Given the roots of two binary trees p and q, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, and the nodes have the same value.
Example 1:
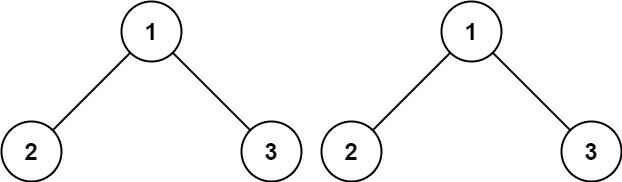
Input: p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3] Output: true
Example 2:
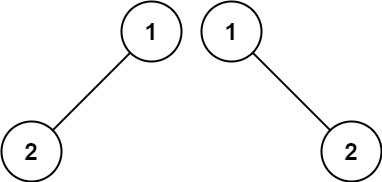
Input: p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2] Output: false
Example 3:
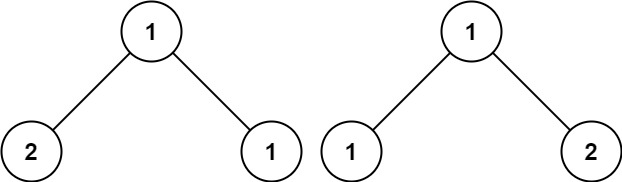
Input: p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2] Output: false
- The number of nodes in both trees is in the range
[0, 100]. -104 <= Node.val <= 104
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def isSameTree(self, p: Optional[TreeNode], q: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
# If both nodes are None, they are the same
if not p and not q:
return True
# If one node is None and the other is not, they are not the same
if not p or not q:
return False
# If the values of the nodes are different, they are not the same
if p.val != q.val:
return False
# Recursively check the left and right subtrees
return self.isSameTree(p.left, q.left) and self.isSameTree(p.right, q.right)The time complexity is O(n), where n is the smaller of the number of nodes in the two trees. This is because we visit each node in the two trees at most once.
The space complexity is O(h), where h is the height of the shorter tree. This is due to the recursive call stack. In the worst case, the tree could be linear (i.e., a linked list), in which case the height of the tree would be equal to the number of nodes, leading to a space complexity of O(n).