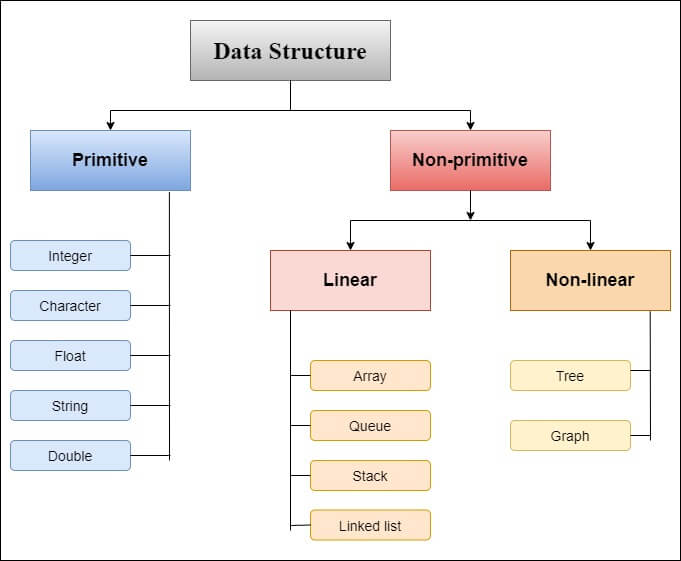
A data structure is a way of organizing data so that it can be accessed and manipulated efficiently. It is a collection of data elements, and the relationships between them. Data structures are used to store data in a way that makes it easy to find, sort, and update.
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem. It is a set of instructions that can be followed to achieve a specific outcome. Algorithms are used to solve a wide variety of problems, including sorting, searching, and data compression.
The definition of a data structure and algorithm is as follows:
Data structure: A data structure is a way of organizing data so that it can be accessed and manipulated efficiently.
Algorithm: An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem.
Type: There are two main types of data structures:
linear and non-linear.
Linear data structures are those in which the data elements are arranged in a sequential order. Non-linear data structures are those in which the data elements are not arranged in a sequential order.
Linear data structures:
Arrays,
Linked lists,
Stacks, and
Queues.
Non-linear data structures:
Trees,
Graphs, and
Hash tables.
Sorting algorithms:
Bubble sort,
Selection sort, and
Merge sort.
Searching algorithms:
Linear search,
Binary search, and
Hash table search.
Compression algorithms:
Huffman coding,
LZW compression, and
JPEG compression.