| Health | Release | Other |
|---|---|---|
 |
||
 |
||
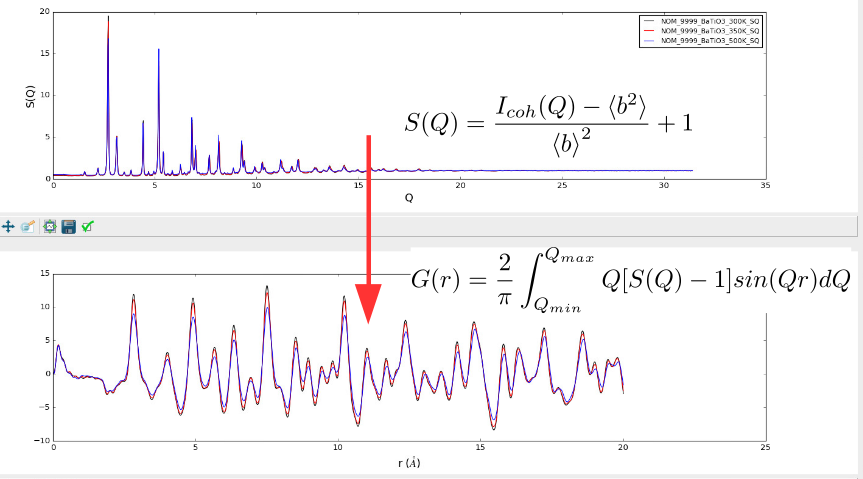
From total scattering functions, we have reciprocal-space structure factors and real-space pair distribution functions that are related via a Fourier transform. PyStoG is a package that allows for:
- Converting between the various functions used by different "communities" (ie researchers who study crystalline versus amorphous or glass materials). Conversions are for either real-space or reciprocal-space.
- Perform the transform between the different available functions of choice
- Fourier filter to remove spurious artificats in the data (ie aphysical, sub-angstrom low-r peaks in G(r) from experiments)
The name PyStoG comes from the fact that this is a Pythonized version of StoG, a ~30 year old Fortran program that is part of the RMCProfile software suite. StoG means "S(Q) to G(r)" for the fact that it takes recirpocal-space S(Q) patterns from files and transforms them into a single G(r) pattern. The original StoG program has been developed, in reverse chronological order, by:
- Matthew Tucker and Martin Dove (~2009)
- Spencer Howells (~1989)
- Jack Carpenter (prior to 1989)
A current state of the StoG program is kept in the fortran directory of this package.
This project was initially just a "sandbox" for taking the capabilities of StoG and migrating them over to the Mantid Framework. Yet, with more and more use cases, PyStoG was further developed as the stand-alone project it is now. Yet, migration to the Mantid Framework is still a goal since it feeds into the ADDIE project
Installation is available via pip:
pip install pystog
And conda:
conda install -c neutrons pystog
Once installed, you can access the packages classes that perform the function manipulation.
import pystog
from pystog import Converter
from pystog import Transformer
from pystog import FourierFilter
from pystog import StoG** WARNING: Testing of the CLI is still ongoing**
Also, there is a beta-version of a python script in the package that can be run on JSON input files and operates similarly to the original StoG program.
This is python cli and can be used as follows:
pystog_cli --json <input json>An example JSON can be found here
The official documentation is hosted on readthedocs.org: https://pystog.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
Also, a useful example reference is the PDFFourierTransform algorithm in the Mantid Framework that has similar yet limited capabilities.
Finally, tutorials in the form of Jupyter Notebooks can be launched via Binder by clicking the badge here or at the top of the page.
The following are ways to setup the virtual environment, lint and test the package.
With pipenv installed, run the following:
pipenv install --dev .You can use virtualenv to setup an environment, here named ENV:
python -m virtualenv /path/to/ENV
source /path/to/ENV/bin/activate
pip install pystogAlso, direnv is a useful and recommended way to manage the virtual environment.
You can simply use an .envrc file which contains:
layout python3
Then, once inside the development directory, just install via pip as described above.
pytest is used to write the test suite. Tox is the general tool for running both linting and testing (single and multiple python version testing). pyenv is the recommended tool for python version management. From the parent directory of the module, run:
pytest
Using pipenv:
pipenv run pytest
Using tox for a single python version,
where py<XY> is one of [py36, py37, py38, py39]:
tox -e py<XY>
or with pipenv:
pipenv run tox -e py<XY>
Using tox for all stages of testing (all python versions and linting), just run:
tox
NOTE: You must have the version of python installed to run a test suite against that version via tox.
Recommended way to install python versions is pyenv
pre-commit is used for style enforcement and static analysis. To install, after creating the environment run
pre-commit installand it will run for every commit.
pre-commit run --allwill run it without committing.