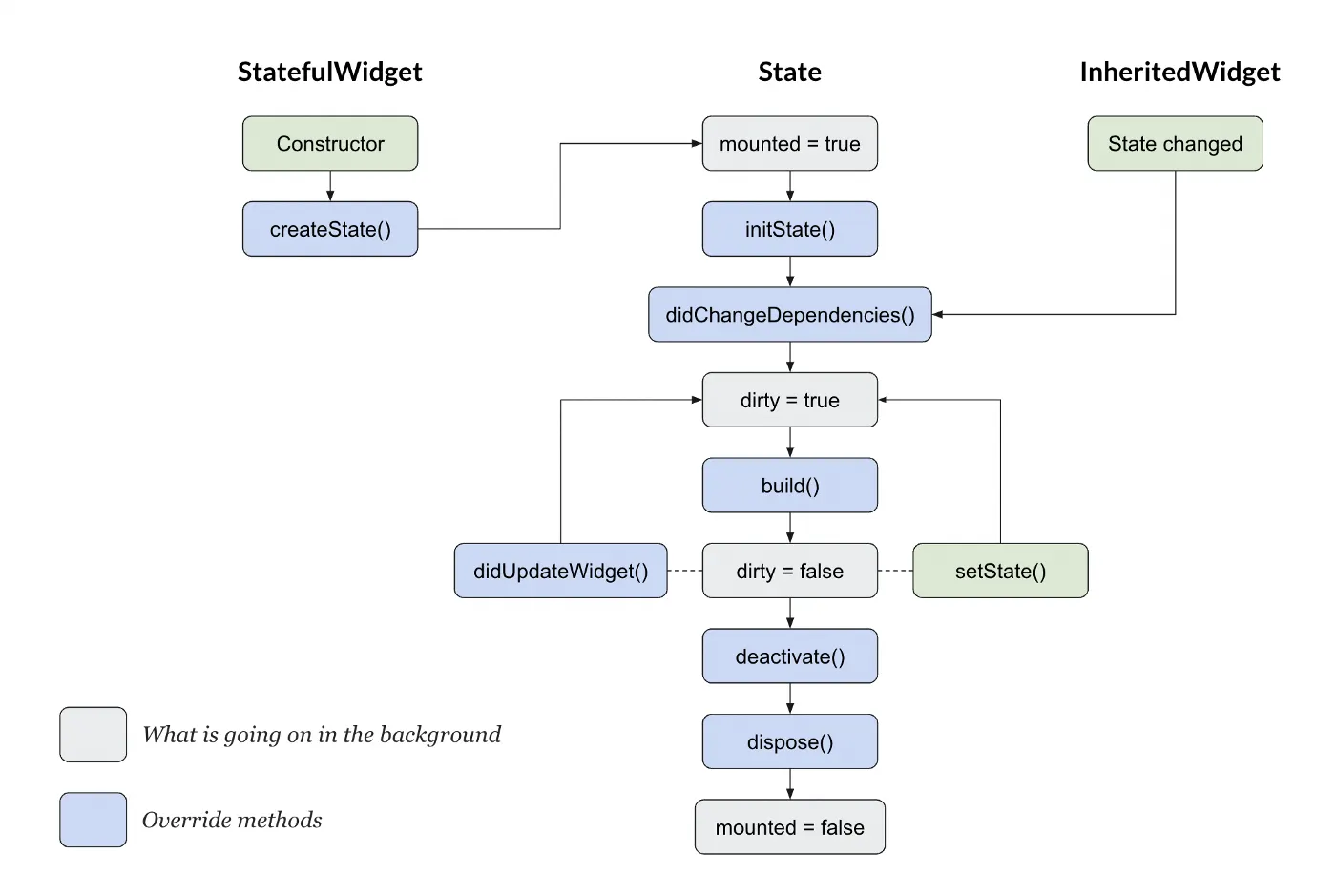
A Flutter State Management Project. A Quick look through inside the state management solutions provided by Flutter itself and packages.
- Create State: Create a state object for the widget.
- Mounted =
true - Init State: Called once when the state object is inserted into the widget tree.
- Did Change Dependencies: Rebuilds the widget when dependencies change.
- Dirty =
true: Indicates the widget needs to rebuild. - Build: Builds the widget UI.
- Dirty =
false: Indicates the widget is up-to-date. - Did Update Widget: Called when the widget’s configuration changes.
- Set State: Triggers
dirty = trueto rebuild the widget. - Deactivate: Triggered when the widget is removed/changed in the tree.
