A Note on Piecewise Linear and Multilinear Table Interpolation in Many Dimensions\", _Mathematics of Computation_ 50 (181), p. 189-196\r\n* Davies (1996), \"Multidimensional Triangulation and Interpolation for Reinforcement Learning\", _Proceedings of Neural Information Processing Systems 1996_\r\n\r\n### C++ interface\r\nHere is an example in C++:\r\n```c++\r\n#include <ctime>\r\n#include \"linterp.h\"\r\n\r\n// return an evenly spaced 1-d grid of doubles.\r\nstd::vector<double> linspace(double first, double last, int len) {\r\n std::vector<double> result(len);\r\n double step = (last-first) / (len - 1);\r\n for (int i=0; i<len; i++) { result[i] = first + i*step; }\r\n return result;\r\n}\r\n\r\n// the function to interpolate.\r\ndouble fn (double x1, double x2) { return sin(x1 + x2); }\r\n\r\nint main (int argc, char **argv) {\r\n const int length = 10;\r\n \r\n // construct the grid in each dimension. \r\n // note that we will pass in a sequence of iterators pointing to the beginning of each grid\r\n std::vector<double> grid1 = linspace(0.0, 3.0, length);\r\n std::vector<double> grid2 = linspace(0.0, 3.0, length);\r\n std::vector< std::vector<double>::iterator > grid_iter_list;\r\n grid_iter_list.push_back(grid1.begin());\r\n grid_iter_list.push_back(grid2.begin());\r\n \r\n // the size of the grid in each dimension\r\n array<int,2> grid_sizes;\r\n grid_sizes[0] = length;\r\n grid_sizes[1] = length;\r\n \r\n // total number of elements\r\n int num_elements = grid_sizes[0] * grid_sizes[1];\r\n \r\n // fill in the values of f(x) at the gridpoints. \r\n // we will pass in a contiguous sequence, values are assumed to be laid out C-style\r\n std::vector<double> f_values(num_elements);\r\n for (int i=0; i<grid_sizes[0]; i++) {\r\n for (int j=0; j<grid_sizes[1]; j++) {\r\n\t f_values[i*grid_sizes[0] + j] = fn(grid1[i], grid2[j]);\r\n\t}\r\n }\r\n \r\n // construct the interpolator. the last two arguments are pointers to the underlying data\r\n InterpMultilinear<2, double> interp_ML(grid_iter_list.begin(), grid_sizes.begin(), f_values.data(), f_values.data() + num_elements);\r\n \r\n // interpolate one value\r\n array<double,2> args = {1.5, 1.5};\r\n printf(\"%f, %f -> %f\\n\", args[0], args[1], interp_ML.interp(args.begin()));\r\n\r\n // interpolate multiple values: create sequences for each coordinate\r\n std::vector<double> interp_grid = linspace(0.0, 3.0, length*10);\r\n int num_interp_elements = interp_grid.size() * interp_grid.size();\r\n std::vector<double> interp_x1(num_interp_elements);\r\n std::vector<double> interp_x2(num_interp_elements);\r\n for (int i=0; i<interp_grid.size(); i++) {\r\n for (int j=0; j<interp_grid.size(); j++) {\r\n\t interp_x1[i*interp_grid.size() + j] = interp_grid[i];\r\n\t interp_x2[i*interp_grid.size() + j] = interp_grid[j];\r\n\t}\r\n }\r\n