Zuul act as gateway, put after the AWS elastic load balancer. Need to route the traffic, filter request, authentication, encrypt, etc.
Zuul core is composed by a bunch of filters, each filter is independent, communicate through the requestContext.
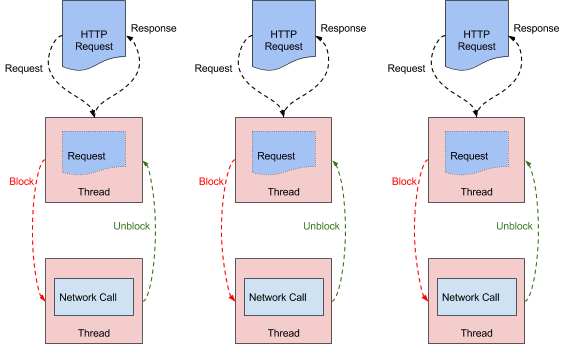
Problem:
- Estimate Capacity: 100 concurrent connections each instance.
- cost of each connection: a thread (with heavy memory and system overhead, like ctx switch)
- high latency, especially when error happens and retry, eg, backend latency increases or device retries due to errors, the count of active connections and threads increases.
- Zuul 1 solution: bandwidth throttling.
One thread per CPU core handling all requests and responses.
- Estimate Capacity: 10 thousand concurrent connections each instance.
- cost of each connection: a file descriptor, and the addition of a listener.
CPU bound task: zuul1
- Highly CPU-bound work loads
- Desire operational simplicity
- Desire development simplicity
- Run legacy systems that are blocking
I/O bound task: zuul2
- Highly I/O bound workloads, most time is waiting for response
- Long requests and large files
- Streaming data from queues
- Massive amounts of connections



