Declaratively build a 4 node Kubernetes cluster on Proxmox using Ansible and QEMU. Optionally enable advanced features including ingress, load balancing, unattended upgrades etc.
Approximate deployment time: 25 minutes
- Proxmox server
- DNS Server*
- Ansible 2.7.0+. Known incompatibility with a previous build.
*A DNS server is not technically required, it is possible to manually add entries corresponding to your node hostnames to your Proxmox's hosts file.
Required:
- Modify the
vars.ymlfile with values specific to your environment. - Provision DNS A records for the IP Addresses & Hostnames you defined for your nodes in the
vars.ymlfile. - Modify the
inventory.inifile to reflect your chosen DNS records and the location of the SSH keys used to connect to the nodes. - Run the deployment:
ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini site.yml - After deployment, a
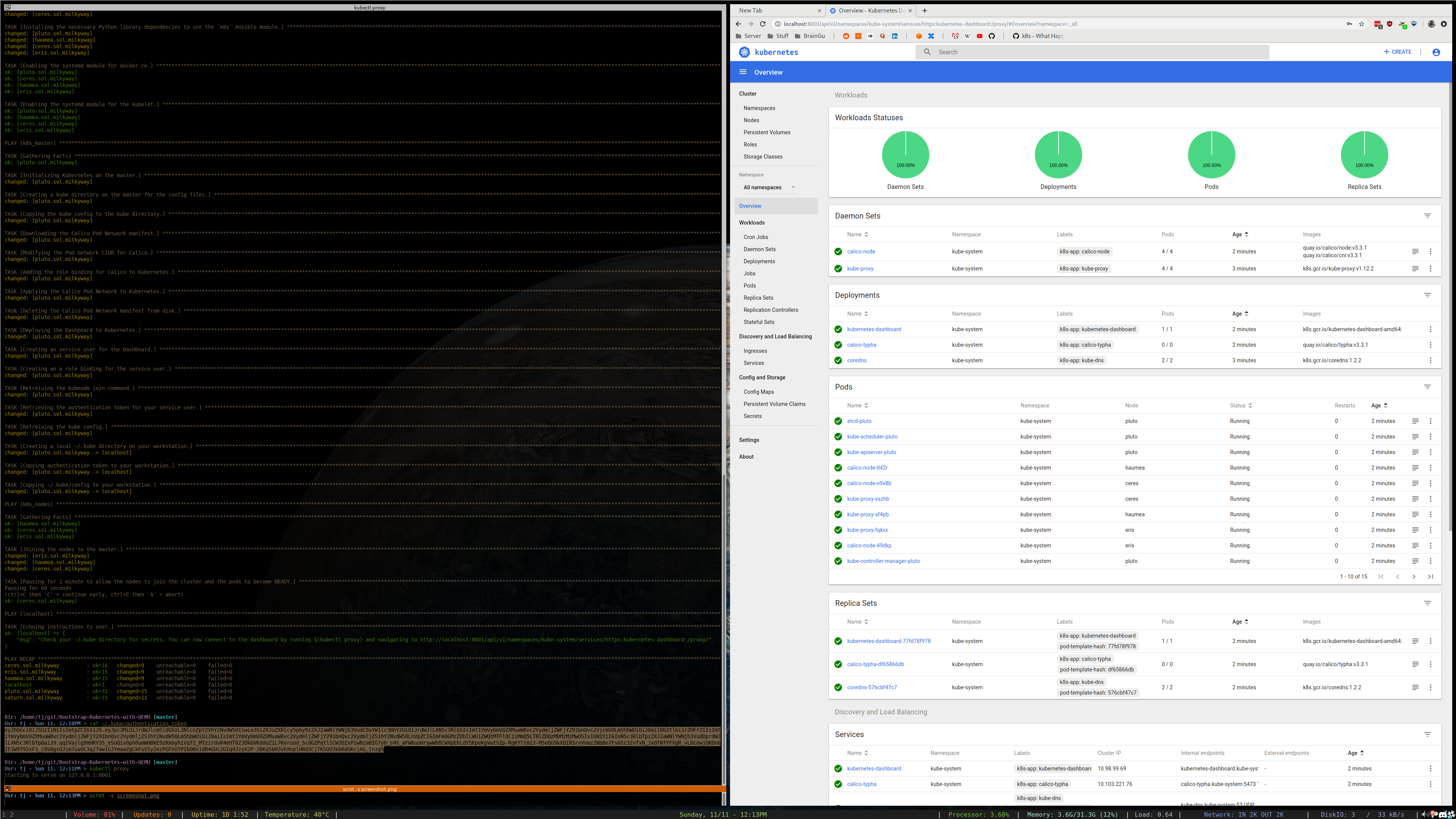
~/.kubedirectory will be created on your workstation. Within yourconfiganauthentication_tokenfile can be be found. This token is used to authenticate against the Kubernetes API and Dashboard using your account. To connect to the dashboard, installkubectlon your workstation and runkubectl proxythen navigate to the Dashboard Endpoint in your browser.
Optional:
To enable an optional feature, fill in the additional parameters in vars.yml and execute a playbook listed below.
| Feature | Command | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| NFS backed persistent storage | ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/deploy_nfs_provisioner.yml |
|
| MetalLB Load Balancer | ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/deploy_metallb.yml |
|
| NGINX Ingress Controller | ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/deploy_ingress-nginx.yml |
MetalLB or other Load Balancer integration |
| DataDog agents | ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/deploy_datadog.yml |
|
| Unattended Upgrades | ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/enable_unattended_upgrades.yml |
- You can rollback the entire deployment with:
ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/delete_all_resources.yml - If Calico isn't deploying correctly it's likely the CIDR you assigned to it in
vars.ymlconflicts with your network. - There appears to be an issue with Proxmox's
cloud-initimplementation. Perhaps just with Debian? As a result, your VM might not have the correct information in/etc/resolv.confand may also have multiple IP Addresses assigned to theeth0network interfaces. Furthermore, if you do not have a DHCP server active in the network that you are provisoning the VMs to, it is entirely possible that nothing will be present at all in/etc/resolv.conf. - See this repository to do this with LXC instead. Benefits of using LXC include:
* No virtualization overhead means better performance
* Ability to directly mount volumes from your server into your containers.
- Add better support for multi-node Proxmox clusters.
- Perform security audit and enhance if necessary.
- Add info to README about updating inventory file and how to handle SSH key generation and propegation.
- Create playbook to upgrade kubernetes version for kubeadm cluster.
- Move dashboard deployment to optional features.
- The
proxmox_kvmmodule is out of date and does not support cloudinit related api calls. Meaning shell commands must be used instead to performqm createtasks. - The
k8smodule does not support applying Kubernetes Deployments from URL. Instead of usingget_urlto download them first, and then apply them withk8s, I just useshellto run akubectl apply -f. Feature Request here. - Miscellaneous
qcow2image issues:
| OS | Issue |
|---|---|
| CentOS | A nameserver is baked into /etc/resolv.conf by default. Bug Report here |
| CoreOS | Proxmix issued cloud-init does not seem to configure networking properly. |