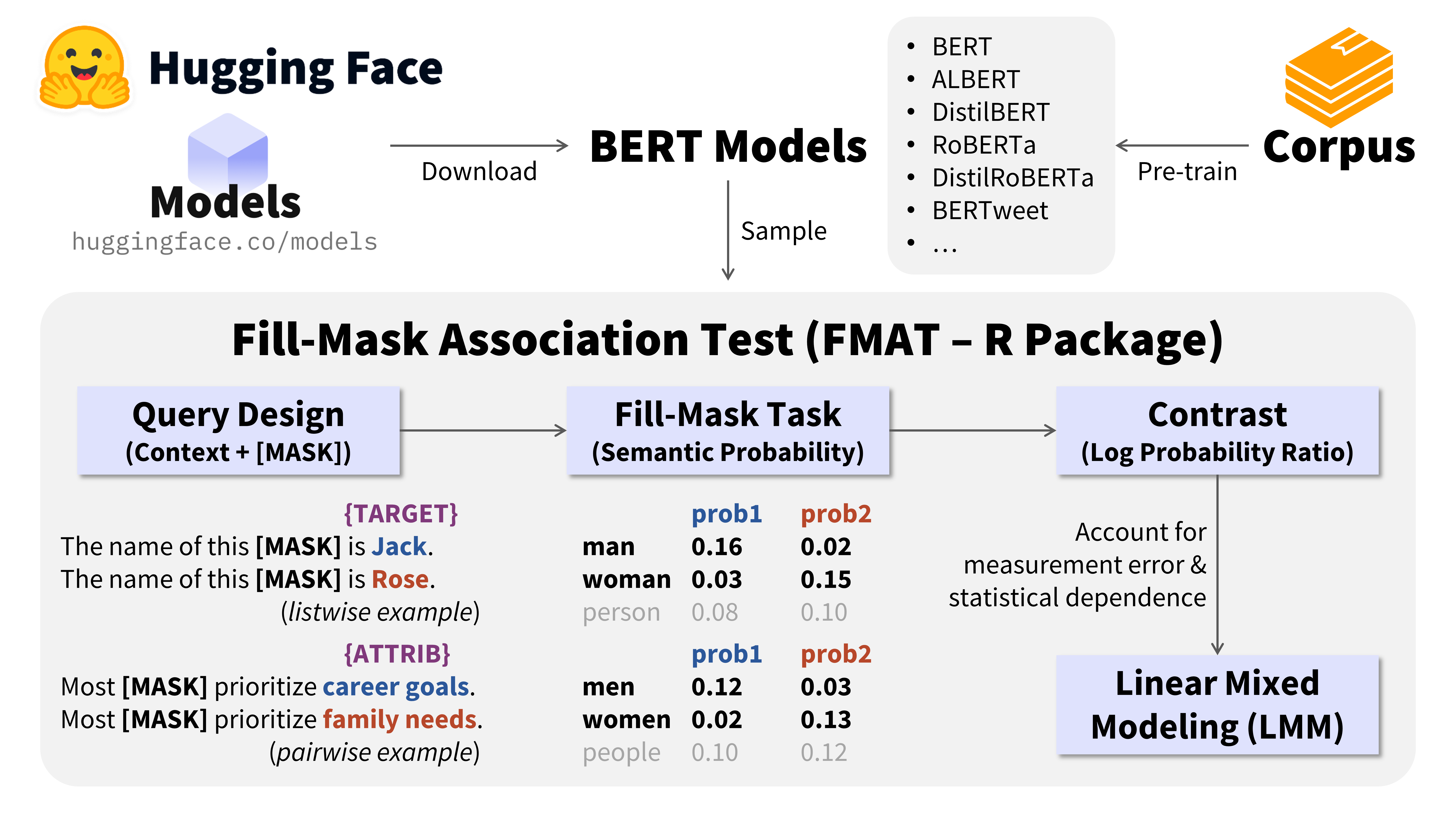
😷 The Fill-Mask Association Test (掩码填空联系测验).
The Fill-Mask Association Test (FMAT) is an integrative and probability-based method using [BERT Models] to measure conceptual associations (e.g., attitudes, biases, stereotypes, social norms, cultural values) as propositions in natural language (Bao, 2024, JPSP).
Han-Wu-Shuang (Bruce) Bao 包寒吴霜
- Bao, H.-W.-S. (2023). FMAT: The Fill-Mask Association Test. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=FMAT
- Note: This is the original citation. Please refer to the information when you
library(FMAT)for the APA-7 format of the version you installed.
