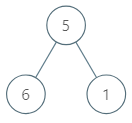
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum average value of a subtree of that tree. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
A subtree of a tree is any node of that tree plus all its descendants.
The average value of a tree is the sum of its values, divided by the number of nodes.
Example 1:
Input: root = [5,6,1] Output: 6.00000 Explanation: For the node with value = 5 we have an average of (5 + 6 + 1) / 3 = 4. For the node with value = 6 we have an average of 6 / 1 = 6. For the node with value = 1 we have an average of 1 / 1 = 1. So the answer is 6 which is the maximum.
Example 2:
Input: root = [0,null,1] Output: 1.00000
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. 0 <= Node.val <= 105
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maximumAverageSubtree(self, root: TreeNode) -> float:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return 0, 0
ls, ln = dfs(root.left)
rs, rn = dfs(root.right)
s = ls + root.val + rs
n = ln + 1 + rn
nonlocal ans
ans = max(ans, s / n)
return s, n
ans = 0
dfs(root)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private double ans;
public double maximumAverageSubtree(TreeNode root) {
ans = 0;
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private int[] dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new int[] {0, 0};
}
int[] l = dfs(root.left);
int[] r = dfs(root.right);
int s = l[0] + root.val + r[0];
int n = l[1] + 1 + r[1];
ans = Math.max(ans, s * 1.0 / n);
return new int[] {s, n};
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
double ans;
double maximumAverageSubtree(TreeNode* root) {
ans = 0;
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
pair<int, int> dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return {0, 0};
auto l = dfs(root->left);
auto r = dfs(root->right);
int s = l.first + root->val + r.first;
int n = l.second + 1 + r.second;
ans = max(ans, s * 1.0 / n);
return {s, n};
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func maximumAverageSubtree(root *TreeNode) float64 {
var ans float64
var dfs func(root *TreeNode) []int
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) []int {
if root == nil {
return []int{0, 0}
}
l, r := dfs(root.Left), dfs(root.Right)
s := l[0] + root.Val + r[0]
n := l[1] + 1 + r[1]
ans = math.Max(ans, float64(s)/float64(n))
return []int{s, n}
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}