JVM系列之:JIT中的Virtual Call接口
上一篇文章我们讲解了Virtual Call的定义并举例分析了Virtual Call在父类和子类中的优化。
JIT对类可以进行优化,那么对于interface可不可以做同样的优化么?
一起来看看吧。
List应该是大家最最常用的接口了,我想这个大家应该不会反驳。
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {今天我们就拿List来做例子,体验一下JIT优化接口的奥秘。
还是上代码,要分析的代码如下:
public class TestVirtualListCall {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
doWithVMethod(list);
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
public static void doWithVMethod(List<String> list)
{
list.add("www.flydean.com");
}
}如果在命令行运行,大家记得在运行时添加参数-XX:+UnlockDiagnosticVMOptions -XX:+PrintAssembly -XX:-Inline
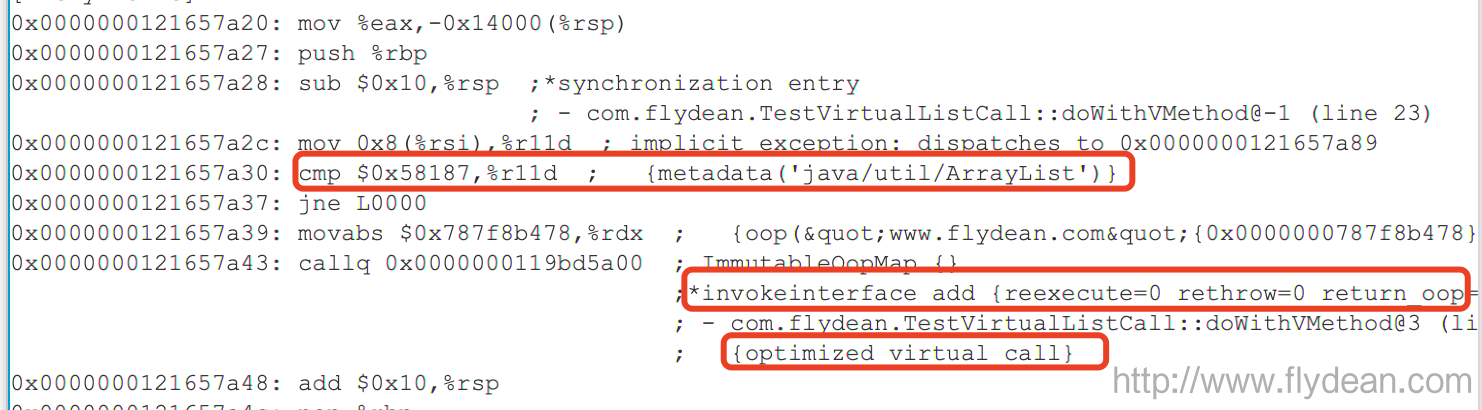
直接看JIT Watcher的结果:
我们可以看到JIT中先对ArrayList的实现类做了一个比较。