- Note: This is the original citation. Please refer to the information when you
- Bao, H.-W.-S. (2024). The Fill-Mask Association Test (FMAT): Measuring propositions in natural language. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 127(3), 537–561. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspa0000396
- Bao, H.-W.-S., & Gries, P. (2024). Intersectional race–gender stereotypes in natural language. British Journal of Social Psychology, 63(4), 1771–1786. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjso.12748
To use the FMAT, the R package FMAT and three Python packages (transformers, torch, huggingface-hub) all need to be installed.
## Method 1: Install from CRAN
install.packages("FMAT")
## Method 2: Install from GitHub
install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("psychbruce/FMAT", force=TRUE)Install Anaconda (a recommended package manager which automatically installs Python, Python IDEs like Spyder, and a large list of necessary Python package dependencies).
Specify the Anaconda's Python interpreter in RStudio.
RStudio → Tools → Global/Project Options
→ Python → Select → Conda Environments
→ Choose ".../Anaconda3/python.exe"
Install specific versions of Python packages "transformers", "torch", and "huggingface-hub".
(RStudio Terminal / Anaconda Prompt / Windows Command)
For CPU users:
pip install transformers==4.40.2 torch==2.2.1 huggingface-hub==0.20.3
For GPU (CUDA) users:
pip install transformers==4.40.2 huggingface-hub==0.20.3
pip install torch==2.2.1 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121
- See [Guidance for GPU Acceleration] for installation guidance if you have an NVIDIA GPU device on your PC and want to use GPU to accelerate the pipeline.
- According to the May 2024 releases, "transformers" ≥ 4.41 depends on "huggingface-hub" ≥ 0.23. The suggested versions of "transformers" (4.40.2) and "huggingface-hub" (0.20.3) ensure the console display of progress bars when downloading BERT models while keeping these packages as new as possible.
- Proxy users should use the "global mode" (全局模式) to download models.
- If you see the error
HTTPSConnectionPool(host='huggingface.co', port=443), please try to (1) reinstall Anaconda so that some unknown issues may be fixed or (2) downgrade the "urllib3" package to version ≤ 1.25.11 (pip install urllib3==1.25.11) so that it will use HTTP proxies (rather than HTTPS proxies as in later versions) to connect to Hugging Face.
Use BERT_download() to download [BERT models]. Model files are saved to your local folder "%USERPROFILE%/.cache/huggingface". A full list of BERT models are available at Hugging Face.
Use BERT_info() and BERT_vocab() to find detailed information of BERT models.
Design queries that conceptually represent the constructs you would measure (see Bao, 2024, JPSP for how to design queries).
Use FMAT_query() and/or FMAT_query_bind() to prepare a data.table of queries.
Use FMAT_run() to get raw data (probability estimates) for further analysis.
Several steps of preprocessing have been included in the function for easier use (see FMAT_run() for details).
- For BERT variants using
<mask>rather than[MASK]as the mask token, the input query will be automatically modified so that users can always use[MASK]in query design. - For some BERT variants, special prefix characters such as
\u0120and\u2581will be automatically added to match the whole words (rather than subwords) for[MASK].
- Improvements are ongoing, especially for adaptation to more diverse (less popular) BERT models.
- If you find bugs or have problems using the functions, please report them at GitHub Issues or send me an email.
By default, the FMAT package uses CPU to enable the functionality for all users. But for advanced users who want to accelerate the pipeline with GPU, the FMAT_run() function now supports using a GPU device, about 3x faster than CPU.
Test results (on the developer's computer, depending on BERT model size):
- CPU (Intel 13th-Gen i7-1355U): 500~1000 queries/min
- GPU (NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2050): 1500~3000 queries/min
Checklist:
- Ensure that you have an NVIDIA GPU device (e.g., GeForce RTX Series) and an NVIDIA GPU driver installed on your system.
- Install PyTorch (Python
torchpackage) with CUDA support.- Find guidance for installation command at https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/.
- CUDA is available only on Windows and Linux, but not on MacOS.
- If you have installed a version of
torchwithout CUDA support, please first uninstall it (command:pip uninstall torch) and then install the suggested one. - You may also install the corresponding version of CUDA Toolkit (e.g., for the
torchversion supporting CUDA 12.1, the same version of CUDA Toolkit 12.1 may also be installed).
Example code for installing PyTorch with CUDA support:
(RStudio Terminal / Anaconda Prompt / Windows Command)
pip install torch==2.2.1 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121
The reliability and validity of the following 12 representative BERT models have been established in my research articles, but future work is needed to examine the performance of other models.
