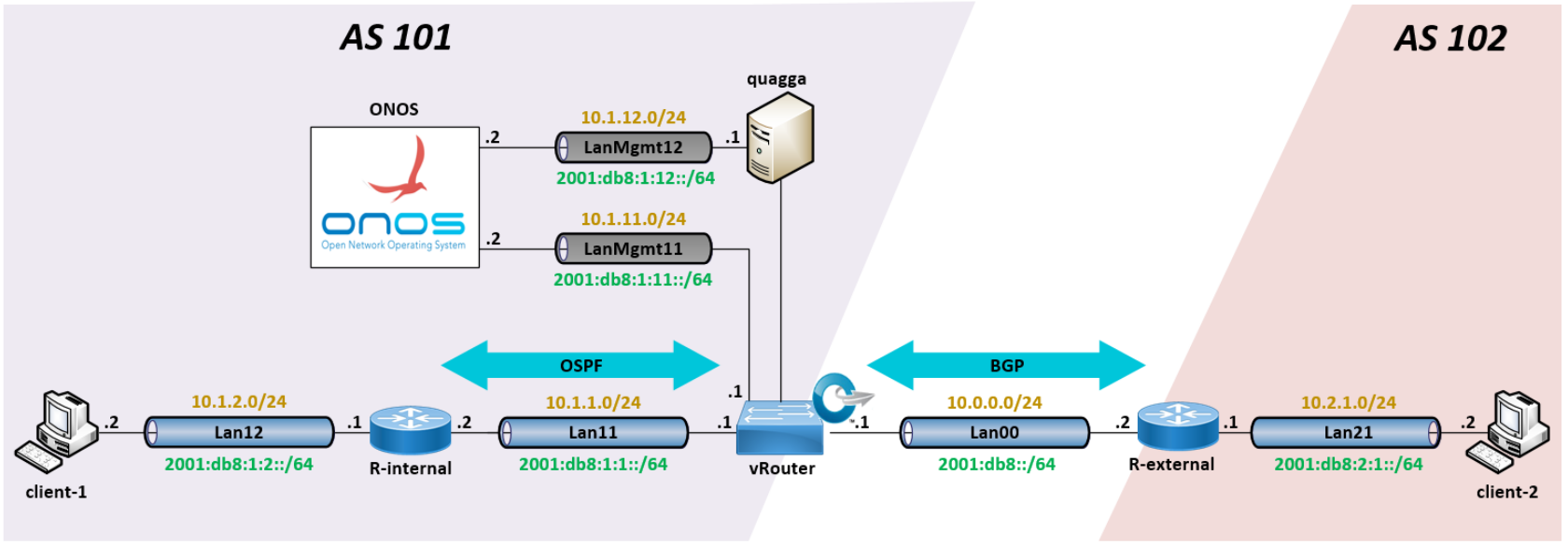
This repository provides a virtual scenario to explore the vRouter service of the ONOS / CORD Project.
Demo scenario has been created using Virtual Networks over linuX (VNX).
Index:
- VNX installed (VNX Installation Guide)
- Operating System: Ubuntu 14.04 / Ubuntu 16.04
- Hard Drive: 3,5 GB avaible space (Filesystem size)
- Memory: 4 GB RAM or more
STEP 1: Clone this repository
$ git clone https://github.com/ralvarep/ONOS-vRouter.git
STEP 2: Build filesystem
The virtual scenario has been configured using the filesystem in copy-on-write (COW) mode. This allows you to use a single filesystem for all virtual machines, thereby optimizing the disk space occupied.
Depending on your operating system, execute:
$ filesystems/create-rootfs_ubuntu14.04
$ filesystems/create-rootfs_ubuntu16.04
This step takes about 20-30 min. It will download all the necessary packages of the demo scenario.
STEP 3: Create virtual scenario
$ sudo vnx -f ONOS-vRouter.xml -t
When the scenario is created, you can login to consoles with root:xxxx.
STEP 4: Check ONOS (SDN Controller)
Enter in the ONOS console and execute the following command to check if ONOS is running:
root@ONOS:~# ~/Applications/apache-karaf-3.0.5/bin/status
Running ...
To enter in the Karaf Console, execute:
root@ONOS:~# ~/Applications/apache-karaf-3.0.5/bin/client
Logging in as onos
Welcome to Open Network Operating System (ONOS)!
____ _ ______ ____
/ __ \/ |/ / __ \/ __/
/ /_/ / / /_/ /\ \
\____/_/|_/\____/___/
onos>
In the event that ONOS is not running, you can launch it by hand executing #ok clean.
Once you are in the Karaf Console, you can check the active applications, such as the vRouter application:
onos> apps -s -a
* 13 org.onosproject.mobility 1.6.1.SNAPSHOT Host Mobility App
* 14 org.onosproject.openflow-base 1.6.1.SNAPSHOT OpenFlow Provider
* 15 org.onosproject.hostprovider 1.6.1.SNAPSHOT Host Location Provider
* 16 org.onosproject.lldpprovider 1.6.1.SNAPSHOT LLDP Link Provider
* 17 org.onosproject.openflow 1.6.1.SNAPSHOT OpenFlow Meta App
* 31 org.onosproject.fwd 1.6.1.SNAPSHOT Reactive Forwarding App
* 33 org.onosproject.proxyarp 1.6.1.SNAPSHOT Proxy ARP/NDP App
* 39 org.onosproject.drivers 1.6.1.SNAPSHOT Default Device Drivers
* 87 org.onosproject.vrouter 1.6.1.SNAPSHOT Virtual Router App
and the learned routes:
onos> routes
Table: ipv4
Network Next Hop
10.1.2.0/24 10.1.1.2
10.2.1.0/24 10.0.0.2
Total: 2
Table: ipv6
Network Next Hop
2001:db8:2:1::/64 2001:db8::2
Total: 1
In this step ONOS is launched to manage the OpenFlow switch (vRouter VM) of the topology setting the gateway of the AS 101 and speaking routing protocols with both R-internal (AS 101) and R-external (AS 102).
In addition, ONOS GUI is avaible from your host through http://10.250.0.10:8181/onos/ui/login.html. To login karaf:karaf.
STEP 4: Connectivity Test between clients (client-1 <==> client-2)
Now you can test the connectivity between the clients. For example, entering in the client-1 console:
root@client-1:~# ping 10.2.1.2
PING 10.2.1.2 (10.2.1.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.2.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=62 time=0.362 ms
64 bytes from 10.2.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=62 time=0.085 ms
64 bytes from 10.2.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=62 time=0.077 ms
OTHER OPTIONS:
- Launch terminal of some virtual machine
$ sudo vnx -f ONOS-vRouter.xml --console -M VM-NAME
- Shutdown scenario
$ sudo vnx -f ONOS-vRouter.xml --shutdown
- Start scenario that has previously been shutdown
$ sudo vnx -f ONOS-vRouter.xml --start
- Destroy scenario
$ sudo vnx -f ONOS-vRouter.xml -P
- IPv6 is not totally support in vRouter application. In this scenario ONOS is learning IPv6 routes through a established IPv4 BGP session between the Quagga Server and R-external.
This project has been developed by Raúl Álvarez Pinilla.