然后调用的是invokeinterface,但是其本质还是invokevirtual,并且我们可以看到这个调用是被优化过了:optimized virtual call。
同样的,我们可以测试一下多个list子类的情况下怎么调用:
public class TestVirtualListCall2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List<String>[] lists=new List[]{new ArrayList<>(),new LinkedList<>()};
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
doWithVMethod(lists[i%2]);
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
public static void doWithVMethod(List<String> list)
{
list.add("www.flydean.com");
}
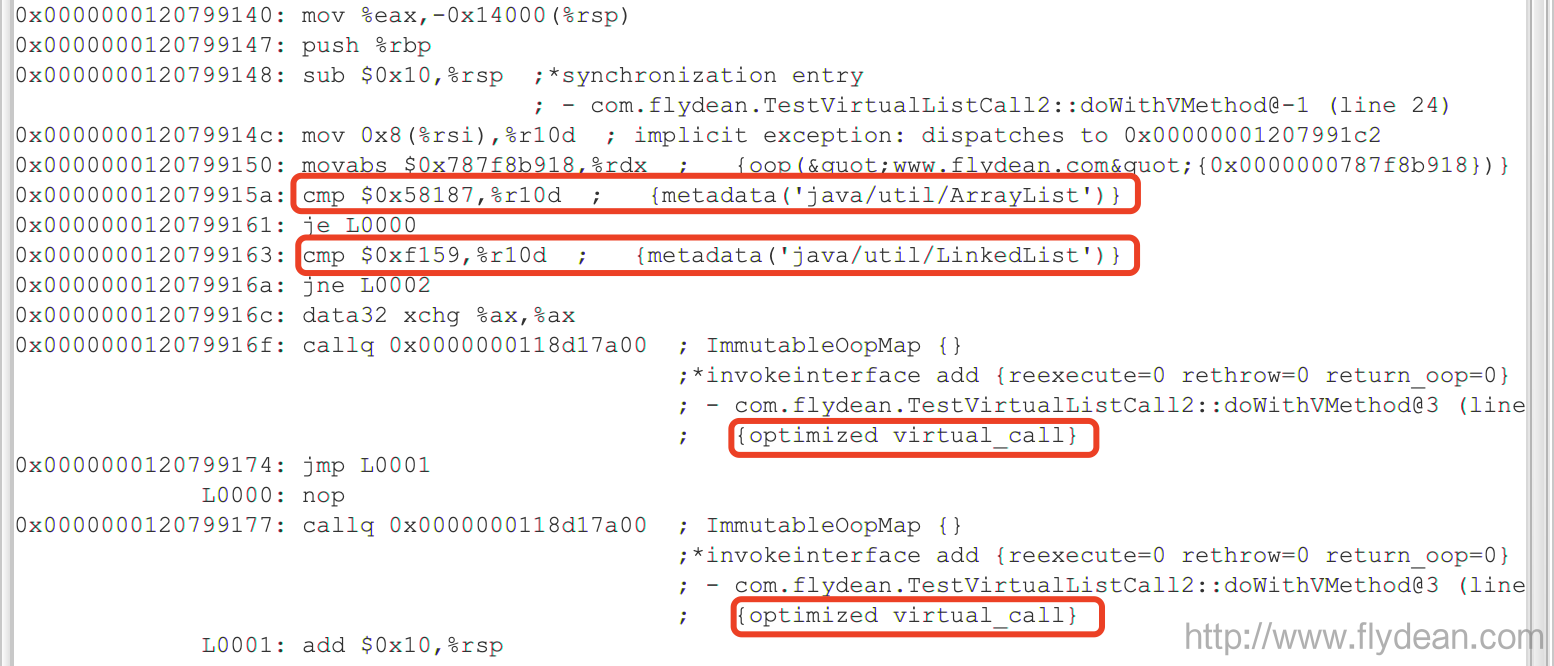
}同样,使用JIT Watcher来运行:
我们可以看到JIT做了两次对象类型的比较,然后对两个invokeinterface都做了优化。
结果和我们的父类子类结果是一样的。
上面我们在做多个list调用的时候,是轮循着来调用的,如果我们先调用ArrayList的方法,再调用LinkedList的方法,会有什么不同呢?