(model name on Hugging Face - downloaded model file size)
- bert-base-uncased (420 MB)
- bert-base-cased (416 MB)
- bert-large-uncased (1283 MB)
- bert-large-cased (1277 MB)
- distilbert-base-uncased (256 MB)
- distilbert-base-cased (251 MB)
- albert-base-v1 (45 MB)
- albert-base-v2 (45 MB)
- roberta-base (476 MB)
- distilroberta-base (316 MB)
- vinai/bertweet-base (517 MB)
- vinai/bertweet-large (1356 MB)
If you are new to BERT, these references can be helpful:
- What is Fill-Mask? [HuggingFace]
- An Explorable BERT [HuggingFace]
- BERT Model Documentation [HuggingFace]
- BERT Explained
- Breaking BERT Down
- Illustrated BERT
- Visual Guide to BERT
library(FMAT)
models = c(
"bert-base-uncased",
"bert-base-cased",
"bert-large-uncased",
"bert-large-cased",
"distilbert-base-uncased",
"distilbert-base-cased",
"albert-base-v1",
"albert-base-v2",
"roberta-base",
"distilroberta-base",
"vinai/bertweet-base",
"vinai/bertweet-large"
)
BERT_download(models)ℹ Device Info:
R Packages:
FMAT 2024.5
reticulate 1.36.1
Python Packages:
transformers 4.40.2
torch 2.2.1+cu121
NVIDIA GPU CUDA Support:
CUDA Enabled: TRUE
CUDA Version: 12.1
GPU (Device): NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2050
── Downloading model "bert-base-uncased" ──────────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 570/570 [00:00<00:00, 114kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
tokenizer_config.json: 100%|██████████| 48.0/48.0 [00:00<00:00, 23.9kB/s]
vocab.txt: 100%|██████████| 232k/232k [00:00<00:00, 1.50MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 466k/466k [00:00<00:00, 1.98MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
model.safetensors: 100%|██████████| 440M/440M [00:36<00:00, 12.1MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "bert-base-uncased"
── Downloading model "bert-base-cased" ────────────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 570/570 [00:00<00:00, 63.3kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
tokenizer_config.json: 100%|██████████| 49.0/49.0 [00:00<00:00, 8.66kB/s]
vocab.txt: 100%|██████████| 213k/213k [00:00<00:00, 1.39MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 436k/436k [00:00<00:00, 10.1MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
model.safetensors: 100%|██████████| 436M/436M [00:37<00:00, 11.6MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "bert-base-cased"
── Downloading model "bert-large-uncased" ─────────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 571/571 [00:00<00:00, 268kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
tokenizer_config.json: 100%|██████████| 48.0/48.0 [00:00<00:00, 12.0kB/s]
vocab.txt: 100%|██████████| 232k/232k [00:00<00:00, 1.50MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 466k/466k [00:00<00:00, 1.99MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
model.safetensors: 100%|██████████| 1.34G/1.34G [01:36<00:00, 14.0MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "bert-large-uncased"
── Downloading model "bert-large-cased" ───────────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 762/762 [00:00<00:00, 125kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
tokenizer_config.json: 100%|██████████| 49.0/49.0 [00:00<00:00, 12.3kB/s]
vocab.txt: 100%|██████████| 213k/213k [00:00<00:00, 1.41MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 436k/436k [00:00<00:00, 5.39MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
model.safetensors: 100%|██████████| 1.34G/1.34G [01:35<00:00, 14.0MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "bert-large-cased"
── Downloading model "distilbert-base-uncased" ────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 483/483 [00:00<00:00, 161kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
tokenizer_config.json: 100%|██████████| 48.0/48.0 [00:00<00:00, 9.46kB/s]
vocab.txt: 100%|██████████| 232k/232k [00:00<00:00, 16.5MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 466k/466k [00:00<00:00, 14.8MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
model.safetensors: 100%|██████████| 268M/268M [00:19<00:00, 13.5MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "distilbert-base-uncased"
── Downloading model "distilbert-base-cased" ──────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 465/465 [00:00<00:00, 233kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
tokenizer_config.json: 100%|██████████| 49.0/49.0 [00:00<00:00, 9.80kB/s]
vocab.txt: 100%|██████████| 213k/213k [00:00<00:00, 1.39MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 436k/436k [00:00<00:00, 8.70MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
model.safetensors: 100%|██████████| 263M/263M [00:24<00:00, 10.9MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "distilbert-base-cased"
── Downloading model "albert-base-v1" ─────────────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 684/684 [00:00<00:00, 137kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