std::vector<double> result(num_interp_elements);\r\n \r\n // pass in a sequence of iterators, one for each coordinate\r\n std::vector< std::vector<double>::iterator > interp_x_list;\r\n interp_x_list.push_back(interp_x1.begin());\r\n interp_x_list.push_back(interp_x2.begin());\r\n \r\n // interpolate a sequence of values\r\n clock_t t1, t2;\r\n t1 = clock();\t\r\n interp_ML.interp_vec(num_interp_elements, interp_x_list.begin(), interp_x_list.end(), result.begin());\r\n t2 = clock();\r\n printf(\"multilinear: %d interpolations, %d clocks, %f sec\\n\", num_interp_elements, (t2-t1), ((double)(t2 - t1)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);\r\n\r\n // calculate the squared errors\r\n std::vector<double> true_f_vals(num_interp_elements);\r\n double SSE = 0.0;\r\n for (int i=0; i<num_interp_elements; i++) {\r\n true_f_vals[i] = fn(interp_x1[i], interp_x2[i]);\r\n\tdouble diff = true_f_vals[i] - result[i];\r\n\tSSE += diff*diff;\r\n }\r\n printf(\"sum of squared errors: %f\\n\", SSE);\r\n return 0;\r\n}\r\n```\r\nproduces\r\n```\r\n1.500000, 1.500000 -> 0.137236\r\nmultilinear: 10000 interpolations, 1 clocks, 0.001000 sec\r\nsum of squared errors: 1.812171\r\n```\r\n\r\n### Python interface\r\nA Python interface is provided, using Andreas Klöckner's [pyublas] (http://mathema.tician.de/software/pyublas) library. Scipy's [griddata](http://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.interpolate.griddata.html) command provides similar functionality and can interpolate unstructured data, but is slower and can handle fewer points.\r\n\r\nAn example: \r\n```python\r\nimport _linterp_python as _linterp\r\nx = scipy.linspace(-3, 3, 10)\r\nxi = scipy.linspace(-3.5, 3.5, 30)\r\ny = scipy.sin(x)\r\nf = _linterp.Interp_1_ML([x], y)\r\nyi = f.interp_vec([xi])\r\nscatter(x, y)\r\nscatter(xi, yi, marker='x')\r\n```\r\nproduces\r\n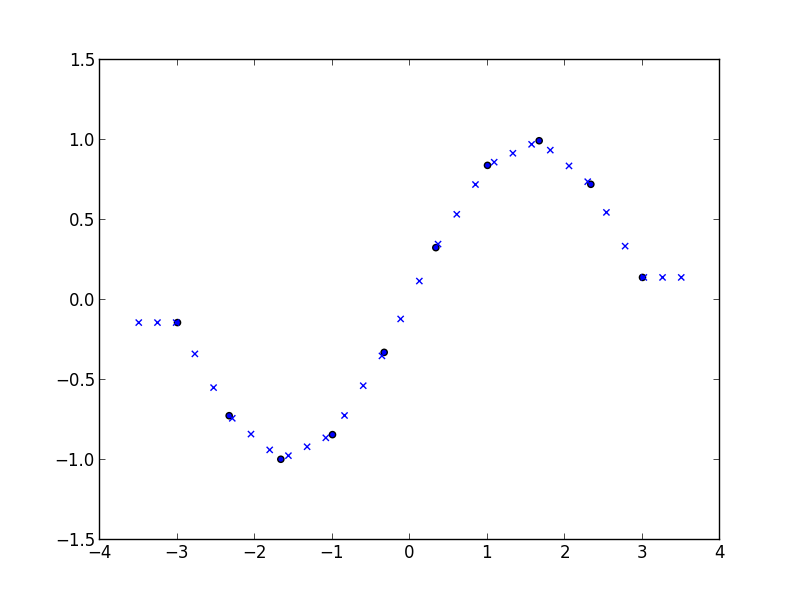\r\n\r\n### Matlab interface \r\nA Matlab interface is provided. To compile it with `mex`, supply the appropriate include directory for the Boost headers:\r\n```matlab\r\nmex -IC:/boost/boost_1_49_0 linterp_matlab.cpp\r\n```\r\nExample:\r\n```matlab\r\ngrid_min = -2;\r\ngrid_max = 2;\r\ngrid_size = 10;\r\nxi_min = grid_min * 1.2;\r\nxi_max = grid_max * 1.2;\r\nxi_size = grid_size * 10;\r\n\r\n% function to interpolate\r\nsin_sum_1 = @(x) sin(x);\r\nsin_sum_2 = @(x1, x2) sin(x1+x2);\r\n\r\n% max error, error sum of squares\r\nerr_ss = @(true_y, y) [max(abs(y-true_y)), sum((y-true_y) .