- Activate: Triggered when the widget’s location changes in the tree.
- Dispose: Triggered when the widget is permanently removed from the tree.
- Mounted =
false
State management can be broadly categorized into three approaches based on how state is handled:
- Focus on explicitly instructing the framework on how to update the UI.
- State changes trigger direct updates to the widget tree.
- Example: setState, ChangeNotifier, ValueNotifier.
- Emphasize declaring the UI as a function of the state.
- State changes automatically propagate to the UI.
- Example: InheritedWidget, InheritedModel, Inherited Notifier, Provider, Riverpod.
- Focus on reacting to changes in the state by observing streams or observables.
- Example: Flutter Bloc, RxDart, MobX, Riverpod.
| Aspect | Imperative | Declarative | Reactive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Low | Medium | High |
| Learning Curve | Easy | Moderate | Steep |
| Performance | Minimal overhead | Efficient updates | Handles large-scale updates efficiently |
| Best For | Simple state management | Medium complexity apps | Complex apps with highly dynamic data flows |
| Examples | setState, ChangeNotifier, ValueNotifier | InheritedWidget, InheritedModel, Inherited Notifier, Provider, Riverpod | Bloc, RxDart, MobX, Riverpod |
- Imperative: Use for small-scale, straightforward applications with minimal state.
- Declarative: Use for medium complexity apps requiring clear and manageable state propagation.
- Reactive: Use for large, complex applications where state depends on dynamic or asynchronous streams of data.
-
setState- ✅ Key Terms: [setState, Dirty, Build].
- Directly updates the UI by marking it dirty and rebuilding.
- Suitable for small-scale, simple state changes.
-
Change Notifier- ✅ Key Terms: [ChangeNotifier, notifyListeners, ListenableBuilder].
- Provides a way to notify listeners when changes occur.
- A
ListenableBuilderwill rebuild the widget.
-
Value Notifier- ✅ Key Terms: [ValueNotifier, value, ValueListenableBuilder].
- A special kind of
ChangeNotifierholding a single state or value. - A
ValueListenableBuilderrebuilds the widget.
-
Inherited Widget- ✅ Key Terms: [InheritedWidget, dependOnInheritedWidgetOfExactType, updateShouldNotify].
- Passes data from the top level to deep down in the widget tree.
- Rebuilds widgets whenever its instance variable’s value changes.
- Should be accessed inside
didChangeDependenciesorbuildmethods.
-
Inherited Model- ✅ Key Terms: [InheritedModel, inheritFrom, dependencies, updateShouldNotify, updateShouldNotifyDependent].
- Similar to
InheritedWidget, but rebuilds only specific widgets. - Accepts "aspect" for determining which widgets to rebuild.
-
Inherited Notifier- ✅ Key Terms: [InheritedNotifier, Change Notifier, dependOnInheritedWidgetOfExactType].
- Combines
InheritedWidgetwithChangeNotifier. - Rebuilds widgets whenever the
ChangeNotifieris called.
-
Provider- ✅ Key Terms: [Provider, ChangeNotifier, notifyListeners, ChangeNotifierProvider, MultiProvider].
- Offers an easy-to-use state propagation solution.
Consumerrebuilds widgets whenever provider’s value changes.
-
Flutter Bloc- ✅ Key Terms: [Bloc, Cubit, State, Event, BlocProvider, BlocBuilder, BlocListener].
- Separates business logic (Bloc/Cubit) from UI.
BlocBuilderrebuilds UI on state changes;BlocListenerlistens for state changes to trigger actions.
-
Rx Dart- ✅ Key Terms: [Observable, BehaviorSubject, Stream, Sink, StreamController, debounceTime].
- Uses reactive streams to handle state dynamically.
- Ideal for asynchronous operations, form validation, and complex state dependencies.
-
MobX- ✅ Key Terms: [Store, @observable, @action, Observer, autorun].
- Simplifies state management using observables and actions.
Observerrebuilds UI automatically when state changes.
-
Riverpod- ✅ Key Terms: [ProviderScope, ProviderContainer, ConsumerWidget, ref, read, watch, select].
- Allows dependency injection and advanced state management.
- Provides an easy way to manage state both inside and outside the widget tree.
- It can be used declaratively with providers and reactively with streams and providers.
-
Flutter Hooks- ✅ Key Terms: [HookWidget, useTextEditingController, useAnimationController].
- Simplifies widget lifecycle management.
- Reduces code duplication and offers flexibility with custom hooks.
- Handles disposable components automatically like
TextEditingController,AnimationController.