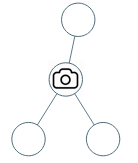
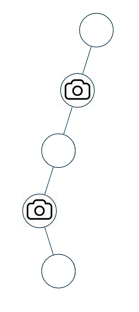
给定一个二叉树,我们在树的节点上安装摄像头。
节点上的每个摄影头都可以监视其父对象、自身及其直接子对象。
计算监控树的所有节点所需的最小摄像头数量。
示例 1:
输入:[0,0,null,0,0] 输出:1 解释:如图所示,一台摄像头足以监控所有节点。
示例 2:
输入:[0,0,null,0,null,0,null,null,0] 输出:2 解释:需要至少两个摄像头来监视树的所有节点。 上图显示了摄像头放置的有效位置之一。
提示:
- 给定树的节点数的范围是
[1, 1000]。 - 每个节点的值都是 0。
方法一:动态规划(树形 DP)
对于每个节点,我们定义三种状态:
a:当前节点有摄像头b:当前节点无摄像头,但被子节点监控c:当前节点无摄像头,也没被子节点监控
接下来,我们设计一个函数 root 为根的子树中,三种状态下的最小摄像头数量。那么答案就是
函数
如果 root 为空,则返回 inf 表示一个很大的数,它用于表示不可能的情况。
否则,我们递归计算 root 的左右子树,分别得到
- 如果当前节点有摄像头,那么它的左右节点必须都是被监控的状态,即
$a = \min(la, lb, lc) + \min(ra, rb, rc) + 1$ 。 - 如果当前节点无摄像头,但被子节点监控,那么子节点可以是其中之一或者两个都有摄像头,即
$b = \min(la + rb, lb + ra, la + ra)$ 。 - 如果当前节点无摄像头,也没被子节点监控,那么子节点必须被其子节点监控,即
$c = lb + rb$ 。
最后,我们返回
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minCameraCover(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return inf, 0, 0
la, lb, lc = dfs(root.left)
ra, rb, rc = dfs(root.right)
a = min(la, lb, lc) + min(ra, rb, rc) + 1
b = min(la + rb, lb + ra, la + ra)
c = lb + rb
return a, b, c
a, b, _ = dfs(root)
return min(a, b)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) {
int[] ans = dfs(root);
return Math.min(ans[0], ans[1]);
}
private int[] dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new int[] {1 << 29, 0, 0};
}
var l = dfs(root.left);
var r = dfs(root.right);
int a = 1 + Math.min(Math.min(l[0], l[1]), l[2]) + Math.min(Math.min(r[0], r[1]), r[2]);
int b = Math.min(Math.min(l[0] + r[1], l[1] + r[0]), l[0] + r[0]);
int c = l[1] + r[1];
return new int[] {a, b, c};
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
struct Status {
int a, b, c;
};
class Solution {
public:
int minCameraCover(TreeNode* root) {
auto [a, b, _] = dfs(root);
return min(a, b);
}
Status dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return {1 << 29, 0, 0};
}
auto [la, lb, lc] = dfs(root->left);
auto [ra, rb, rc] = dfs(root->right);
int a = 1 + min({la, lb, lc}) + min({ra, rb, rc});
int b = min({la + ra, la + rb, lb + ra});
int c = lb + rb;
return {a, b, c};
};
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func minCameraCover(root *TreeNode) int {
var dfs func(*TreeNode) (int, int, int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) (int, int, int) {
if root == nil {
return 1 << 29, 0, 0
}
la, lb, lc := dfs(root.Left)
ra, rb, rc := dfs(root.Right)
a := 1 + min(la, min(lb, lc)) + min(ra, min(rb, rc))
b := min(la+ra, min(la+rb, lb+ra))
c := lb + rb
return a, b, c
}
a, b, _ := dfs(root)
return min(a, b)
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function minCameraCover(root: TreeNode | null): number {
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null): number[] => {
if (!root) {
return [1 << 29, 0, 0];
}
const [la, lb, lc] = dfs(root.left);
const [ra, rb, rc] = dfs(root.right);
const a = 1 + Math.min(la, lb, lc) + Math.min(ra, rb, rc);
const b = Math.min(la + ra, la + rb, lb + ra);
const c = lb + rb;
return [a, b, c];
};
const [a, b, _] = dfs(root);
return Math.min(a, b);
}