* (y-true_y))];\r\n\r\n% 1D\r\ngrid_1 = linspace(grid_min, grid_max, grid_size);\t\t% original grid\r\nxi_grid_1 = linspace(xi_min, xi_max, xi_size);\t\t\t% grid of points to interpolate on\r\nf = sin_sum_1(grid_1);\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t% f evaluated on original grid\r\nxi_mesh_1 = xi_grid_1;\r\ntrue_y = sin_sum_1(xi_mesh_1);\r\n\r\n% matlab's interp1\r\nyi_1 = interp1(grid_1,f,xi_mesh_1); \t\t\t\t\t% interpolated value\r\nnot_nans = not(isnan(yi_1));\r\ndisp('interp1: max err, err SS');\r\ndisp(err_ss(true_y(not_nans), yi_1(not_nans)));\r\nfigure('Name', 'interp1');\r\nplot(grid_1,f,'o', xi_grid_1,yi_1,'x')\r\n\r\n% linterp\r\nyi_2 = linterp_matlab(grid_1,f,xi_grid_1); \t\t\t\t% interpolated value\r\ndisp('linterp: max err, err SS');\r\ndisp(err_ss(true_y(not_nans), yi_2(not_nans)));\r\nfigure('Name', 'linterp 1d');\r\nplot(grid_1,f,'o', xi_grid_1,yi_2,'x')\r\n\r\n% 2D\r\ngrid_1 = linspace(grid_min, grid_max, grid_size);\t\t% original grid\r\ngrid_2 = linspace(grid_min, grid_max, grid_size);\r\nxi_grid_1 = linspace(xi_min, xi_max, xi_size);\t\t\t% grid of points to interpolate on\r\nxi_grid_2 = linspace(xi_min, xi_max, xi_size);\r\n[grid_mesh_1, grid_mesh_2] = ndgrid(grid_1, grid_2);\r\n[xi_mesh_1, xi_mesh_2] = ndgrid(xi_grid_1, xi_grid_2);\r\nf = sin_sum_2(grid_mesh_1, grid_mesh_2);\t\t\t\t% f evaluated on original grid\r\ntrue_y = sin_sum_2(xi_mesh_1, xi_mesh_2);\r\nfigure('Name', 'true function');\r\nmesh(grid_1, grid_2, f);\r\n\r\n% matlab's griddata 2d\r\ndisp('griddata:');\r\ntic;\r\nyi_1 = griddata(grid_mesh_1, grid_mesh_2, f, xi_mesh_1, xi_mesh_2); \t\t\t\t% interpolated value\r\ntoc;\r\nnot_nans = not(isnan(yi_1));\r\ndisp(err_ss(true_y(not_nans), yi_1(not_nans)));\r\nfigure('Name', 'griddata 2d');\r\nmesh(xi_grid_1, xi_grid_2, yi_1);\r\nerr = yi_1 - true_y;\r\nfigure('Name', 'griddata 2d errors');\r\nmesh(xi_grid_1, xi_grid_2, err);\r\n\r\n% linterp 2d\r\ndisp('linterp 2d:');\r\ntic;\r\nyi_2 = reshape(linterp_matlab(grid_1, grid_2, f, xi_mesh_1, xi_mesh_2), size(true_y)); \t\t\t\t\t\t\t% interpolated value\r\ntoc;\r\ndisp(err_ss(true_y(not_nans), yi_2(not_nans)));\r\nfigure('Name', 'linterp 2d');\r\nmesh(xi_grid_1, xi_grid_2, yi_2);\r\nerr = yi_2 - true_y;\r\nerr(isnan(yi_1)) = NaN;\r\nfigure('Name', 'linterp 2d errors');\r\nmesh(xi_grid_1, xi_grid_2, err);\r\n```\r\nproduces\r\n```\r\ninterp1: max err, err SS\r\n 0.0240 0.0159\r\n\r\nlinterp: max err, err SS\r\n 0.0240 0.0159\r\n\r\ngriddata:\r\nElapsed time is 0.574771 seconds.\r\n 0.0926 4.8782\r\n\r\nlinterp 2d:\r\nElapsed time is 0.001489 seconds.\r\n 0.0474 3.7872\r\n```\r\noutput of `griddata`:\r\n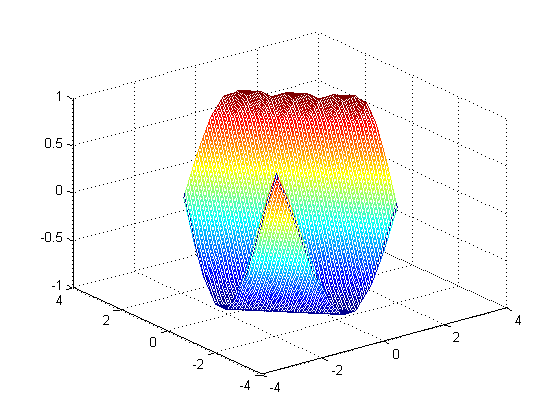\r\noutput of `linterp`:\r\n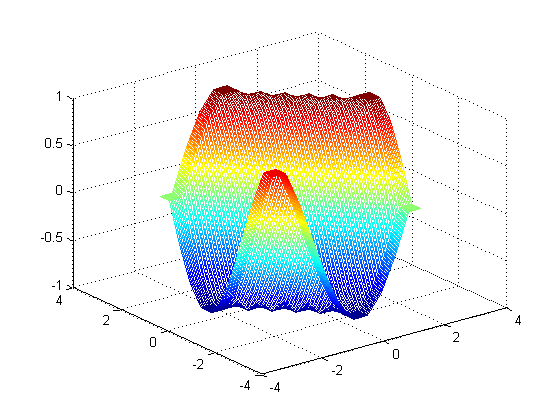\r\n\t\r\n### License\r\n\r\nPermission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee, provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear in supporting documentation. The authors make no representations about the suitability of this software for any purpose. It is provided \"as is\" without express or implied warranty.\r\n","google":"UA-27074418-2","note":"Don't delete this file! It's used internally to help with page regeneration."}