一起来看看。
public class TestVirtualListCall3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> list2 = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
doWithVMethod(list1);
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
doWithVMethod(list2);
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
public static void doWithVMethod(List<String> list)
{
list.add("www.flydean.com");
}
}上面我们先循环ArrayList,然后再循环LinkedList。
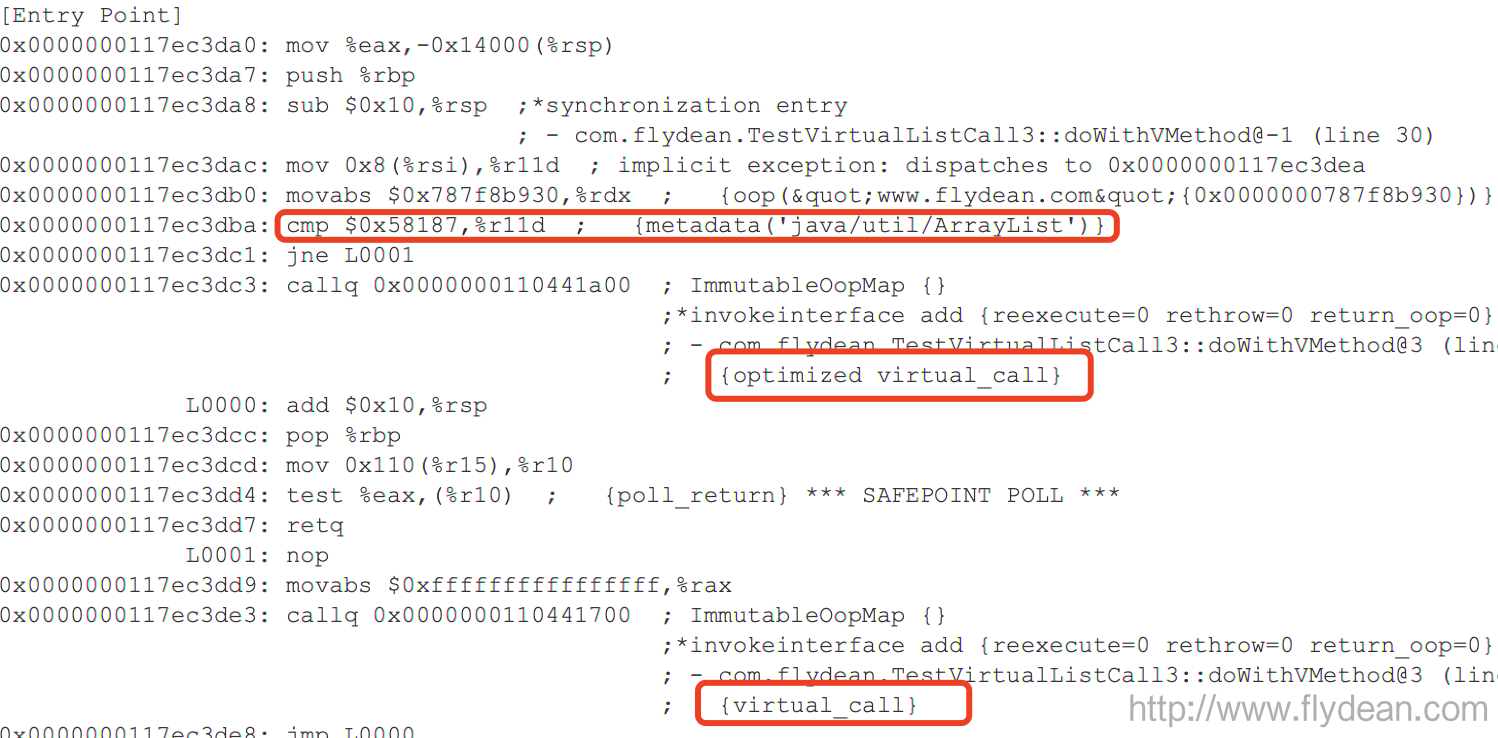
看下结果有什么不同:
可以看到,JIT先比较了ArrayList,然后只做了一次方法的优化。
也就是说LinkedList的调用是没有进行代码优化的。
上面的结果是在C2编译器下,也就是level4的编译水平下解析的。
我们看下如果在C1编译器下,也就是Level3编译水平下有什么不同。
可以看到C1编译下,所有的invokeinterface都没有进行编译优化,只有在C2编译下,才会进行优化。
不同的JVM版本可能优化方式不一样。大家可以自行实验。
本文用实例展示了Virtual Call在interface上面的优化使用。
感兴趣的朋友,可以一起讨论。
本文作者:flydean程序那些事
本文链接:www.flydean.com
本文来源:flydean的博客
欢迎关注我的公众号:程序那些事,更多精彩等着您!