tokenizer_config.json: 100%|██████████| 25.0/25.0 [00:00<00:00, 3.57kB/s]
spiece.model: 100%|██████████| 760k/760k [00:00<00:00, 4.93MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 1.31M/1.31M [00:00<00:00, 13.4MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
model.safetensors: 100%|██████████| 47.4M/47.4M [00:03<00:00, 13.4MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "albert-base-v1"
── Downloading model "albert-base-v2" ─────────────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 684/684 [00:00<00:00, 137kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
tokenizer_config.json: 100%|██████████| 25.0/25.0 [00:00<00:00, 4.17kB/s]
spiece.model: 100%|██████████| 760k/760k [00:00<00:00, 5.10MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 1.31M/1.31M [00:00<00:00, 6.93MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
model.safetensors: 100%|██████████| 47.4M/47.4M [00:03<00:00, 13.8MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "albert-base-v2"
── Downloading model "roberta-base" ───────────────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 481/481 [00:00<00:00, 80.3kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
tokenizer_config.json: 100%|██████████| 25.0/25.0 [00:00<00:00, 6.25kB/s]
vocab.json: 100%|██████████| 899k/899k [00:00<00:00, 2.72MB/s]
merges.txt: 100%|██████████| 456k/456k [00:00<00:00, 8.22MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 1.36M/1.36M [00:00<00:00, 8.56MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
model.safetensors: 100%|██████████| 499M/499M [00:38<00:00, 12.9MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "roberta-base"
── Downloading model "distilroberta-base" ─────────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 480/480 [00:00<00:00, 96.4kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
tokenizer_config.json: 100%|██████████| 25.0/25.0 [00:00<00:00, 12.0kB/s]
vocab.json: 100%|██████████| 899k/899k [00:00<00:00, 6.59MB/s]
merges.txt: 100%|██████████| 456k/456k [00:00<00:00, 9.46MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 1.36M/1.36M [00:00<00:00, 11.5MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
model.safetensors: 100%|██████████| 331M/331M [00:25<00:00, 13.0MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "distilroberta-base"
── Downloading model "vinai/bertweet-base" ────────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 558/558 [00:00<00:00, 187kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
vocab.txt: 100%|██████████| 843k/843k [00:00<00:00, 7.44MB/s]
bpe.codes: 100%|██████████| 1.08M/1.08M [00:00<00:00, 7.01MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 2.91M/2.91M [00:00<00:00, 9.10MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
pytorch_model.bin: 100%|██████████| 543M/543M [00:48<00:00, 11.1MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "vinai/bertweet-base"
── Downloading model "vinai/bertweet-large" ───────────────────────────────────────
→ (1) Downloading configuration...
config.json: 100%|██████████| 614/614 [00:00<00:00, 120kB/s]
→ (2) Downloading tokenizer...
vocab.json: 100%|██████████| 899k/899k [00:00<00:00, 5.90MB/s]
merges.txt: 100%|██████████| 456k/456k [00:00<00:00, 7.30MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|██████████| 1.36M/1.36M [00:00<00:00, 8.31MB/s]
→ (3) Downloading model...
pytorch_model.bin: 100%|██████████| 1.42G/1.42G [02:29<00:00, 9.53MB/s]
✔ Successfully downloaded model "vinai/bertweet-large"
── Downloaded models: ──
size
albert-base-v1 45 MB
albert-base-v2 45 MB
bert-base-cased 416 MB
bert-base-uncased 420 MB
bert-large-cased 1277 MB
bert-large-uncased 1283 MB
distilbert-base-cased 251 MB
distilbert-base-uncased 256 MB
distilroberta-base 316 MB
roberta-base 476 MB
vinai/bertweet-base 517 MB
vinai/bertweet-large 1356 MB
✔ Downloaded models saved at C:/Users/Bruce/.cache/huggingface/hub (6.52 GB)
BERT_info(models) model size vocab dims mask
<fctr> <char> <int> <int> <char>
1: bert-base-uncased 420MB 30522 768 [MASK]
2: bert-base-cased 416MB 28996 768 [MASK]
3: bert-large-uncased 1283MB 30522 1024 [MASK]
4: bert-large-cased 1277MB 28996 1024 [MASK]
5: distilbert-base-uncased 256MB 30522 768 [MASK]
6: distilbert-base-cased 251MB 28996 768 [MASK]
7: albert-base-v1 45MB 30000 128 [MASK]
8: albert-base-v2 45MB 30000 128 [MASK]
9: roberta-base 476MB 50265 768 <mask>
10: distilroberta-base 316MB 50265 768 <mask>
11: vinai/bertweet-base 517MB 64001 768 <mask>
12: vinai/bertweet-large 1356MB 50265 1024 <mask>
(Tested 2024-05-16 on the developer's computer: HP Probook 450 G10 Notebook PC)
While the FMAT is an innovative method for the computational intelligent analysis of psychology and society, you may also seek for an integrative toolbox for other text-analytic methods. Another R package I developed---PsychWordVec---is useful and user-friendly for word embedding analysis (e.g., the Word Embedding Association Test, WEAT). Please refer to its documentation and feel free to use it.