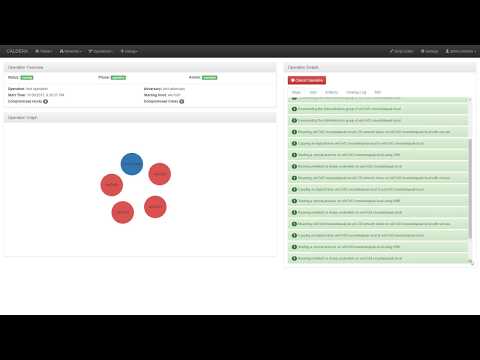
CALDERA is an automated adversary emulation system that performs post-compromise adversarial behavior within Windows Enterprise networks. It generates plans during operation using a planning system and a pre-configured adversary model based on the Adversarial Tactics, Techniques & Common Knowledge (ATT&CK™) project. These features allow CALDERA to dynamically operate over a set of systems using variable behavior, which better represents how human adversaries perform operations than systems that follow prescribed sequences of actions.
CALDERA is useful for defenders who want to generate real data that represents how an adversary would typically behave within their networks. Since CALDERA's knowledge about a network is gathered during its operation and is used to drive its use of techniques to reach a goal, defenders can get a glimpse into how the intrinsic security dependencies of their network allow an adversary to be successful. CALDERA is useful for identifying new data sources, creating and refining behavioral-based intrusion detection analytics, testing defenses and security configurations, and generating experience for training.
BlackHat Europe 2017 presentation slides: CALDERA - Automating Adversary Emulation
CALDERA only supports Windows Enterprise networks that are configured as a Windows Domain. This is because the techniques and tactics currently built into CALDERA are unique to Windows domains. Despite this, the CALDERA server can be installed on either Linux or Windows.
See Requirements for more detailed information.
Detailed installation instructions are included in the Installation documentation.
Documentation is available on Read the Docs
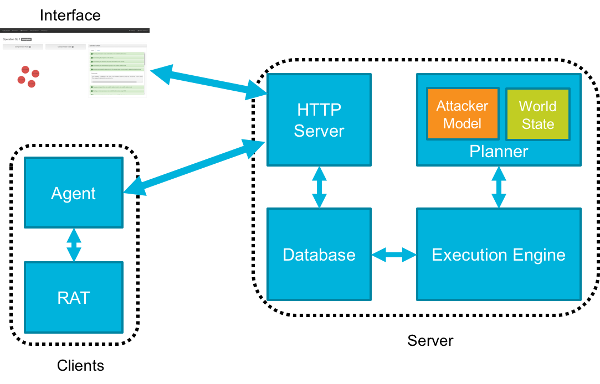
CALDERA consists of:
- Server
- Planner - Decision engine allowing CALDERA to chose actions
- Attacker Model - Actions available based on ATT&CK
- World Model - Representation of the environment
- Execution Engine - Drives actuation of techniques and updates the database
- Database - Stores knowledge learned about the environment
- HTTP Server
- Planner - Decision engine allowing CALDERA to chose actions
- Clients
- Agent - Client on endpoint systems used for communication
- RAT - Remote access tool used during operations to emulate adversary behavior
CALDERA's planning system allows it to "decide" the next best action to take based upon its current knowledge of the environment and the actions available at a given point in time. CALDERA's attacker model is represented by pre-configured ATT&CK-based techniques that have been logically encoded with pre and post conditions allowing CALDERA to chain together sequences of actions to reach an objective state.
The system follows this algorithm:
- Update the world state
- Figure out all valid actions to execute
- Construct plans that lead off with those actions, chain actions together by leveraging model
- Run heuristic to determine best plan
- Execute the first action in the best plan
- Repeat
New techniques can be added to CALDERA without having to recompute new decision models because of how techniques are logically defined. It is encouraged to develop new techniques and variations of techniques to better represent the variations in how adversaries can behave and contribute them back to the project.
The path chaining problems CALDERA's planning system is designed to solve are computationally intensive. While CALDERA's server does not have hardware requirements beyond a typical software developer's system, there are limitations on the number of systems CALDERA can operate over before the planning time between actions will cause significant delays or the system to fail. Thus it is not recommended that CALDERA be used against sets of systems larger than 20.
CALDERA performs real actions on systems when operating. If it is being used in a production network, beyond an isolated lab network, then care should be taken to inform any network security staff, administrators, or users who may be impacted prior to using CALDERA to deconflict any issues that may arise.
CALDERA uses other open source tools as part of its repository of techniques. Some of these tools are categorized as penetration testing or security auditing tools. See Security for more information.
CALDERA does not use or repurpose known adversary malware. It focuses on using adversary behavior documented within ATT&CK, which can be employed in many different ways regardless of specific pieces of malware an adversary may use.
CALDERA does not emulate adversary command and control (C2) channels. The variation in adversary C2 protocols and communication methods is vast and is considered out of scope.
CALDERA also does not use software exploitation. There are many free and commercial tools that can be used to assess software weakness and exploitability. CALDERA should not be used for this purpose.
CALDERA is a MITRE research project and is an implementation of some of the ideas described in the following papers:
Intelligent, Automated Red Team Emulation
Analysis of Automated Adversary Emulation Techniques
BRAWL Game - Data set created by the BRAWL project representing one CALDERA operation with data collected by Microsoft Sysmon and other sensors.
CASCADE - Prototype blue team analysis tool to automate investigative work.