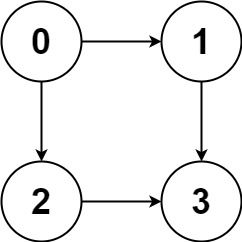
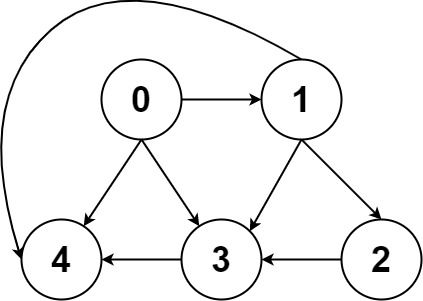
Given a directed acyclic graph (DAG) of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, find all possible paths from node 0 to node n - 1 and return them in any order.
The graph is given as follows: graph[i] is a list of all nodes you can visit from node i (i.e., there is a directed edge from node i to node graph[i][j]).
Example 1:
Input: graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]] Output: [[0,1,3],[0,2,3]] Explanation: There are two paths: 0 -> 1 -> 3 and 0 -> 2 -> 3.
Example 2:
Input: graph = [[4,3,1],[3,2,4],[3],[4],[]] Output: [[0,4],[0,3,4],[0,1,3,4],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,4]]
Constraints:
n == graph.length2 <= n <= 150 <= graph[i][j] < ngraph[i][j] != i(i.e., there will be no self-loops).- All the elements of
graph[i]are unique. - The input graph is guaranteed to be a DAG.
Since there is no ring in the graph, you can simply use DFS or BFS to traverse it.
BFS.
class Solution:
def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
n = len(graph)
q = deque([[0]])
ans = []
while q:
path = q.popleft()
u = path[-1]
if u == n - 1:
ans.append(path)
continue
for v in graph[u]:
q.append(path + [v])
return ansDFS:
class Solution:
def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
def dfs(t):
if t[-1] == len(graph) - 1:
ans.append(t[:])
return
for v in graph[t[-1]]:
t.append(v)
dfs(t)
t.pop()
ans = []
dfs([0])
return ansBFS:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {
int n = graph.length;
Queue<List<Integer>> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(Arrays.asList(0));
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> path = queue.poll();
int u = path.get(path.size() - 1);
if (u == n - 1) {
ans.add(path);
continue;
}
for (int v : graph[u]) {
List<Integer> next = new ArrayList<>(path);
next.add(v);
queue.offer(next);
}
}
return ans;
}
}DFS:
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> ans;
private int[][] graph;
public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {
ans = new ArrayList<>();
this.graph = graph;
List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>();
t.add(0);
dfs(t);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(List<Integer> t) {
int cur = t.get(t.size() - 1);
if (cur == graph.length - 1) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(t));
return;
}
for (int v : graph[cur]) {
t.add(v);
dfs(t);
t.remove(t.size() - 1);
}
}
}DFS:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> graph;
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
this->graph = graph;
vector<int> path;
path.push_back(0);
dfs(0, path);
return ans;
}
void dfs(int i, vector<int> path) {
if (i == graph.size() - 1) {
ans.push_back(path);
return;
}
for (int j : graph[i]) {
path.push_back(j);
dfs(j, path);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};DFS:
func allPathsSourceTarget(graph [][]int) [][]int {
var path []int
path = append(path, 0)
var ans [][]int
var dfs func(i int)
dfs = func(i int) {
if i == len(graph)-1 {
ans = append(ans, append([]int(nil), path...))
return
}
for _, j := range graph[i] {
path = append(path, j)
dfs(j)
path = path[:len(path)-1]
}
}
dfs(0)
return ans
}/**
* @param {number[][]} graph
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var allPathsSourceTarget = function (graph) {
const ans = [];
const t = [0];
const dfs = t => {
const cur = t[t.length - 1];
if (cur == graph.length - 1) {
ans.push([...t]);
return;
}
for (const v of graph[cur]) {
t.push(v);
dfs(t);
t.pop();
}
};
dfs(t);
return ans;
};impl Solution {
fn dfs(i: usize, path: &mut Vec<i32>, res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, graph: &Vec<Vec<i32>>) {
path.push(i as i32);
if i == graph.len() - 1 {
res.push(path.clone());
}
for j in graph[i].iter() {
Self::dfs(*j as usize, path, res, graph)
}
path.pop();
}
pub fn all_paths_source_target(graph: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut res = Vec::new();
Self::dfs(0, &mut vec![], &mut res, &graph);
res
}
}